1 0 pr ogr amming examples – HEIDENHAIN TNC 410 User Manual
Page 241
10 Programming: Q Parameters
228
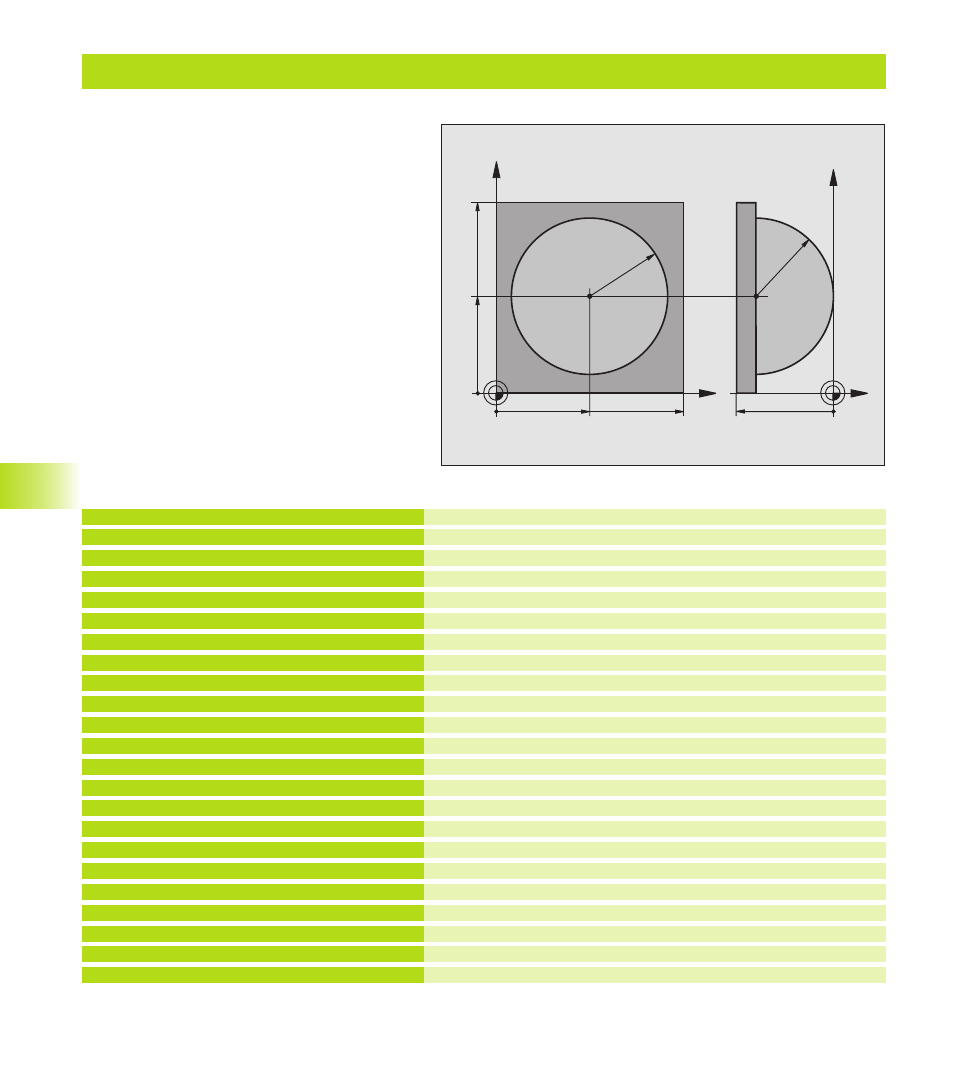
Example: Convex sphere machined with end mill
Example: Convex sphere machined with end mill
Center in X axis
Center in Y axis
Starting angle in space (Z/X plane)
End angle in space (Z/X plane)
Angle increment in space
Radius of the sphere
Starting angle of rotational position in the X/Y plane
End angle of rotational position in the X/Y plane
Angle increment in the X/Y plane for roughing
Allowance in sphere radius for roughing
Setup clearance for pre-positioning in the tool axis
Feed rate for milling
Define the blank form
Define the tool
Call the tool
Retract the touch probe
Call machining operation
Reset allowance
Angle increment in the X/Y plane for finishing
Call machining operation
Retract in the tool axis, end of program
0 BEGIN PGM BALL MM
1 FN 0: Q1 = +50
2 FN 0: Q2 = +50
3 FN 0: Q4 = +90
4 FN 0: Q5 = +0
5 FN 0: Q14 = +5
6 FN 0: Q6 = +45
7 FN 0: Q8 = +0
8 FN 0: Q9 = +360
9 FN 0: Q18 = +10
10 FN 0: Q10 = +5
11 FN 0: Q11 = +2
12 FN 0: Q12 = +350
13 BLK FORM 0.1 Z X+0 Y+0 Z-50
14 BLK FORM 0.2 X+100 Y+100 Z+0
15 TOOL DEF 1 L+0 R+7.5
16 TOOL CALL 1 Z S4000
17 L Z+250 R0 F MAX
18 CALL LBL 10
19 FN 0: Q10 = +0
20 FN 0: Q18 = +5
21 CALL LBL 10
22 L Z+100 R0 FMAX M2
Program sequence
■
This program requires an end mill.
■
The contour of the sphere is approximated by
many short lines (in the Z/X plane, defined via
Q14). The smaller you define the angle increment,
the smoother the curve becomes.
■
You can determine the number of contour cuts
through the angle increment in the plane (defined
in Q18).
■
The tool moves upward in three-dimensional
cuts.
■
The tool radius is compensated automatically.
X
Y
50
100
100
Z
Y
-50
R45
50
R45
1
0.1
0 Pr
ogr
amming Examples
