7 fault checking sequence, 1 alignment fault, Fault checking sequence -19 – Epson ARM.POWERED ARM720T User Manual
Page 115: Figure 7-14, Sequence for checking faults -19, Alignment fault, Translation fault, Domain fault, Permission fault, On page 7-19
7: Memory Management Unit
ARM720T CORE CPU MANUAL
EPSON
7-19
7.7
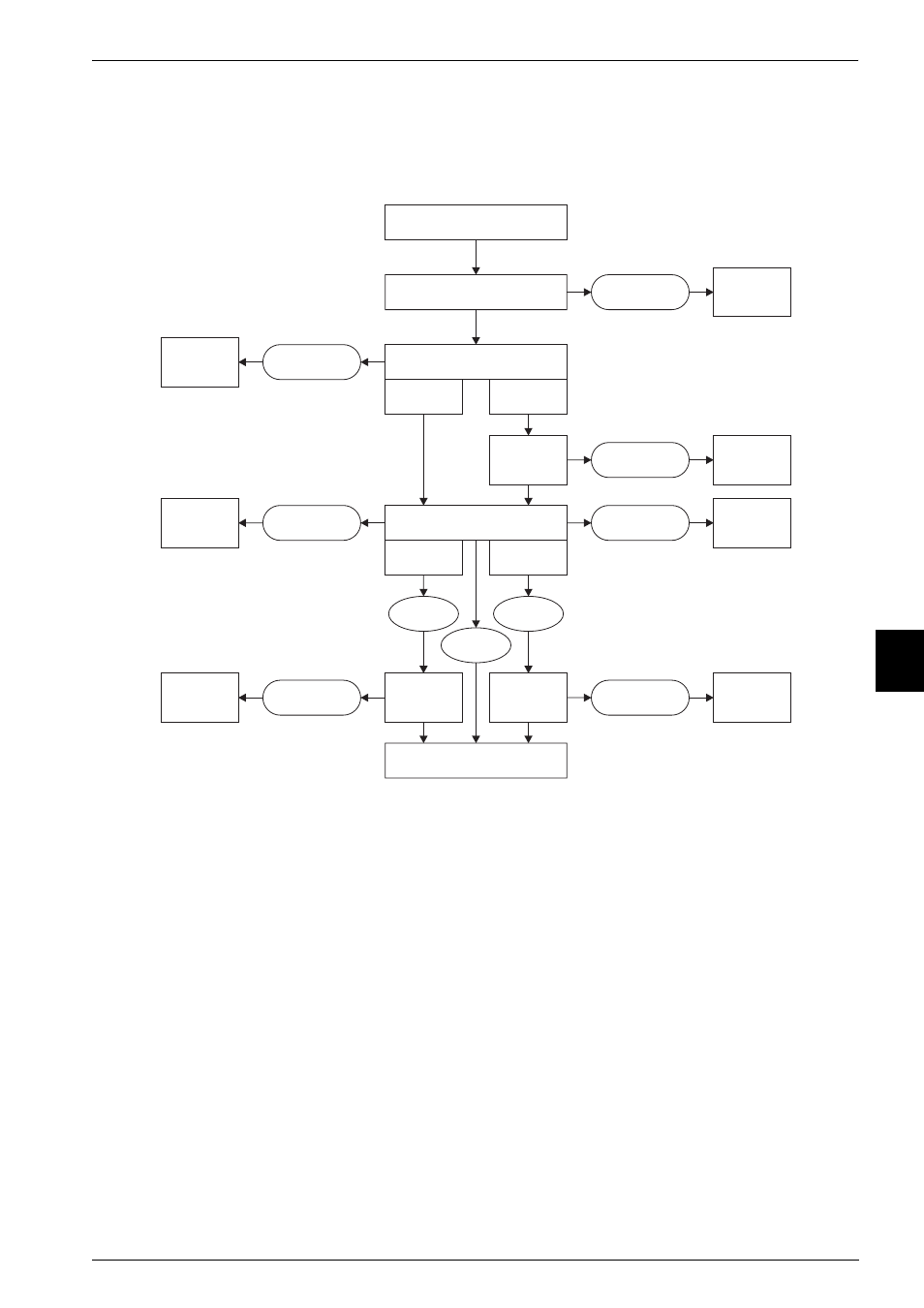
Fault checking sequence
The sequence the MMU uses to check for access faults is different for sections and pages. The
sequence for both types of access is shown in Figure 7-14.
Figure 7-14 Sequence for checking faults
The conditions that generate each of the faults are described in:
•
•
•
•
7.7.1
Alignment fault
If alignment fault is enabled (A bit in CP15 register c1 set), the MMU generates an alignment
fault on any data word access, if the address is not word-aligned, or on any halfword access, if
the address is not halfword-aligned, irrespective of whether the MMU is enabled or not. An
alignment fault is not generated on any instruction fetch, nor on any byte access.
Note:
If the access generates an alignment fault, the access sequence aborts without
reference to more permission checks.
Modified virtual address
Check address alignment
Misaligned
Alignment
fault
Get level one descriptor
Invalid
Section
translation
fault
Section
Page
Get page
table entry
Check domain status
Section
Page
Invalid
Page
translation
fault
No access (00)
Reserved (10)
Page
domain
fault
Section
domain
fault
No access (00)
Reserved (10)
Client (01)
Client (01)
Manager
(11)
Check
access
permissions
Check
access
permissions
Physical address
Violation
Page
permission
fault
Violation
Section
permission
fault
