IAI America RCP2-CF User Manual
Page 92
72
The relationships of movement command inputs/position complete outputs and corresponding position numbers
are shown below.
For easier identification, each input/output signal has a name similar to the naming convention used with air
cylinders.
However, note that the target position is determined by the value set in the [Target position] field under each
position number. Therefore, changing the magnitude correlation of the settings in Nos. 0 to 3 will change the
meanings of the corresponding input/output signals.
Accordingly, the settings in the respective position numbers should match the semantic meanings of the
corresponding signal names used in this operation manual, unless doing so will pose a problem.
Input signal
Output signal Target
position
Rear end move (ST0)
Rear end complete (PE0)
Setting in the [Target position] field under
position No. 0
Example: 5 mm
Front end move (ST1)
Front end complete (PE1)
Setting in the [Target position] field under
position No. 1
Example: 390 mm
Intermediate point 1 move (ST2) Intermediate point 1 complete (PE2)
Setting in the [Target position] field under
position No. 2
Example: 100 mm
Intermediate point 2 move (ST3) Intermediate point 2 complete (PE3)
Setting in the [Target position] field under
position No. 3
Example: 250 mm
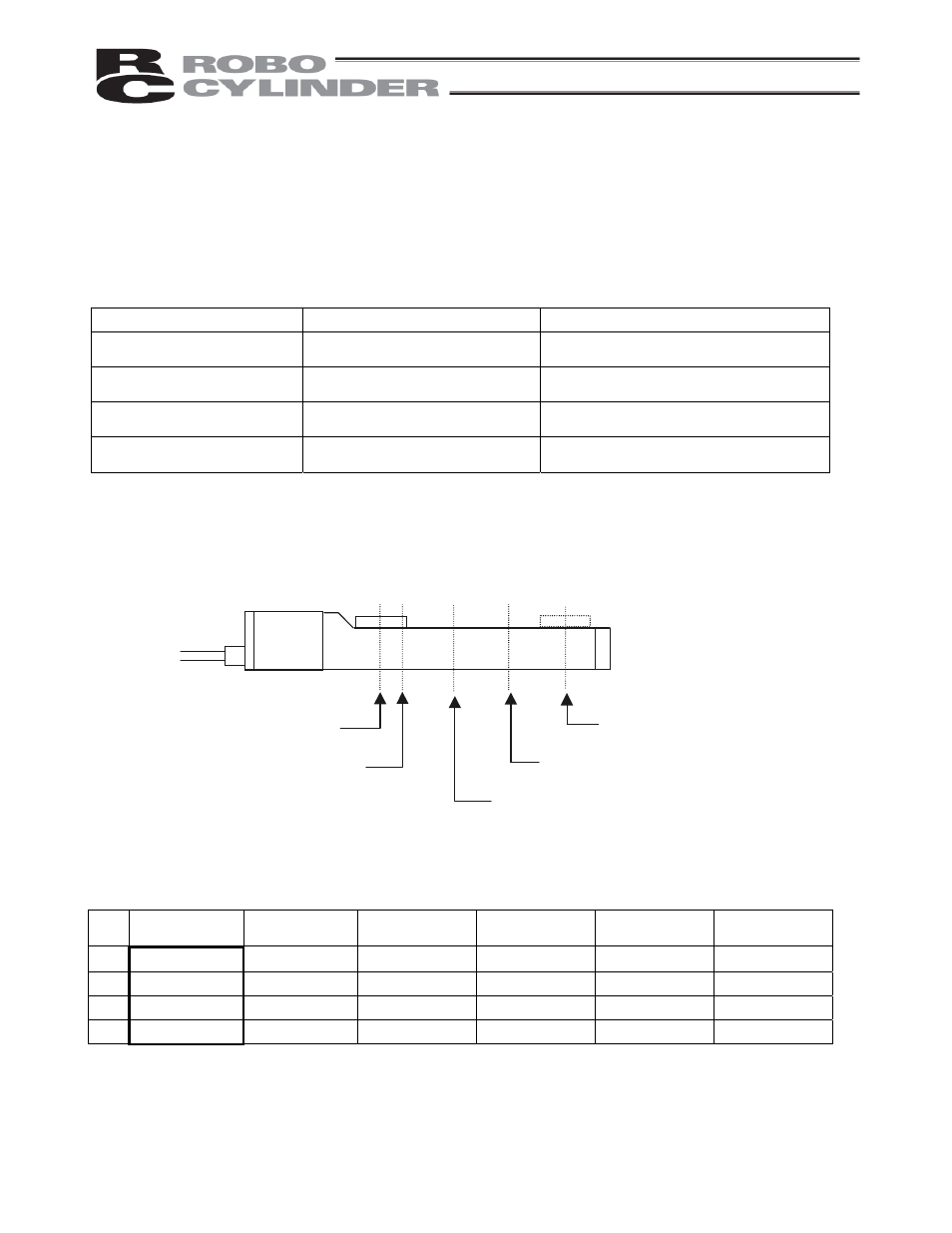
Positioning relationship on the ROBO Cylinder
An example of a slider type with a stroke of 400 mm is explained.
[Motor side]
[Counter-motor side]
Position table (Enter in the fields indicated in bold)
No. Position
Speed
Acceleration/
deceleration
Push
Positioning
band
Acceleration
only MAX
0
5 500
0.3 0 0.1 0
1
390
500
0.3 0 0.1 0
2
100
500
0.3 0 0.1 0
3
250
500
0.3 0 0.1 0
Home position (0 mm)
Rear end complete (5 mm)
Front end complete (390 mm)
Intermediate point 2 complete (250 mm)
Intermediate point 1 complete (100 mm)
