3 state machine, 1 state transitions and conditions - overview, State machine – Lenze PLC Designer ApplicationTemplate (PLC Designer R3-x) User Manual
Page 77: State transitions and conditions - overview, Architecture: the applicationtemplate in detail
Lenze · ApplicationTemplate · 1.3 EN - 04/2013
77
Architecture: The ApplicationTemplate in detail
State machine
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
9.3
State machine
The machine module (which is on the highest level of the MachineModuleTree MMT) controls the
state machine of all lower-level machine modules.
• The resulting state transitions have an impact on the subordinated machine modules.
9.3.1
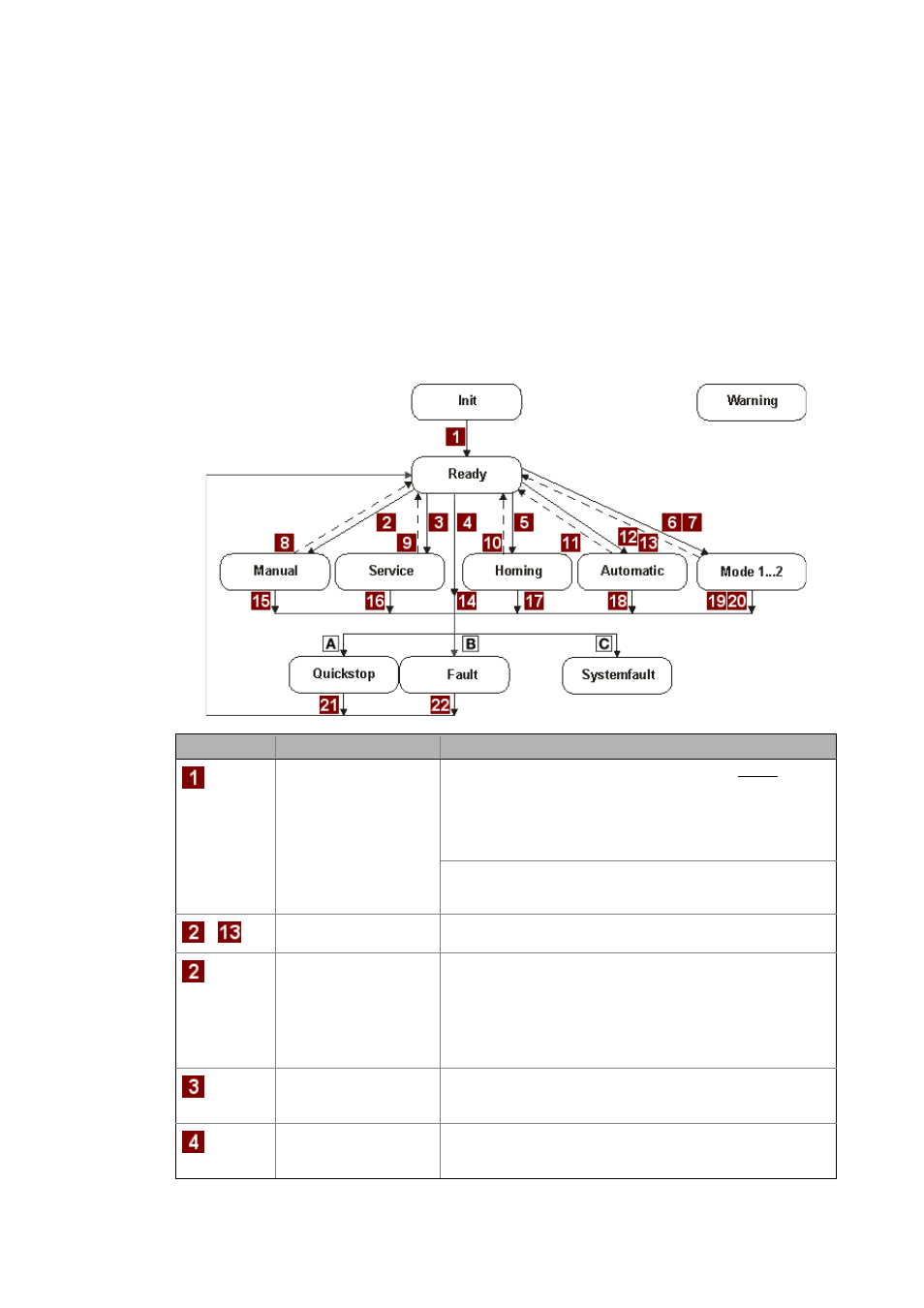
State transitions and conditions - overview
This section illustrates the individual state transitions of the ApplicationTemplate state machine.
For each state transition, the conditions required in each case are specified. The state transitions are
numbered and then described in the text:
Labelled with
State/identifier
Description
Initialisation
Init
Initialisation of the module / module application is always required.
• After a RESET, the "Init""Ready" state transition is inhibited.
• Then the "Init""Ready" state transition is to be enabled by the
module application (when initialisation has been completed).
• The SMEnableInitToReady(TRUE/FALSE) method enables /
inhibits the state transition.
Enable/inhibit mechanism
• ...permits the module applications to inhibit/enable the
respective state transition.
...
Idle state
Ready
Ready for operation. This is the basic state of the state machine.
Manual operation
Manual
Enable/inhibit mechanism
• In this state, the controller can be controlled in manual mode, for
instance for cleaning or changing the tool.
• By setting the individual control bits, the controller can be
controlled manually (Jog1, Jog2, QSP, ErrorReset...).
• This state permits the module applications to inhibit/enable the
underlying state transition.
Service
Service operation for maintenance purposes
• MM_Module1: Load value (example: 123)
• MM_Module2: Load value (example: 567)
Automatic
Automatic operation
• MM_Module1: Incrementing (50 units per second)
• MM_Module2: Incrementing (20 units per second)
