Asynchronous periodic mode, 1 latency, 2 asynchronous periodic mode – HP 3PAR Remote Copy Software User Manual
Page 40
2.24
Remote Copy Operation
Remote Copy User’s Guide
InForm OS Version 2.3.1
2.9.1.1.1 Latency
Synchronous mode adds more latency to the write because the I/O needs to be sent to the
backup server over the IP network or SAN and then an acknowledgement must be received
from the backup server before acknowledging the host. As the distance between the primary
and backup storage servers increases, the latency also increases. For example, a one-way
distance of 100 miles adds approximately two milliseconds to the write latency. Even with the
primary and backup storage systems side-by-side, Remote Copy running in synchronous mode
adds some latency to a host write.
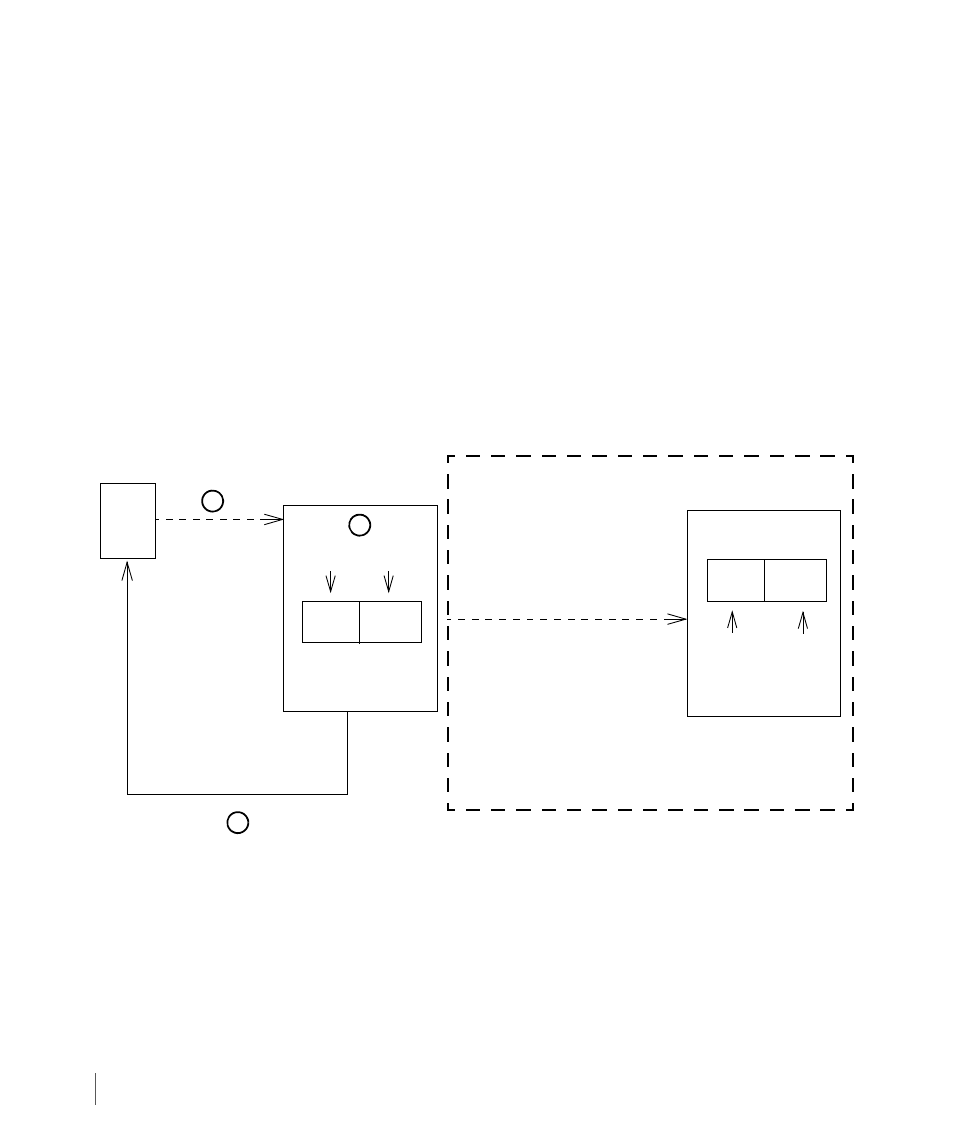
2.9.1.2 Asynchronous Periodic Mode
In the asynchronous periodic mode, host writes are performed only on the primary server and
the host write is acknowledged as soon as the data is written into cache on the primary storage
server (
Figure 2-14. Remote Copy in Asynchronous Periodic Mode
The primary and backup volumes are resynchronized periodically, for example, when
scheduled or when resynchronization is manually initiated through the
syncrcopy
command.
If, between two resynchronizations, an area of the volume is written to multiple times, only
the last write needs to be sent over to the other storage server. Therefore, when using Remote
Copy in asynchronous periodic mode, less data is transferred relative to the synchronous mode.
Primary
Backup
Storage Server
Storage Server
Host
Write request
Data written to caches
on two nodes
data written to cache
1
2
3
Primary acknowledges host
Scheduled or manual resynchronization
Only most recent data copied over
Only most recent
on the nodes
