Root complex, Chaining dma, Hard ip for pci express – Altera Arria 10 Avalon-ST User Manual
Page 205
Note: The chaining DMA design example only supports dword-aligned accesses. The chaining DMA
design example does not support ECRC forwarding.
The BFM driver writes the descriptor tables into BFM shared memory, from which the chaining DMA
design engine continuously collects the descriptor tables for DMA read, DMA write, or both. At the
beginning of the transfer, the BFM programs the Endpoint chaining DMA control register. The chaining
DMA control register indicates the total number of descriptor tables and the BFM shared memory
address of the first descriptor table. After programming the chaining DMA control register, the chaining
DMA engine continuously fetches descriptors from the BFM shared memory for both DMA reads and
DMA writes, and then performs the data transfer for each descriptor.
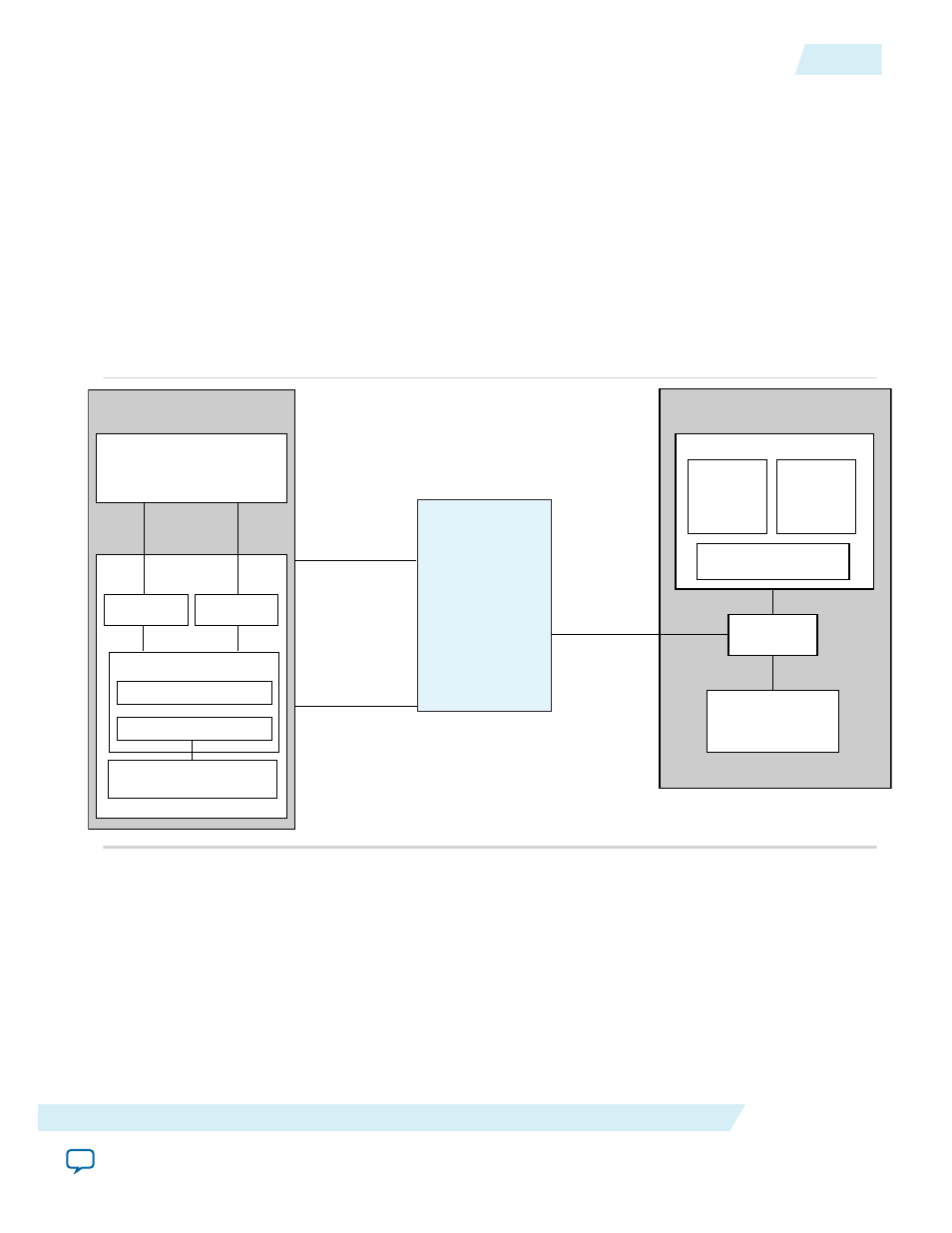
The following figure shows a block diagram of the design example connected to an external RC CPU. For
a description of the DMA write and read registers, Chaining DMA Control and Status Registers.
Figure 17-2: Top-Level Chaining DMA Example for Simulation
Root Complex
CPU
Root Port
Memory
Write
Descriptor
Table
Data
Chaining DMA
Endpoint Memory
Avalon-MM
interfaces
Hard IP for
PCI Express
DMA Control/Status Register
DMA Read
Avalon-ST
Configuration
PCI Express
DMA Write
DMA Wr Cntl (0x0-4)
DMA Rd Cntl (0x10-1C)
RC Slave
Read
Descriptor
Table
UG-01145_avst
2015.05.04
Chaining DMA Design Examples
17-5
Testbench and Design Example
Altera Corporation
