Rights, Filters – 2N NetStar Admin manual User Manual
Page 93
93
Rights
Name – define the name of the right to be created. This name is displayed in the
selection.
Users
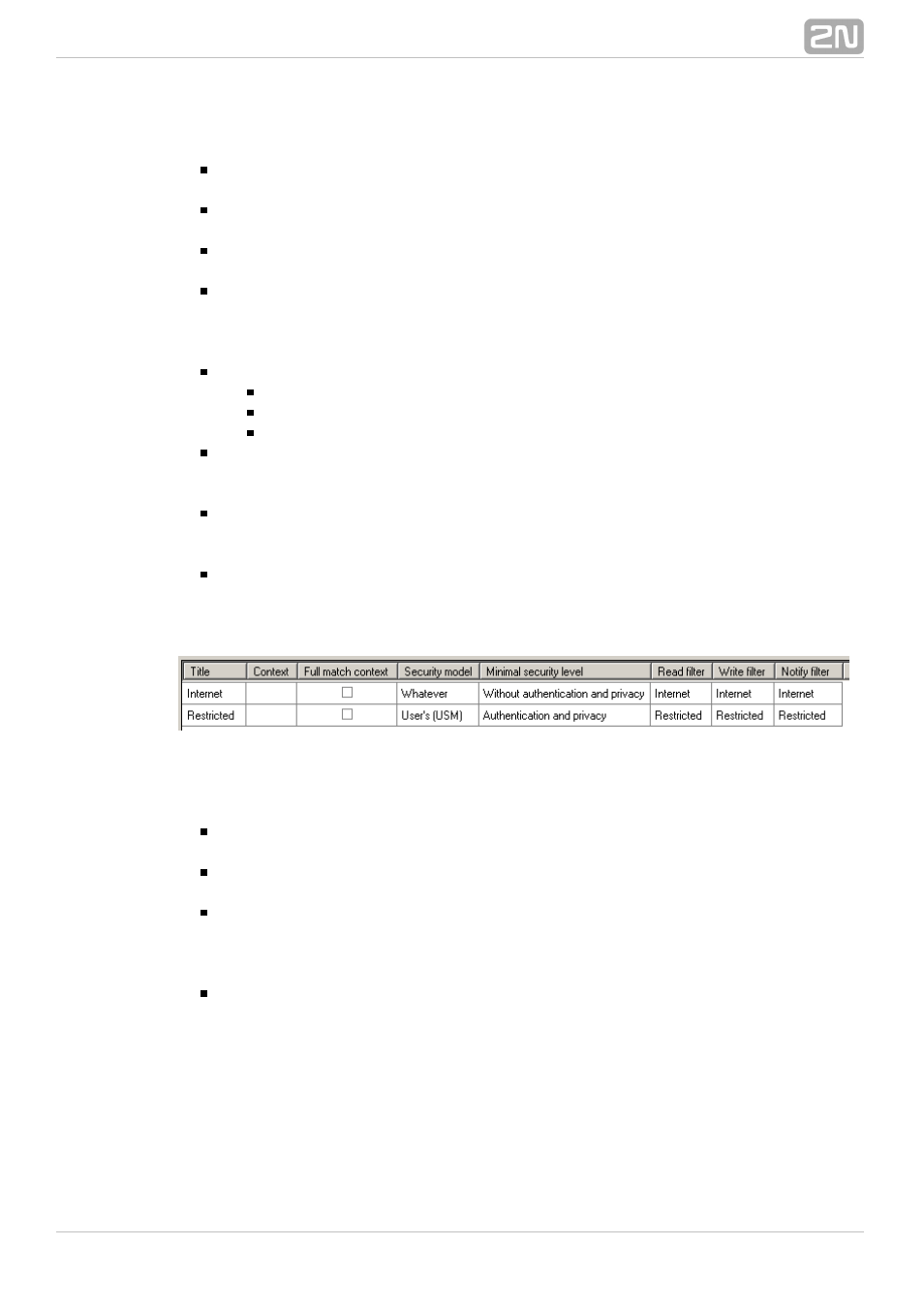
Context – use a text string to identify the SNMP module within the client
address. This parameter need not be filled in.
Full match context – use this option to enable requirement of full match
including context. It is mostly unnecessary.
Security model – in this parameter choose either a specific security model
(SNMP v1, SNMP v2c, USM = SNMP v3) or the
option. Any selection
Whatever
has to be supported by the other party too since no communication feedback is
available.
Minimum security level – the parameter offers three different models:
Authentication and privacy
Without authentication and privacy
Authentication only
Read filter – use this parameter to set the Read filter by choosing an item from
the list of available filters in the
tag. The filter restricts access to the PBX
Filters
information for selected users.
Write filter – use this parameter to set the Write filter by choosing an item from
the list of available filters in the
tag. The filter restricts writing within the
Filters
PBX for selected users.
Notify filter – use this parameter to set the Notify filter by choosing an item
from the list of available filters in the
tag. The filter restricts notifications
Filters
from the PBX for selected users.
Figure: View of SNMP User Right Setting Menu
Filters
Derive – use this option to create a filter with the same setting as the currently
selected one has.
OID root – use the parameter to set the OID tree root to be used as a base for
filter setting. You can view the OID structure in a tree or an alphabetical list.
Exception – use the parameter to change the meaning of a filter rule. If this
option is not checked, the defined OID subtree is used. If it is checked, the use of
a subtree from this row is denied. With this parameter you can specify that the
whole section 2.1 will be used except for subsection 2.1.3.
OID subtree – here choose restrictions for a subtree. If the row is empty, the
whole of the above specified OID root is used. Every filter should have one rule
at least, even an empty row. It is because the filter compares rules with the
subtrees instead of the OID root. If some subtrees overlap, the most common
(the shortest OID) rule is applied.
