16 configuring rip – CANOGA PERKINS CanogaOS Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 108
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
Proprietary & Confidential Canoga Perkins Metro Ethernet Switches
Page 108 of 350
16 Configuring RIP
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is an IP route exchange protocol that uses a distance vector
(a number representing distance) to measure the cost of a given route. The cost is a distance
vector because the cost is often equivalent to the number of router hops between the source and
the destination networks. RIP can receive multiple paths to a destination. The software evaluates
the paths, selects the best path, and saves the path in the IP route table as the route to the
destination. Typically, the best path is the path with the fewest hops. A hop is another router
through which packets must travel to reach the destination. If RIP receives a RIP update from
another router that contains a path with fewer hops than the path stored in the route table, the
software replaces the older route with the newer one. The software then includes the new path in
the updates it sends to other RIP routers. RIP routers also can modify a route’s cost, generally by
adding to it, to bias the selection of a route for a given destination. In this case, the actual number
of router hops may be the same, but the route has an administratively higher cost and is thus less
likely to be used than other, lower-cost routes. A RIP route can have a maximum cost of 15. Any
destination with a higher cost is considered unreachable. Although limiting to larger networks,
the low maximum hop count prevents endless loops in the network.
This chapter contains basic RIP configuration examples. To see details on the commands used in
these examples, or to see the outputs of the Validation commands, refer to the RIP Command
Reference. To avoid repetition, some Common commands, like configure terminal, have not
been listed under the Commands Used section. These Common commands are explained in the
NSM Command Reference.
16.1.1 Enabling RIP
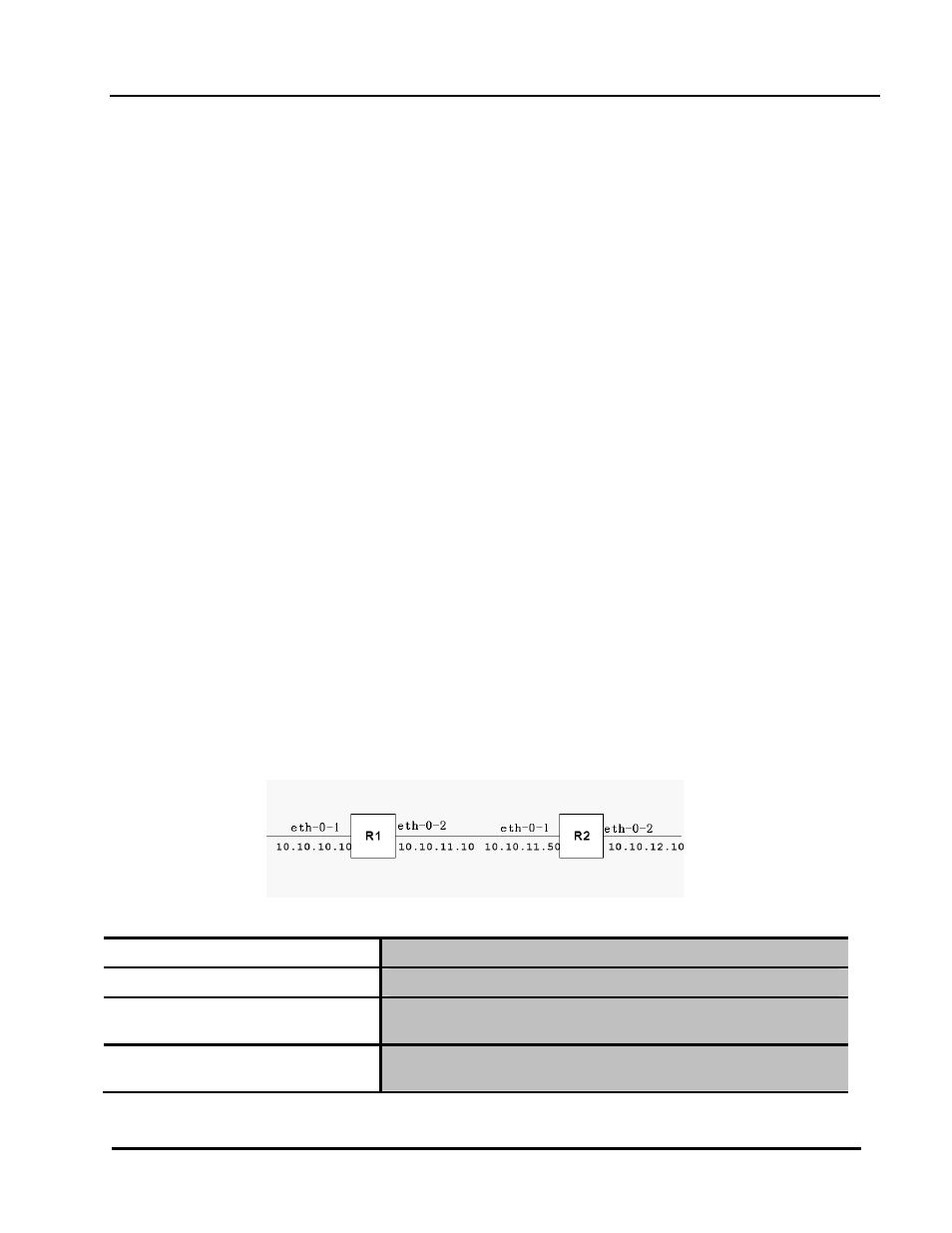
This example shows the minimum configuration required for enabling RIP on an interface. R1
and R2 are two routers connecting to network 10.10.11.0/24. R1 and R2 are also connected to
networks 10.10.10.0/24 and 10.10.12.0/24 respectively. To enable RIP, first define the RIP
routing process and then associated a network with the routing process.
R1
DUT# configure terminal
Enter the Configure mode.
DUT(config)# router rip
Enter the RIP routing process.
DUT(config-router)#network
10.10.10.0/24
Associate networks with the RIP process.
DUT(config-router)#network
10.10.11.0/24
Associate networks with the RIP process.
