Principles of data transfer, 1 serial/parallel, 1 principles of data transfer – HEIDENHAIN TNC 335 Technical Manual User Manual
Page 511
8-4
TNC 360
1 Introduction
8/95
1.1 Principles of data transfer
Since all information is conveyed as data, one first needs to become familiar with a few of the
principles of data transfer. The term "Data" is used to describe all of the information which the
computer is capable of collecting and processing.
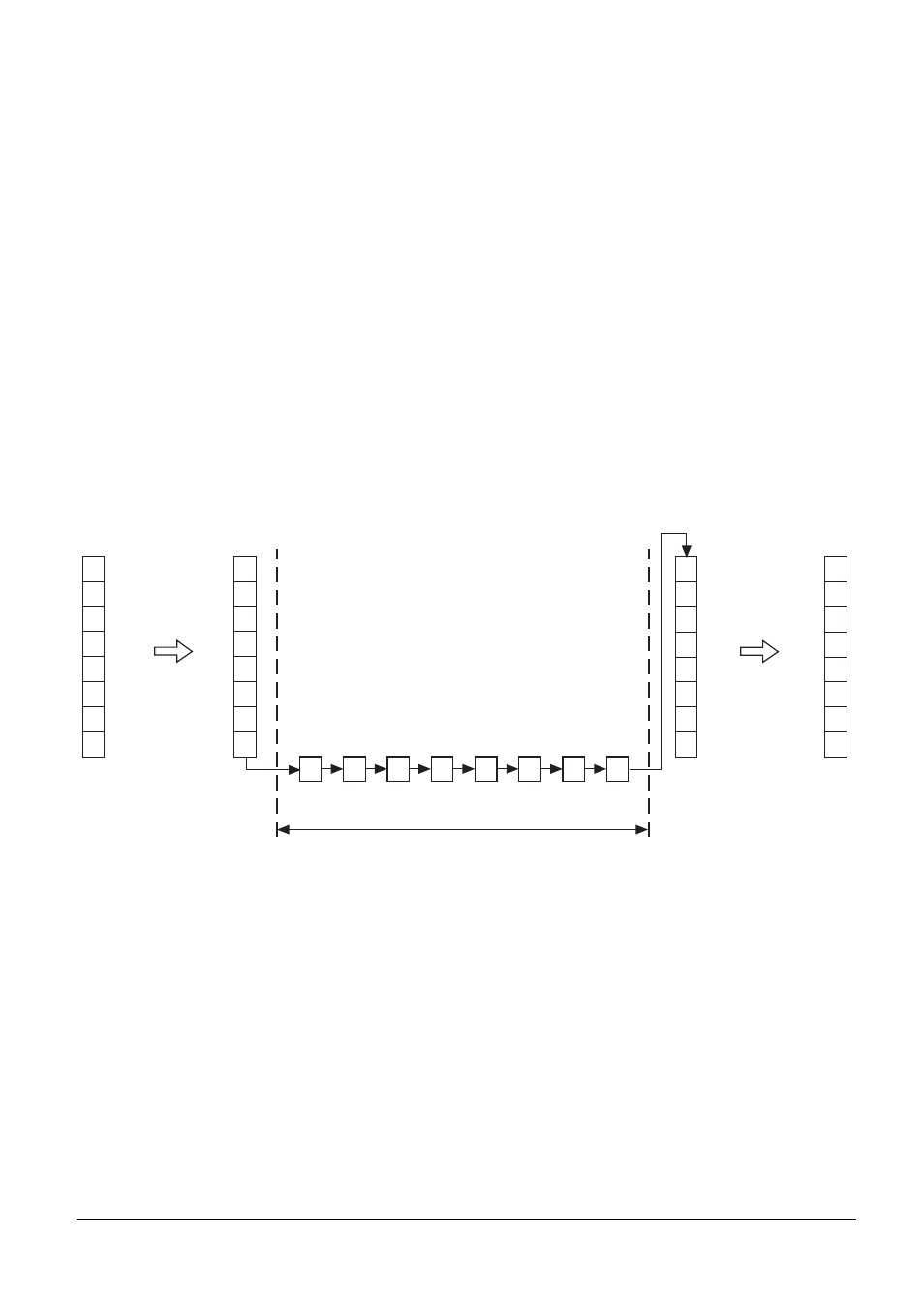
1.1.1 Serial/parallel
Data can be transmitted in either serial or parallel format.
Basically, data is coded in the computer system, e.g. as bytes (8 bits) and supplied to the interface in
parallel.
In the case of serial data transmission, the parallel information from the computer system has to be
converted into a serial data-flow by using an USART (Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitter).
The receiver accepts the serial data-flow and converts it back again into parallel information.
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
Sender
Transmitter
Speicher
Memory
Übertragungsstrecke
Transmission path
Empfänger
Receiver
Schnittstellen-Puffer
Interface buffer
MSB
LSB
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
MSB
LSB
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
Speicher
Memory
Schnittstellen-Puffer
Interface buffer
A parallel interface, on the other hand, does not need a USART: just a line driver. Typically, the
connection between the computer system and a peripheral consists of a 36-way ribbon cable. Its
maximum length is generally about 3 meters.
