Grade choice and effect of milling direction, Should be selected to provide a chip thickness, h – Sandvik Coromant Heat resistant super alloys User Manual
Page 88
86
v
c
h
ex
Grade choice and effect of milling direction
D
3
63 mm, z
n
4, v
c
1000 m/min, a
e
32 mm,
f
z
0.11 mm/tooth, h
ex
0.07 mm, a
p
1.5 mm (no coolant)
Material: Inconel 718 (40 HRC)
5
4
3
2
1
0
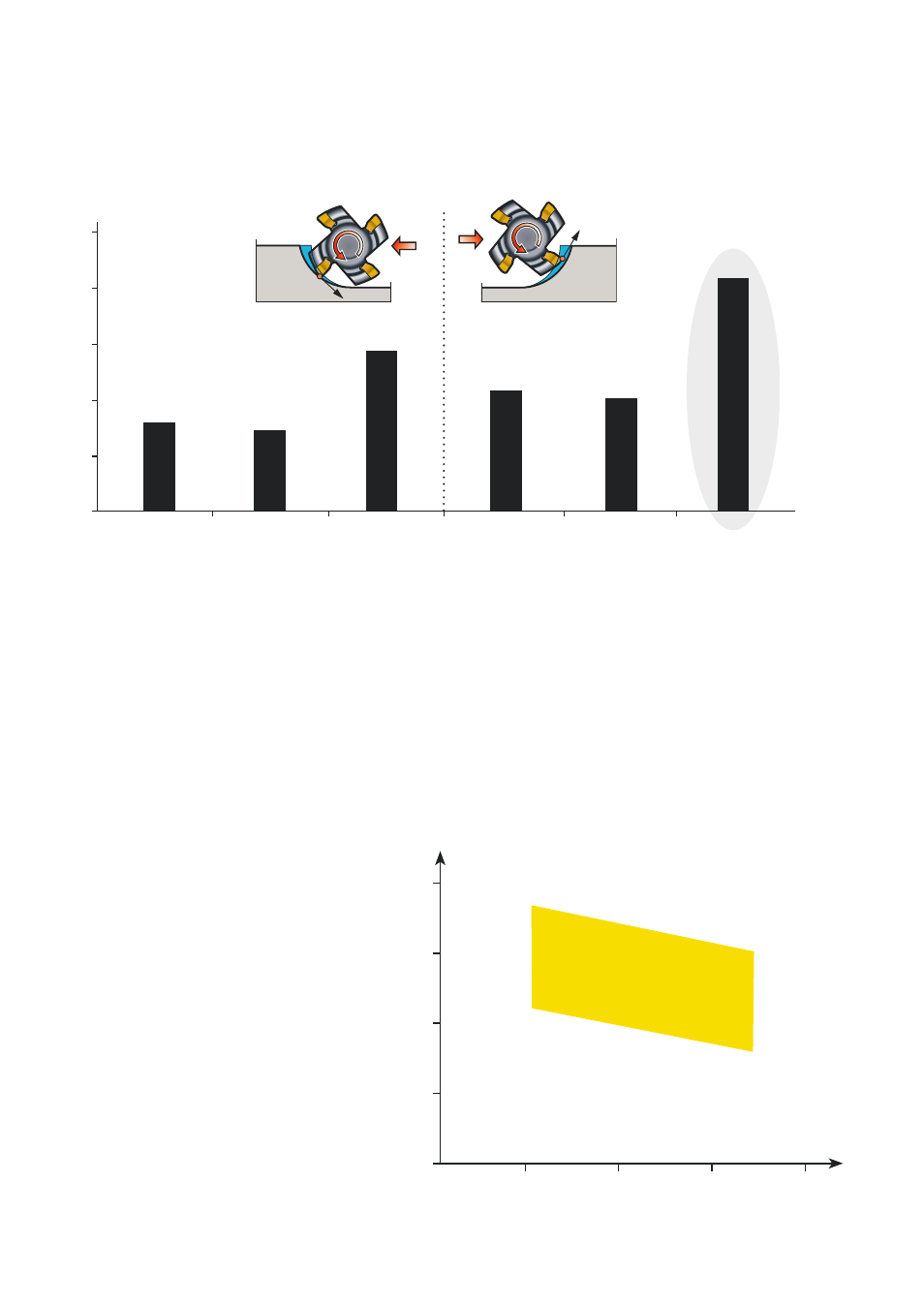
RNGN 670
RNGN 6080
RNGN 6060
RNGN 670
RNGN 6080
RNGN 6060
Down/climb milling
Up/conventional milling
Minutes in cut
The diagram shows that:
• New Sialon grade CC6060 gives the outstanding performance.
• Up/conventional milling provides a longer tool life and more consistent wear compared
to down/climb milling. This is due to the reduced impact force on entering the material
better suited to ceramic material.
Short tool
life – cutting
temperature
too high
Edge line frittering
– cutting
temperature
too low
W
or
k
hardening
of
wor
kpiece
material
Top
slice
–
high
cutting
pressure
Cutting data recommendation
The speed should be balanced to
create enough heat in the cutting
zone to plasticize the chip, but
not so high as to unbalance the
ceramic.
The feed, f
z
, should be selected to
provide a chip thickness, h
ex
, which
is high enough so as not to work-
harden the material, but not so high
as to cause edge frittering.
Higher feeds and depths of cut
require a reduction in the cutting
speed, v
c
.
Application
area
CC6060
1200
900
600
300
0
0.025
0.05
0.075
0.1
