2 basic ospf parameters configuration – CANOGA PERKINS CanogaOS Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 118
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
Proprietary & Confidential Canoga Perkins Metro Ethernet Switches
Page 118 of 350
17.2 Basic OSPF Parameters Configuration
Enabling OSPF requires that you create an OSPF routing process, specify the range of IP
addresses to be associated with the routing process, and assign area IDs to be associated with that
range. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to enable OSPF:
17.2.1 Configurations
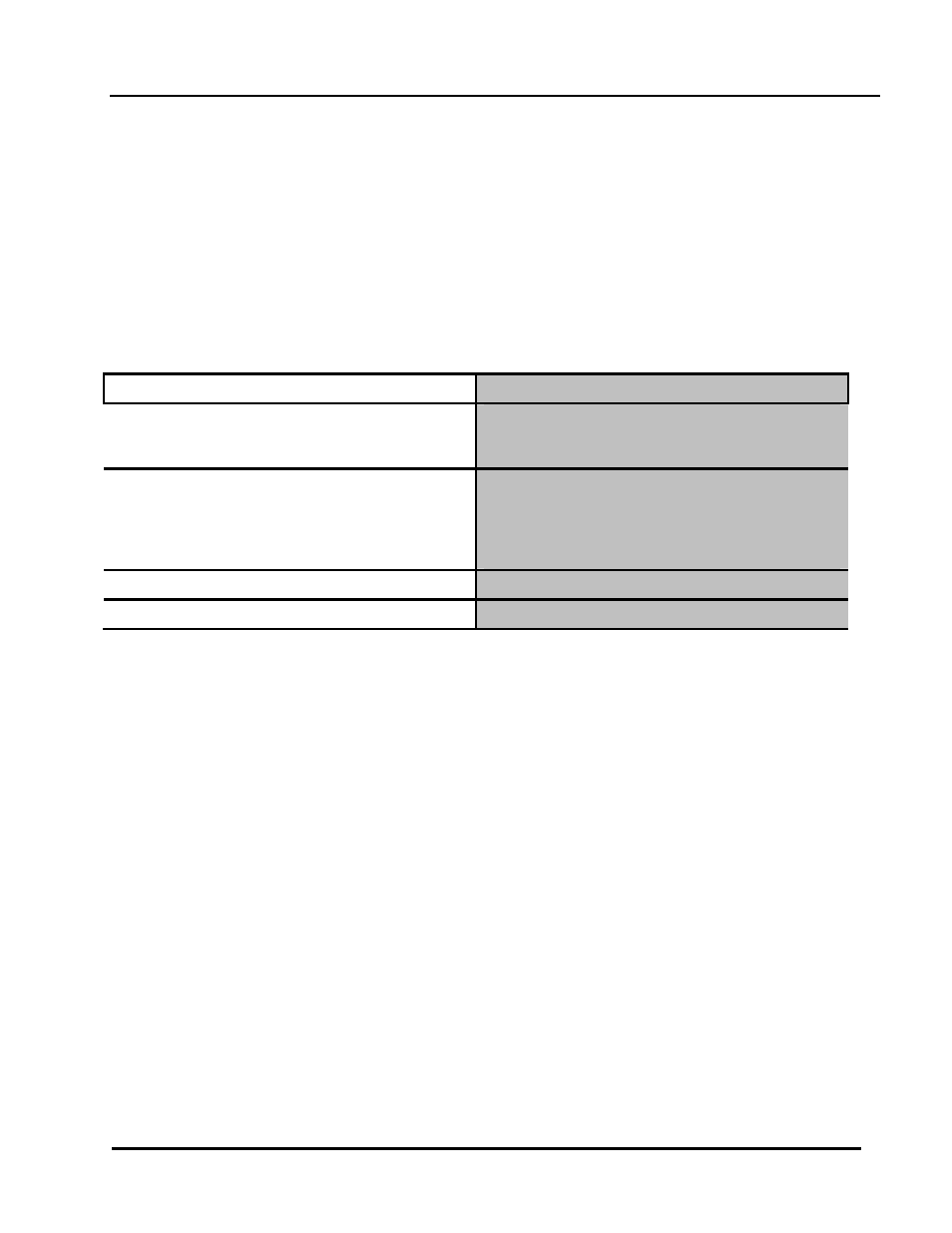
DUT# configure terminal
Enter the Configure mode.
DUT(config)# router ospf 100
Configure the Routing process and specify the Process
ID (100). The Process ID should be a unique positive
integer identifying the routing process.
DUT(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0/24 area 0
Define an interface on which OSPF runs and the area ID
for that interface. You can use the wildcard mask as a
single command to define one or more interfaces to be
associated with a specific OSPF area. The area ID can be
a decimal value or an IP address.
DUT(config-router)# end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
DUT# show ip protocols
Verify your entries.
To end an OSPF routing process, use the “no router ospf process-id” global configuration
command.
This example shows how to configure an OSPF routing process and assign it a process number
of 109:
DUT(config)# router ospf 109
DUT(config-router)# network 131.108.0.0 255.255.255.0 area 24
