7 examples 7: example of bgp vpn – PLANET XGS3-24040 User Manual
Page 330
Chapter 39 BGP
39-24
39.3.7 Examples 7: example of BGP VPN
For the configuration of MPLS VPN, BGP is part of the core routing system and it is also an important utility to
support ILM and FTN entries on the edge devices. For DCNOS, the BGP protocol together with the LDP
protocol, constructs the foundation of the MPLS VPN application. The LDP protocol works at the WLAN side
and for the routers which are not on the edge of the network, the BGP protocol does not function.
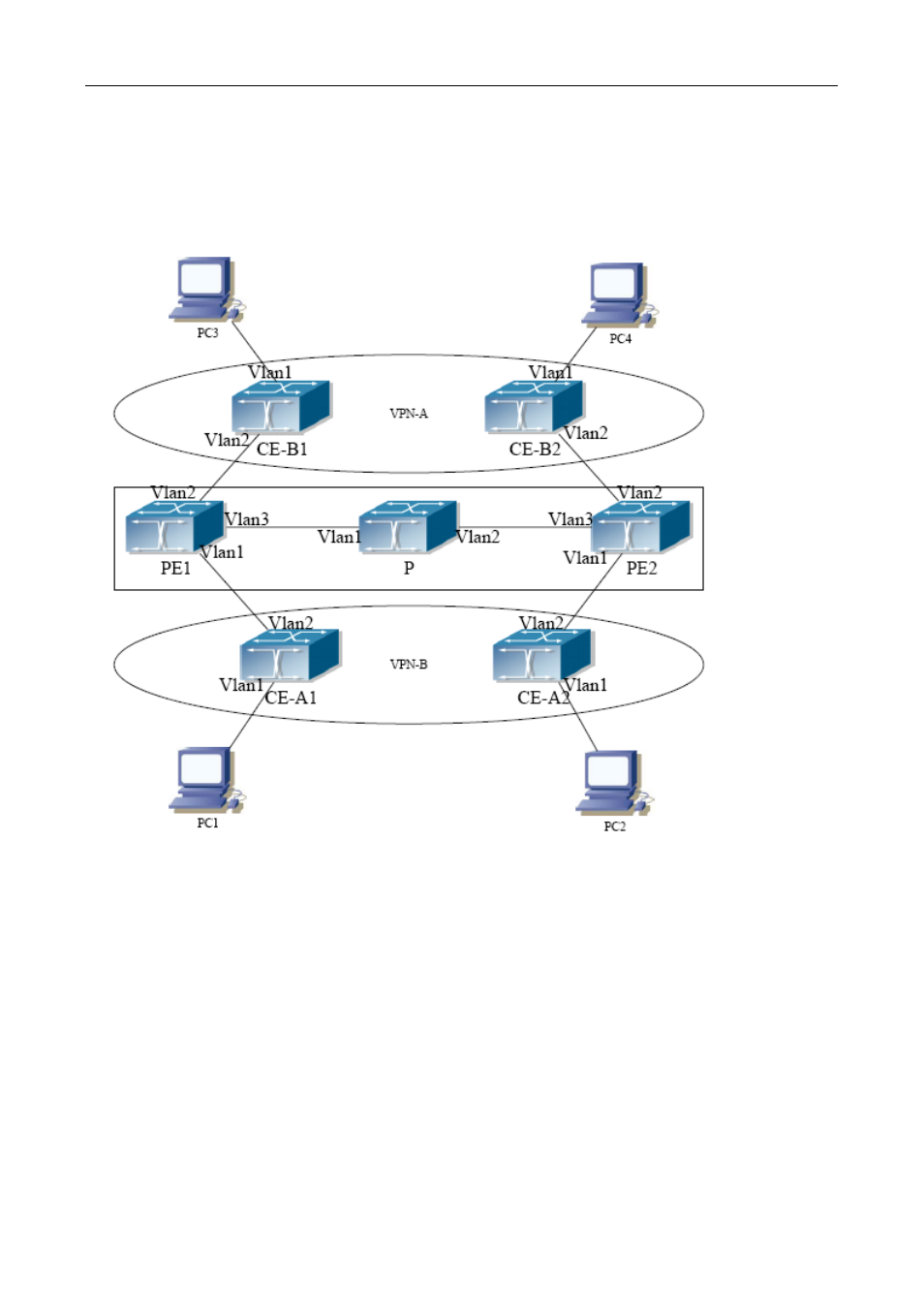
Figure 7-5 Example of MPLS VPN
As the figure shows, for a typical MPLS VPN application, the public network region consists of PE1, P and
PE2, which MPLS is applied for packet transmission. VPN-A consists of CE-A1 and CE-A2, and VPN-B
consists of CE-B1 and CE-B2. These two VPNs are isolated from each other. PE1 and PE2 are edge routers
which are provided by the operators. CE-A1, CE-A2, CE-B1 and CE-B2 are the access switches on the user
side. PC1-PC4 indicate the network users. BGP runs at both the public and private network region. For the
public network region, VPN routing should be supported and the LOOPBACK interface should be used for
connections.
