4 black hole routing configuration exmaples, Lack, Outing – PLANET XGS3-24040 User Manual
Page 340: Onfiguration, Xmaples
Chapter 41 Black Hole Routing Manual
41-2
41.4 Black Hole Routing Configuration Exmaples
Example 1: IPv4 Black Hole Routing function.
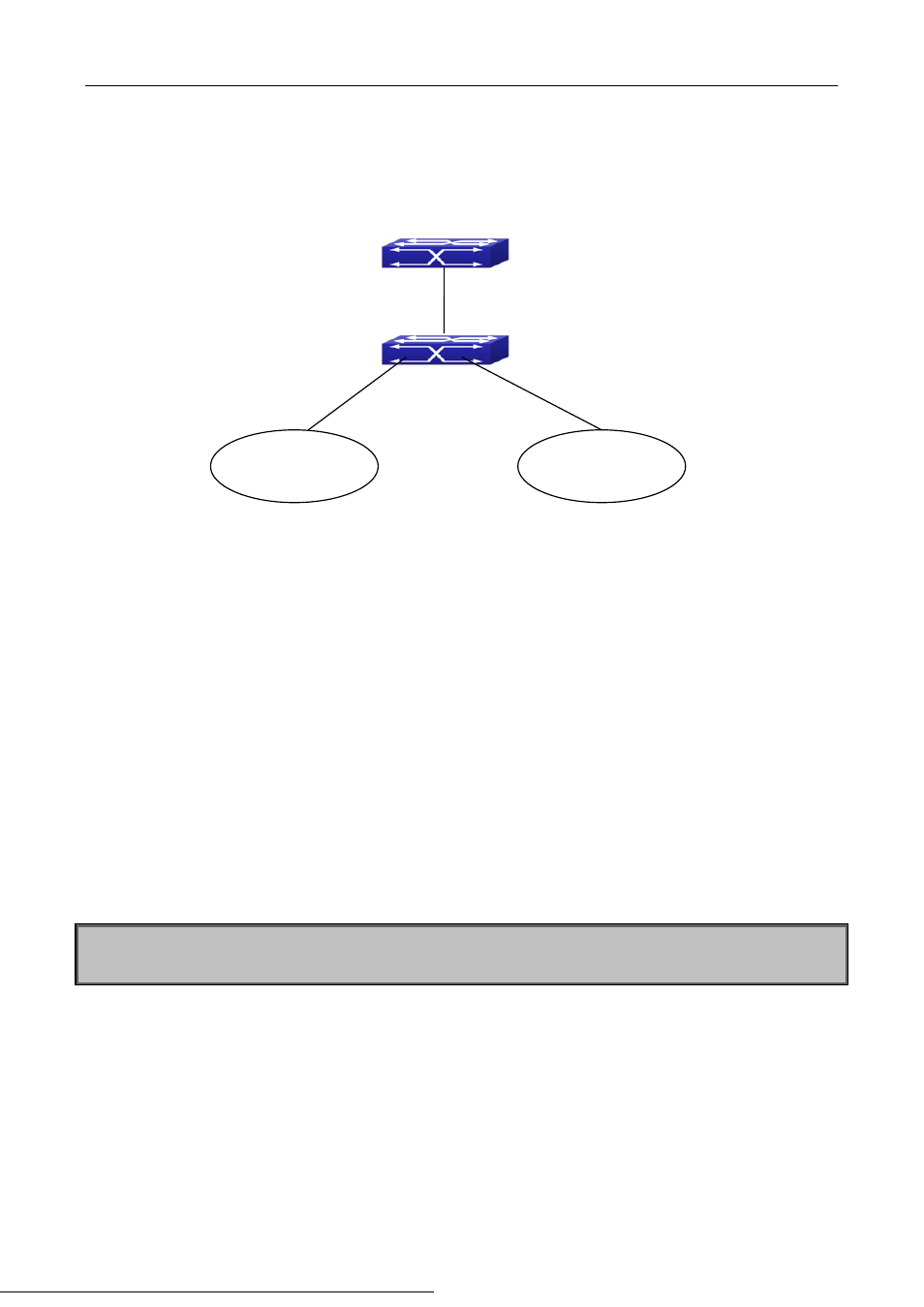
Figure 9-1 IPv4 Black Hole Routing Configuration Example
As it is shown in the figure, in Switch 2, eight in all interfaces are configured as Layer 3 VLAN interfaces for
access interfaces. The network addresses are 192.168.1.0/24 ~ 192.268.7.0/24. A default routing is
configured on Switch 2 to connect to Switch 1. And a backward default routing is configured on Switch 1 to
Switch 2, whose network address is 192.168.0.0/21. Commonly, this configuration will work well. However, if
one of the Layer 3 interfaces in Switch 2 goes down, for example, the interface belonged to 192.168.1.0/24.
When datagrams arrives at VLAN1 in Switch 2, there will be no routing rules for these datagrams. The switch
then will forward these datagrams according to the default routing, back to Switch 1. When Switch 1 receives
these datagrams, it will forward them back to Switch 2. Thus, loopback exists. To solve this problem, Black
Hole Routing can be introduced on Switch 2.
ip route 192.168.0.0/21 null0 50
Then Switch 2 will drop the datagrams from interface VLAN1 that match the Black Hole Routing rule. And
loopback routing is prevented.
Configuration steps are listed as below:
Switch#config
Switch(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0/21 null0 50
192.168.1.0/24
192.168.7.0/24
………
SWITCH2
SWITCH1
192.168.0.1/21
192.168.0.2/21
