Chapter 10: apps guide – hints & ideas – Telos Zephyr Xstream User Manual
Page 177
USER’S MANUAL
Section 10: APPLICATIONS GUIDE 165
10 APPLICATIONS GUIDE – Hints & Ideas
Of course we hope that you will (eventually) read through the other sections of this manual –
we give you a lot of information about audio coding technology and lots of information on how
and when to use the different coding modes. However, here we have included the following
informational guide to get you started.
10.1 Xstream Versatility – types of dial-up connection and modes
The Xstream is the most versatile codec platform on the market at this time, communicating
with a variety of devices in several ways. In this section, we'll give a review of the different
modes available when on ISDN, illustrating the various capabilities of the unit.
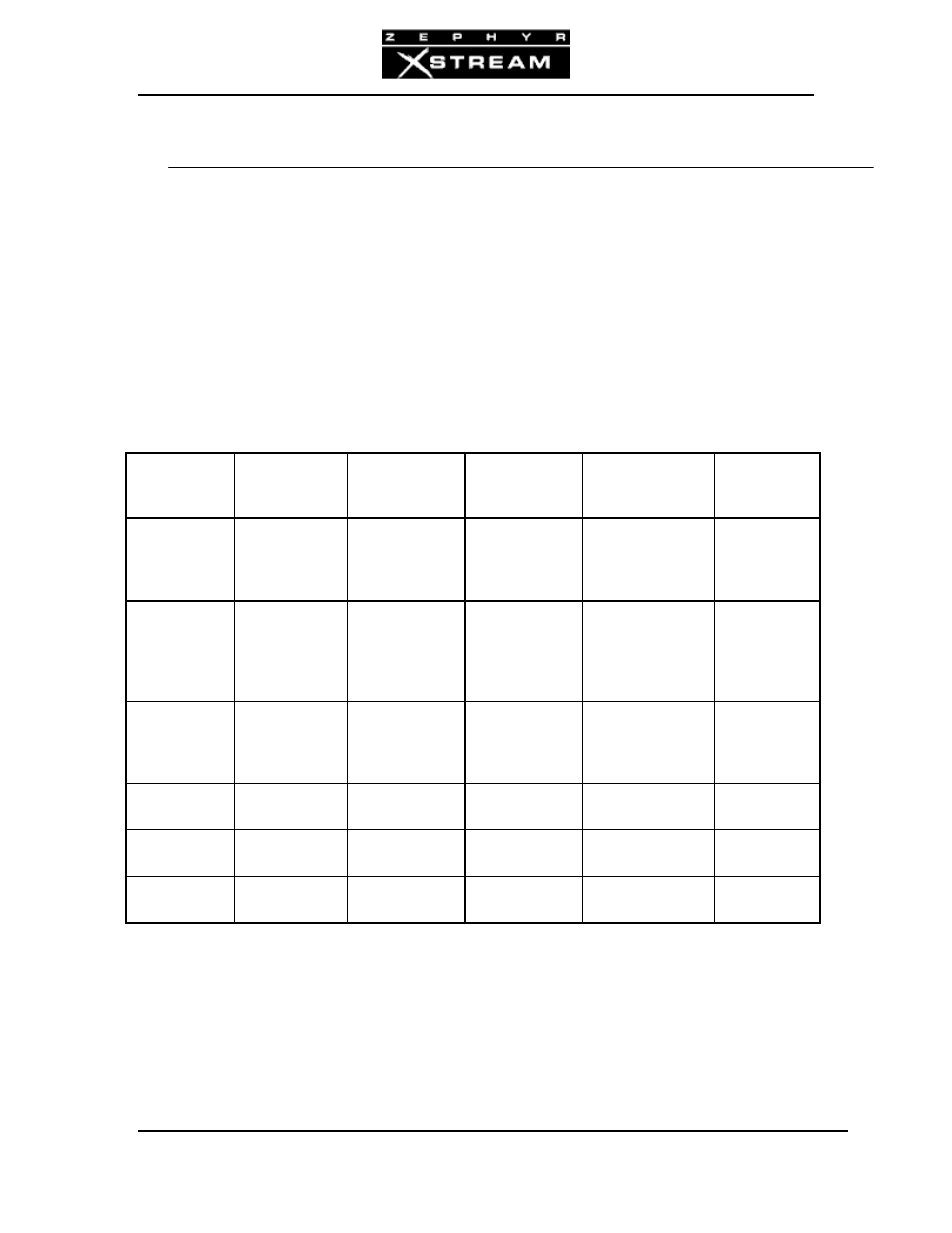
First, let us look at a matrix of the Xstream's abilities:
DIAL MODE
TALKS TO
NETWORK
CALL TYPE
CODEC #
OF
CONNECTIONS
POSSIBLE
NOTES
ZEPHYR
Most ISDN
Codecs
Circuit
Switched Data
(CSD)
Various, as
selected
2, using L3 Dual
or G.722
Maybe be
mixed with a
Phone mode
call
XPORT
Zephyr Xport
on POTS line
Circuit
Switched Voice
(CSV)
G.711 or
aacPlus (ZXP
to ZXS) +
AAC-LD
(ZXS to ZXP)
1 DSP
modem
uses G.711
(A-Law/μ-
Law)
PHONE
POTS
Telephone or
Coupler
Circuit
Switched Voice
(CSV)
G.711 (A-
Law/μ-Law)
2 Maybe
be
mixed with a
Zephyr mode
call
ETHERNET
HTTP
Desktop player
codecs
IP
AAC or L3
Depends on
bitrate
Legacy pull-
only
ETHERNET
RTP
Xstream
IP
AAC or L3
Depends on
bitrate
Push-only
ETHERNET
SIP
Xstream IP
AAC
or
L3
1
Bi-directional
The matrix shows the appropriate Mode to use when placing outbound calls, however the unit
can receive all these same call types, of course. Since the Zephyr mode supports a number of
different codecs (for differing user requirements, as well as compatibility with other codecs) the
Xmt, RCV, and Sample settings must be configured, as well as using the correct call type when
using this mode.
