HP Surestore Disk Array 12h and FC60 User Manual
Page 60
60 Disk Array High Availability Features
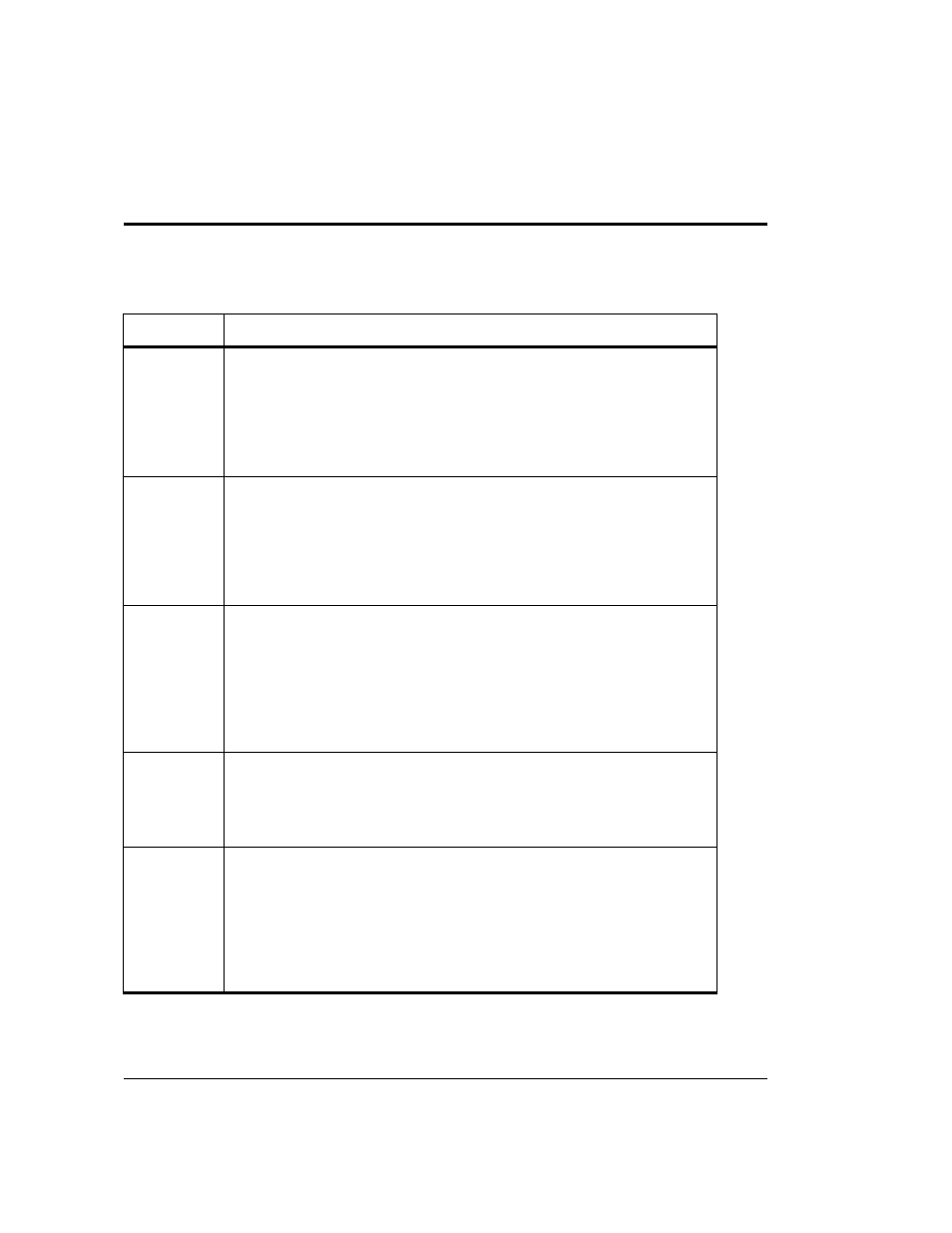
Table 5
RAID Level Comparison: Application and I/O Pattern Performance Characteristics
RAID level
Application and I/O Pattern Performance
RAID 0
RAID 0 is a good choice in the following situations:
– Data protection is not critical. RAID 0 provides no data redundancy for
protection against disk failure.
– Useful for scratch files or other temporary data whose loss will not seriously
impact system operation.
– High performance is important.
RAID 1
RAID 1 is a good choice in the following situations:
– Speed of write access is important.
– Write activity is heavy.
– Applications need logging or recordkeeping.
– Daily updates need to be stored to a database residing on a RAID 5 group.
The database updates on the RAID 1 group can be copied to the RAID 5
group during off-peak hours.
RAID 0/1
RAID 0/1 is a good choice in the following situations:
– Speed of write access is important.
– Write activity is heavy.
– Applications need logging or recordkeeping.
– Daily updates need to be stored to a database residing on a RAID 5 group.
The database updates on the RAID 1 group can be copied to the RAID 5
group during off-peak hours.
RAID 3
RAID 3 is a good choice in the following situations:
– Applications using I/O large sequential transfers of data, such as multimedia
applications.
– Applications on which write operations are 33% or less of all I/O operations.
RAID 5
RAID 5 is a good choice in the following situations:
– Multi-tasking applications using I/O transfers of different sizes.
– Database repositories or database servers on which write operations are
33% or less of all I/O operations.
– Multi-tasking applications requiring a large history database with a high read
rate.
– Transaction processing is required.
