Cause mapping tables – 2N NetStar Admin manual User Manual
Page 138
138
Cause Mapping Tables
In this menu, you can specify changes in selected causes. By assigning causes to
different types of virtual ports you can present identical causes in a different way on
the PBX interfaces. To assign a mapping table to a virtual port use the Basic tag for the
particular virtual port. You can also specify in which direction the mapping table should
be used. One and the same table can be used for different interfaces and both
directions at the same time. Hence, an internal caue can be translated into a cause
towards the ISDN, SIP or GSM interface and also in the opposite direction.
The menu has two sections. You can add, remove and rename mapping tables on the
left. The right–hand section includes two parameters and the mapping table.
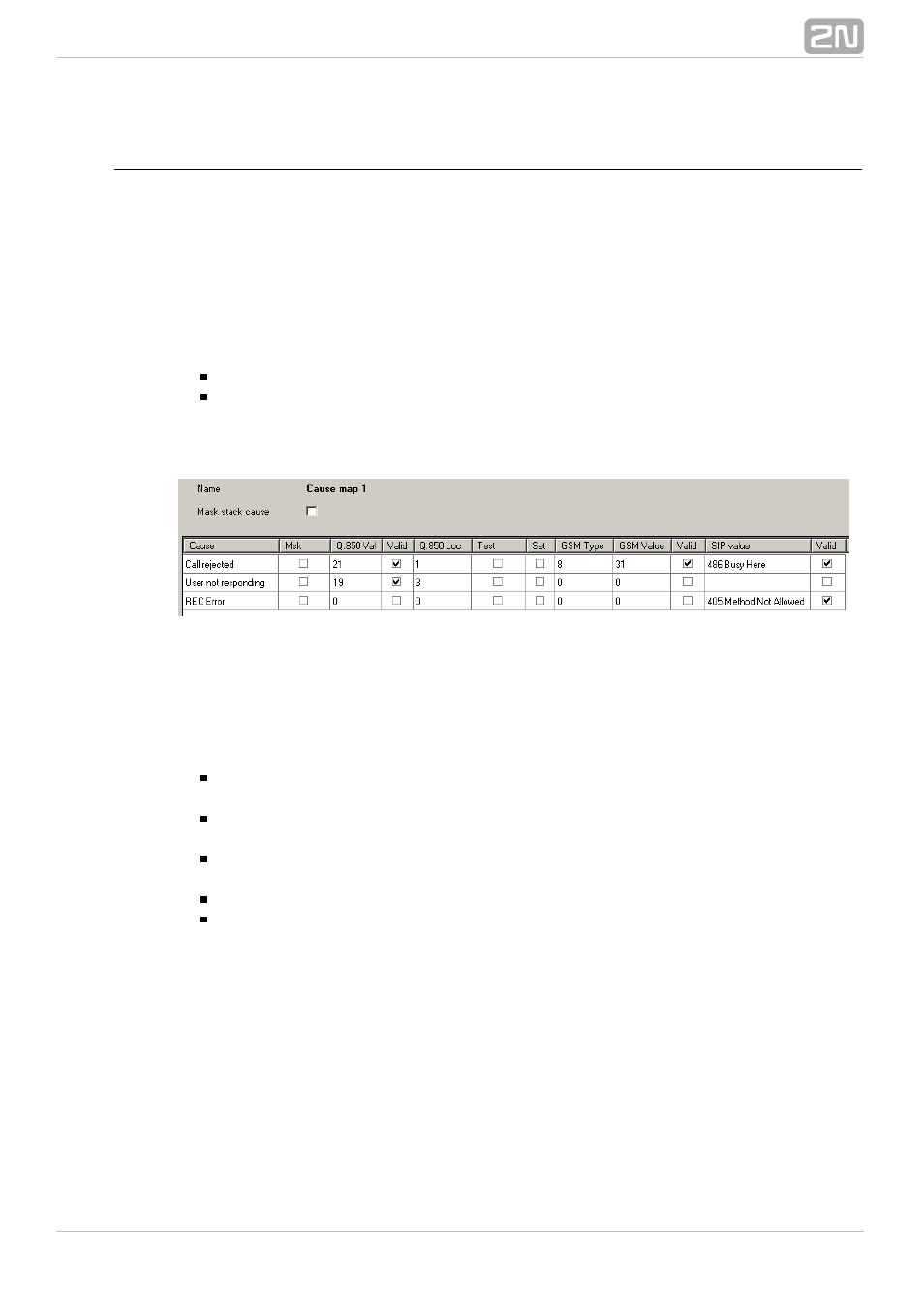
Name – name of the selected mapping table.
Mask stack cause – use this option to disable displaying of the original cause in
the PBX trace for the whole mapping table. In that case, the trace displays
.
Type:None
Mapping table
The context menu helps you add, remove and remove all rows of the table. The table
consists of twelve columns and an unlimited number of rows. The sequence of rows is
irrelevant unless there are two rows with an identical cause and different settings. In
that case, the earlier–added row is applied (the one higher in the configuration).
Cause – choose one of the pre–defined PBX causes. Here user causes are
applied.
Mask – you can disable displaying of the original cause in the PBX trace for a
selected mapping table row.
Q.850 value – you can enter the particular cause value according to Q.850 to be
assigned to the cause in the given row.
Valid – enable translation for an ISDN stack.
Q.850 location – define the Location value to be used in DSS1 for specification
of the network or user from which the cause is coming. For the acceptable values
see the table below.
