INFICON Cygnus Thin Film Deposition Controller User Manual
Page 211
9 - 13
IP
N 07
4-
37
9-
P1
K
Cygnus Operating Manual
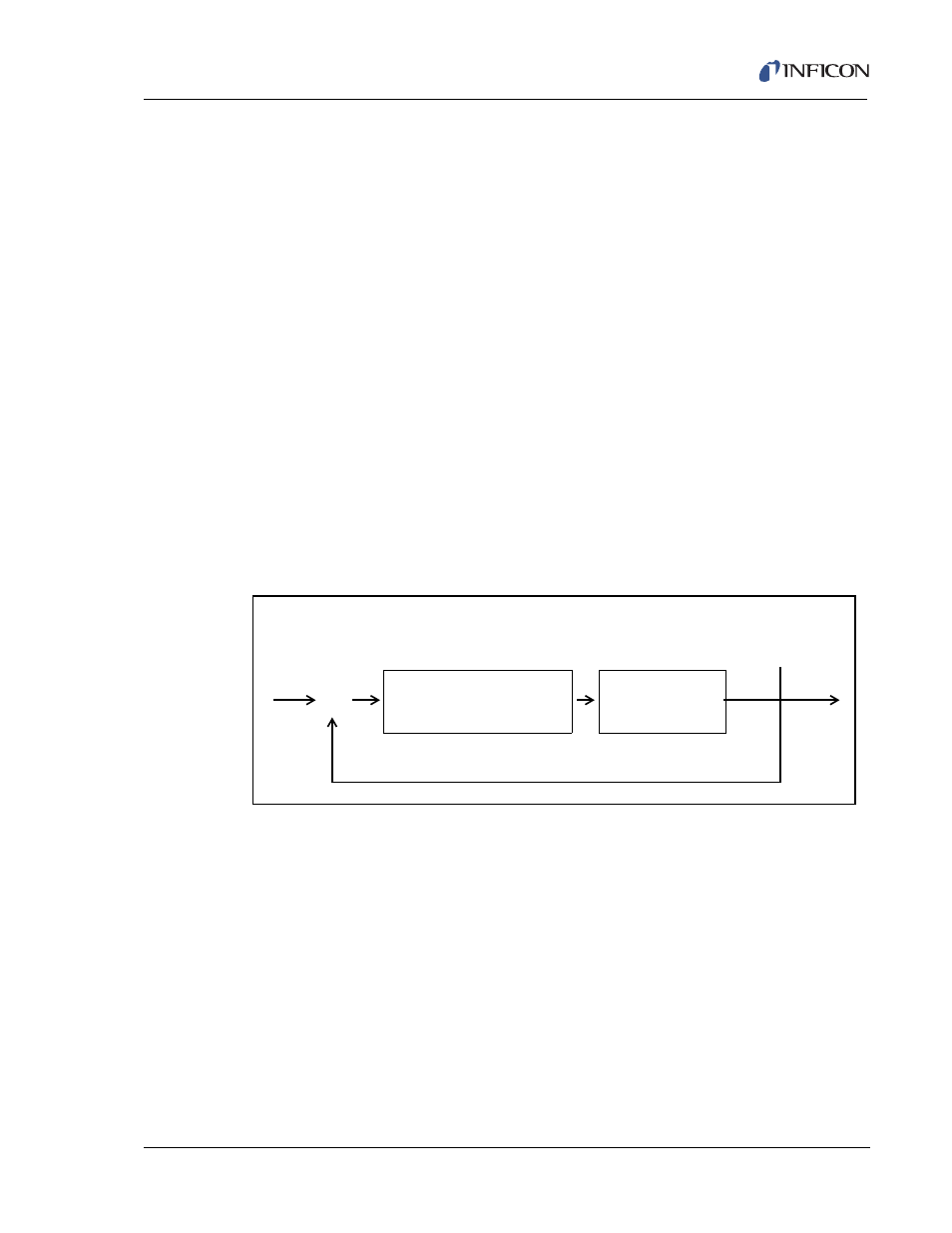
A controller model used extensively is the PID type, shown in Laplace form in
.
[9]
Where
M(s) = manipulated variable or power
K
c
= controller gain (the proportional term)
T
i
= integral time
T
d
= derivative time
E(s) = process error
represents the controller algorithm and a process with first order lag plus
a dead time. The process block implicitly includes the dynamics of the measuring
devices and the final control elements, in our case the evaporator power supply.
R(s) represents the rate setpoint. The feedback mechanism is the error generated
by the difference between the measured deposition rate, C(s), and the rate set
point, R(s).
Figure 9-8 PID Controller Block Diagram
The key to using any control system is to choose the proper values of K
c
, T
d
and
T
i
. Optimum control is a somewhat subjective quantity as noted by the presence of
several mathematical definitions as shown below.
The integral of the squared error (ISE) is a commonly proposed criterion of
performance for control systems.
It can be described as:
[10]
M s
K
c
1
1
T
i
s
------- T
d
s
+
+
Es
=
K
c
1
1
T
i
s
------- T
d
s
+
+
K
p
L
– s
exp
T
1
s 1
+
-------------------------------
R s
E s
S
C s
setpoint
error
[controller]
[process]
+
deposition
rate
ISE
e
2
t
dt
=
