Continuous mode, Bpsk qpsk, 2 continuous mode – Comtech EF Data SNM-1010L User Manual
Page 171: Figure chapter 6-3. bpsk ordering
SNM-1010L Data/Control Modem
Revision 0
Theory of Operation
MN/SNM1010L.OM
6.3.1.2 Continuous
Mode
Data to be transmitted comes from the DAC card. It includes a clock that is synchronous
with the data. At this point, the data signal is clean and free of jitter. The data signal goes
to the scrambler, which provides energy dispersal. It then goes to a differential encoder.
The data signal passes to the Viterbi K = 7 convolutional encoder. When the modulator is
in the QPSK mode, the output of the encoder generates two separate data streams to drive
the I&Q channels of the modulator. One channel can be inverted, causing a spectral
inversion.
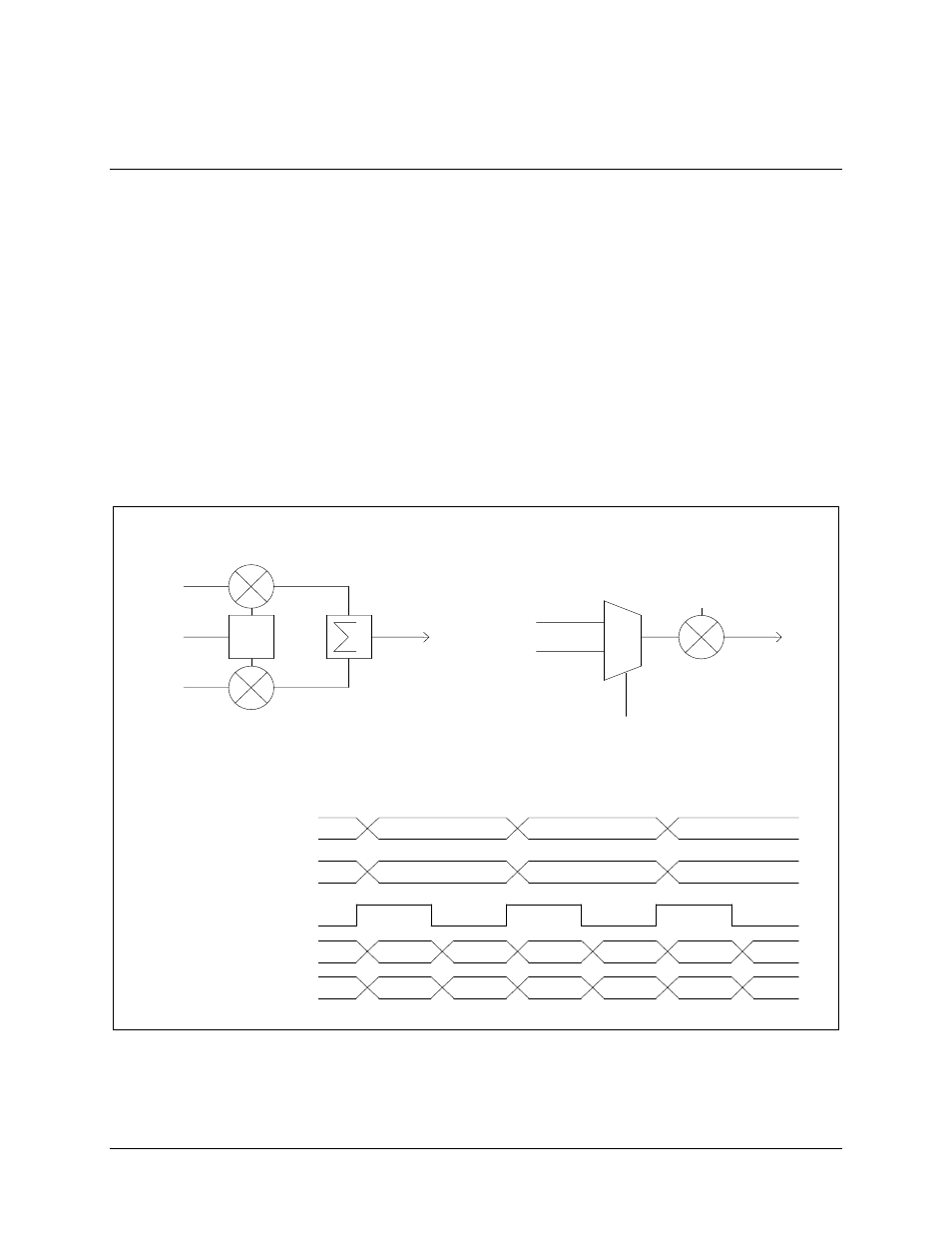
When the modulator is in the BPSK mode, the two data streams are multiplexed into one
data stream to drive the In-phase channel of the modulator. If in Viterbi mode, the BPSK
bit ordering can be selected to conform to either standard: (I0 Q0, I1 Q1) or (Q0I0,
Q1 I1). Figure Chapter 6-3 shows a timing diagram and schematic diagram explaining
BPSK ordering.
BPSK
QPSK
I
LO
0
TX IF
I
1
LO
TX IF
0
Q
-90
Q
SELECT
I
QPSK
Q
Q
I
Q
I
Q
I
SEL
MUX
OUT
BPSK
STANDARD
NON-STANDARD
BPSK
MUX
OUT
Q
I
Q
I
Q
I
Figure Chapter 6-3. BPSK Ordering
6–9
