Label distribution and management – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 15
4
NOTE:
In this document, the term
label distribution protocols represents all protocols for label distribution, and the
term
LDP refers to the Label Distribution Protocol defined in RFC 5036.
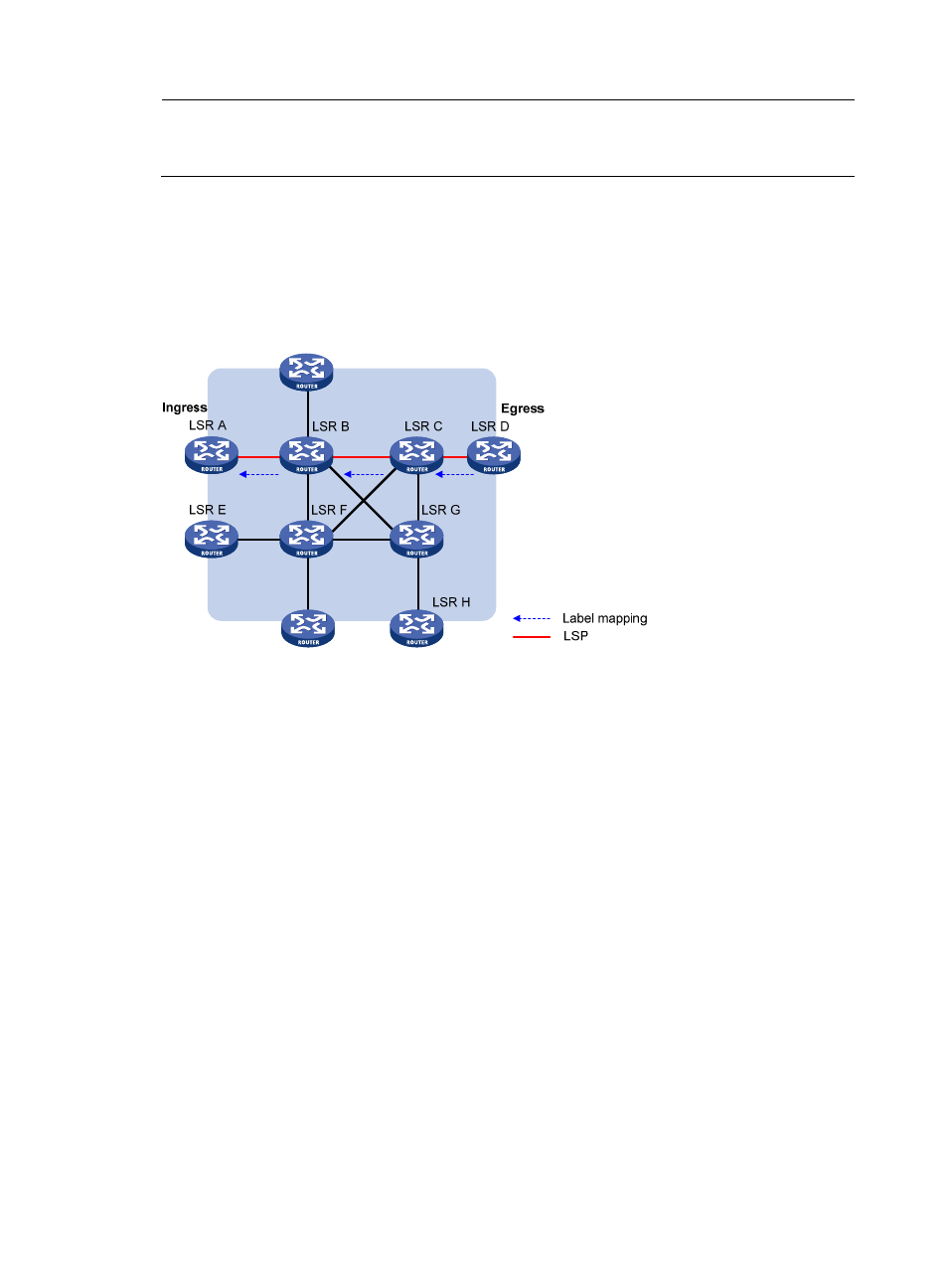
As shown in
, a dynamic LSP is established in the following procedure:
A downstream LSR classifies FECs according to destination addresses, assigns a label to a FEC, and
distributes the FEC-label binding to its upstream LSR, which then establishes an LFIB entry for the FEC
according to the binding information. After all LSRs along the packet forwarding path establish a LFIB
entry for the FEC, an LSP is established for packets of this FEC.
Figure 4 Process of dynamic LSP establishment
Label distribution and management
An LSR informs its upstream LSRs of labels assigned to FECs through label advertisement. According to
the label distribution condition and order, the label advertisement mode can be downstream unsolicited
(DU) and downstream on demand (DoD), and the label distribution control mode can be independent or
ordered.
MPLS has two label retention modes—liberal and conservative—to manage the received label bindings
that are not useful at the moment.
1.
Label advertisement modes
