8 configuring mstp – CANOGA PERKINS CanogaOS Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 48
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
Proprietary & Confidential Canoga Perkins Metro Ethernet Switches
Page 48 of 350
8 Configuring MSTP
The MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol (IEEE 802.1Q-2005)) enables
multiple VLANs to be mapped to the same spanning-tree instance, thereby reducing the number
of spanning-tree instances needed to support a large number of VLANs. The MSTP provides for
multiple forwarding paths for data traffic and enables load balancing. It improves the fault
tolerance of the network because a failure in one instance (forwarding path) does not affect other
instances (forwarding paths). The most common initial deployment of MSTP is in the backbone
and distribution layers of a Layer 2 switched network; this deployment provides the
highly-available network required in a service-provider environment.
When the switch is in the multiple spanning-tree (MST) modes, the Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol (RSTP), which is based on IEEE 802.1w, is automatically enabled. The RSTP provides
rapid convergence of the spanning tree through explicit handshaking that eliminates the IEEE
802.1D forwarding delay and quickly transitions root ports and designated ports to the
forwarding state.
8.1.1 References
IEEE 802.1Q (2005)
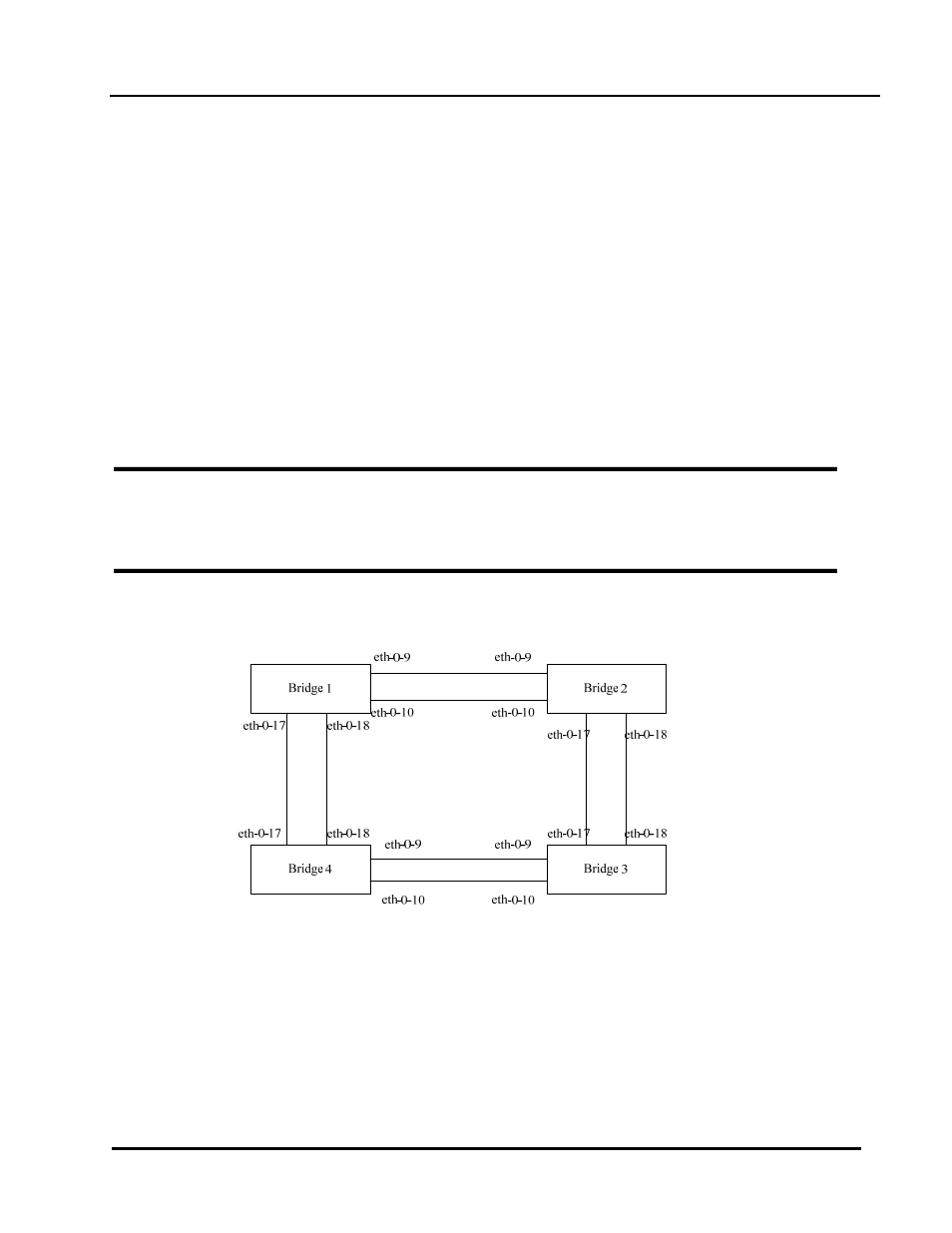
8.1.2 Topology
8.1.3 Configurations
Note: This configuration sample assumes that you are running the Layer-2 module. If you
are using the Layer-2 module, run the switchport command on each port to set the
switching characteristics of Layer-2 protocols.
Bridge1 – Bridge4
