Mpls l3vpn routing information advertisement – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 240
229
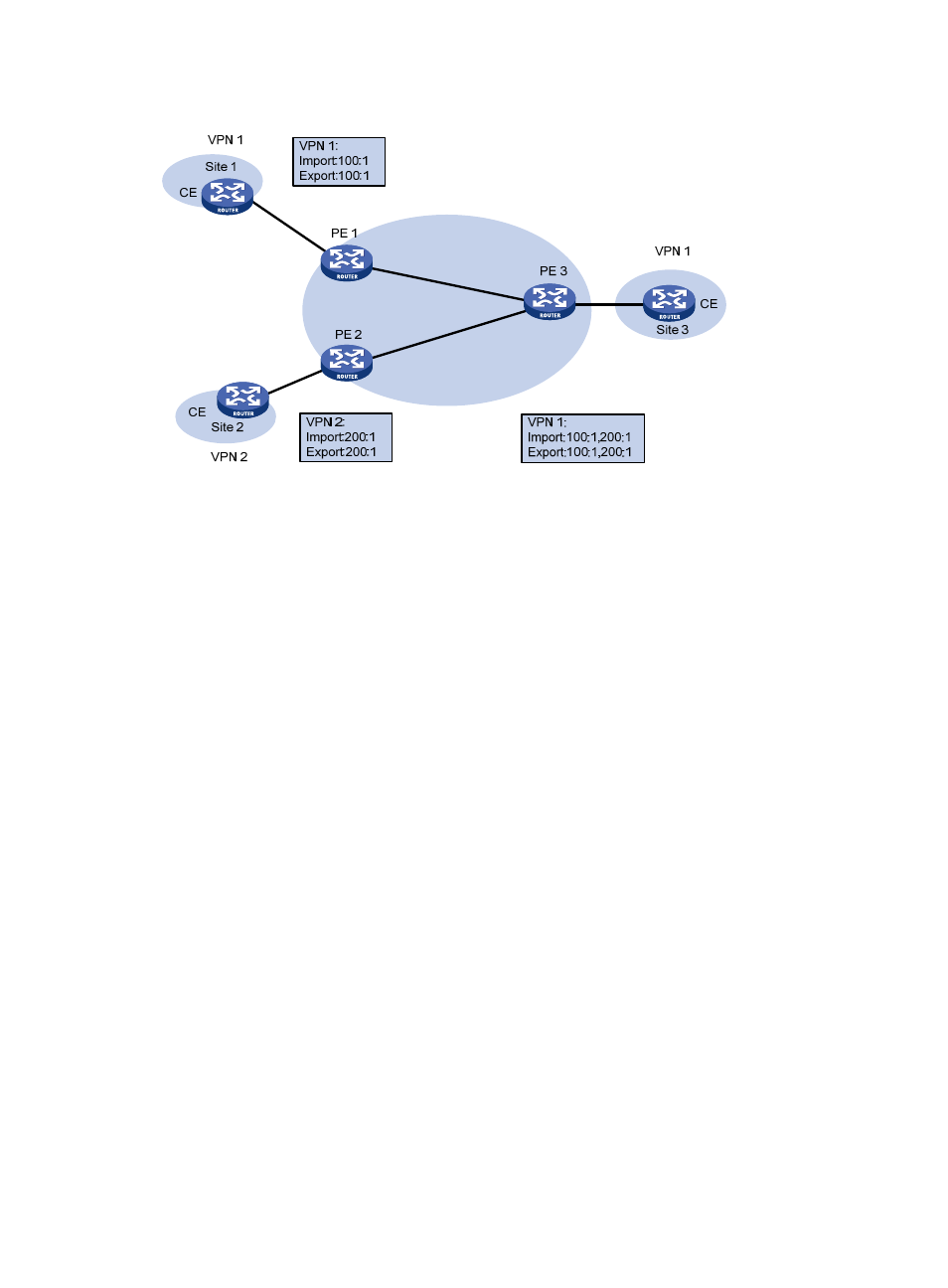
Figure 60 Network diagram for extranet networking scheme
In
, VPN 1 and VPN 2 can access Site 3 of VPN 1.
•
PE 3 can receive the VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by PE 1 and PE 2.
•
PE 1 and PE 2 can receive the VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by PE 3.
•
Based on the above, Site 1 and Site 3 of VPN 1 can communicate with each other, and Site 2 of
VPN 2 and Site 3 of VPN 1 can communicate with each other.
PE 3 advertises neither the VPN-IPv4 routes received from PE 1 to PE 2, nor the VPN-IPv4 routes received
from PE 2 to PE 1 (that is, routes learned from an IBGP neighbor will not be advertised to any other IBGP
neighbor). Therefore, Site 1 of VPN 1 and Site 2 of VPN 2 cannot communicate with each other.
MPLS L3VPN routing information advertisement
In basic MPLS L3VPN networking, the advertisement of VPN routing information involves CEs and PEs. A
P router maintains only the routes of the backbone and does not need to know any VPN routing
information. A PE maintains only the routing information of the VPNs directly connected to it, rather than
that of all VPNs. Therefore, MPLS L3VPN has excellent scalability.
The VPN routing information of a local CE is advertised in three phases:
1.
Advertised from the local CE to the ingress PE.
2.
Advertised from the ingress PE to the egress PE.
3.
Advertised from the egress PE to the remote CE.
Then, a route is available between the local CE and the remote CE, and the VPN routing information can
be advertised on the backbone.
The following describes these phases in detail.
Routing information exchange from the local CE to the ingress PE
After establishing an adjacency with the directly connected PE, a CE advertises its VPN routing
information to the PE.
