1 fundamentals of nc – HEIDENHAIN TNC 410 User Manual
Page 42
29
HEIDENHAIN TNC 410
Absolute and relative workpiece positions
Absolute workpiece positions
Absolute coordinates are position coordinates that are referenced
to the datum of the coordinate system (origin). Each position on the
workpiece is uniquely defined by its absolute coordinates.
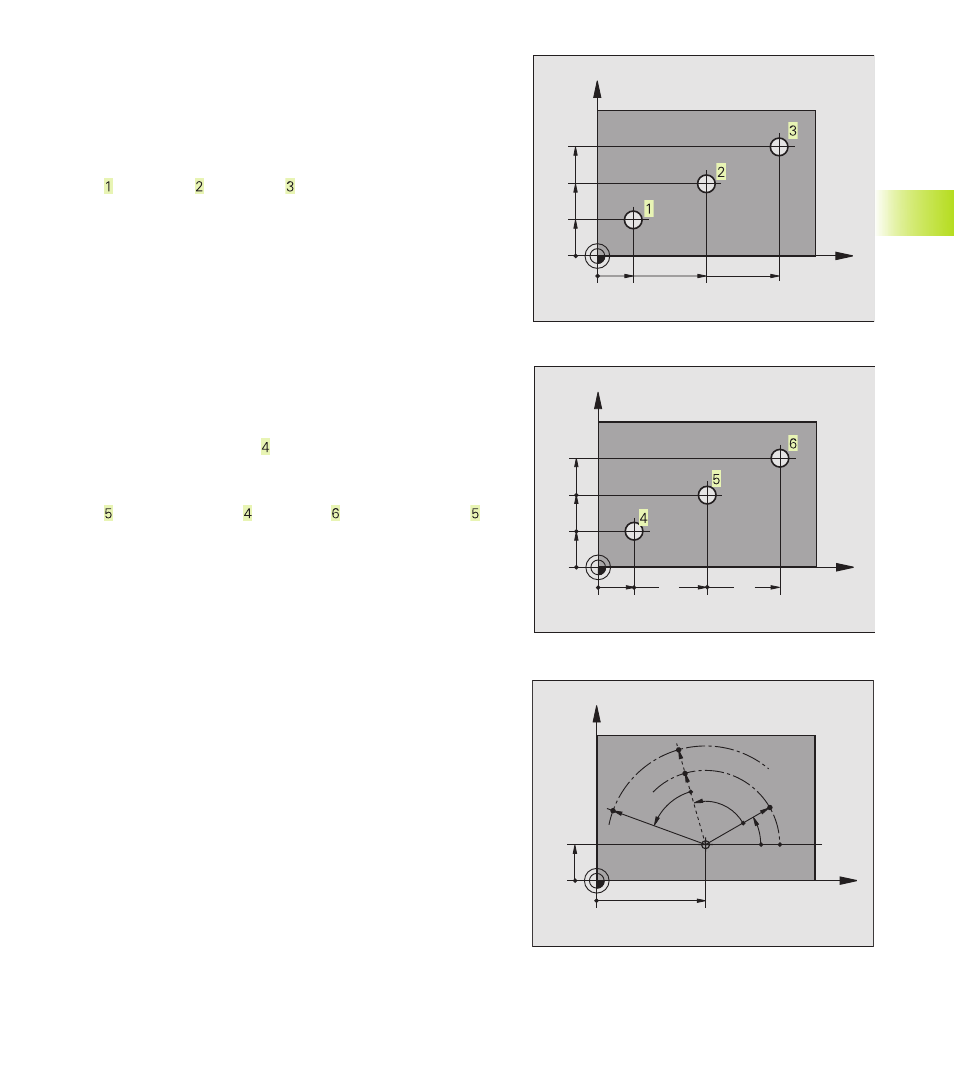
Example 1: Holes dimensioned in absolute coordinates
Hole
Hole
Hole
X=10 mm
X=30 mm
X=50 mm
Y=10 mm
Y=20 mm
Y=30 mm
Relative workpiece positions
Relative coordinates are referenced to the last programmed
nominal position of the tool, which serves as the relative (imaginary)
datum. When you write a part program in incremental coordinates,
you thus program the tool to move by the distance between the
previous and the subsequent nominal positions. Incremental
coordinates are therefore also referred to as chain dimensions.
To program a position in incremental coordinates, enter the prefix
“I” before the axis.
Example 2: Holes dimensioned in relative coordinates
Absolute coordinates of hole :
X= 10 mm
Y= 10 mm
Hole referenced to hole
Hole referenced to hole
IX= 20 mm
IX= 20 mm
IY= 10 mm
IY= 10 mm
Absolute and incremental polar coordinates
Absolute polar coordinates always refer to the pole and the
reference axis.
Incremental polar coordinates always refer to the last programmed
nominal position of the tool.
X
Y
0°
30
10
CC
PR
PA
+IPA
PR
PR
+IPA
+IPR
4.1 Fundamentals of NC
X
Y
30
20
50
30
10
10
X
Y
20
10
10
20
10
10
