Vpls loop avoidance – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 166
155
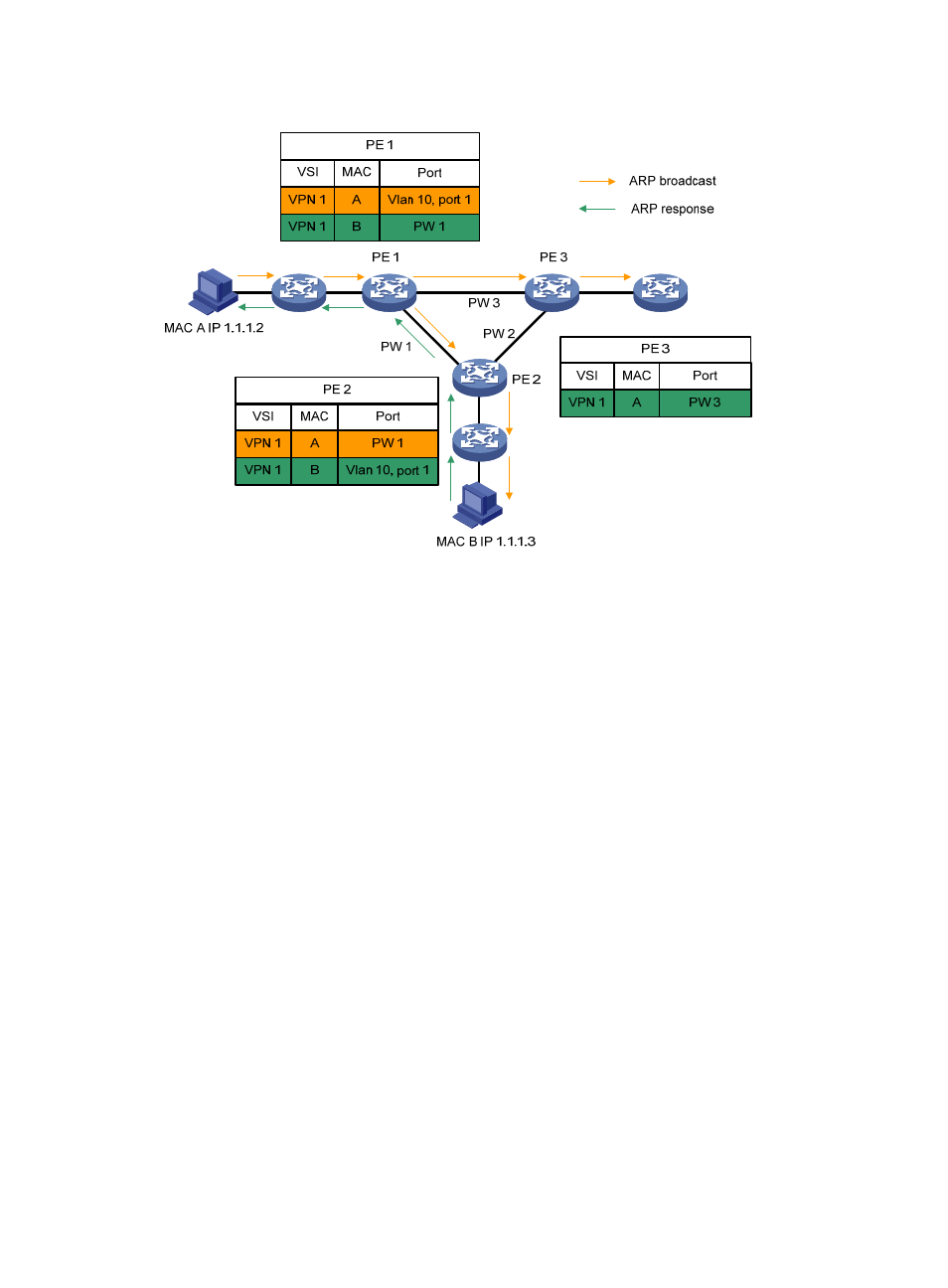
Figure 36 MAC learning and flooding on PEs
2.
MAC address reclaim
Dynamic address learning must support refreshing and relearning. The VPLS draft defines a
dynamic address learning method that uses the address reclaim message, which carries MAC TLV.
Upon receiving such a message, a router removes MAC addresses or relearns them according to
the specified parameters in the TLV. If NULL is specified, the router removes all MAC addresses of
the VSI except for those learned from the PW that received the address reclaim message.
The address reclaim message is very useful when the network topology changes and it is required
to remove the learned MAC addresses quickly. There are two types of address reclaim messages:
those with MAC address lists and those without MAC address lists.
After a backup link becomes active and a message with the instruction of relearning MAC entries
arrives, a PE updates the corresponding MAC entries in the FIB table of the VPLS instance and
sends the message to other PEs that are directly connected through LDP sessions. If the message
contains a null MAC address TLV list, these PEs remove all MAC addresses from the specified VSI,
except for those learned from the PW that sent the message.
3.
MAC address aging
Remote MAC addresses learned by a PE that are related to VC labels but no more in use need to
be aged out by an aging mechanism. The aging mechanism used here is the aging timer
corresponding to the MAC address. When receiving a packet whose source MAC address has an
aging timer started, the PE resets the aging timer.
VPLS loop avoidance
In general, Layer 2 networks use the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to avoid loops. This is not applicable
for VPLS networks because the users cannot sense the service provider network. Therefore, enabling STP
in the private networks means nothing to the service provider network. In VPLS, full mesh and split horizon
forwarding are used to avoid use of STP at the private network side.
Two methods for VPLS loop avoidance are supported:
