Typical wear patterns in hrsa milling – Sandvik Coromant Heat resistant super alloys User Manual
Page 71
69
S30T
GC2040
GC1030
S40T
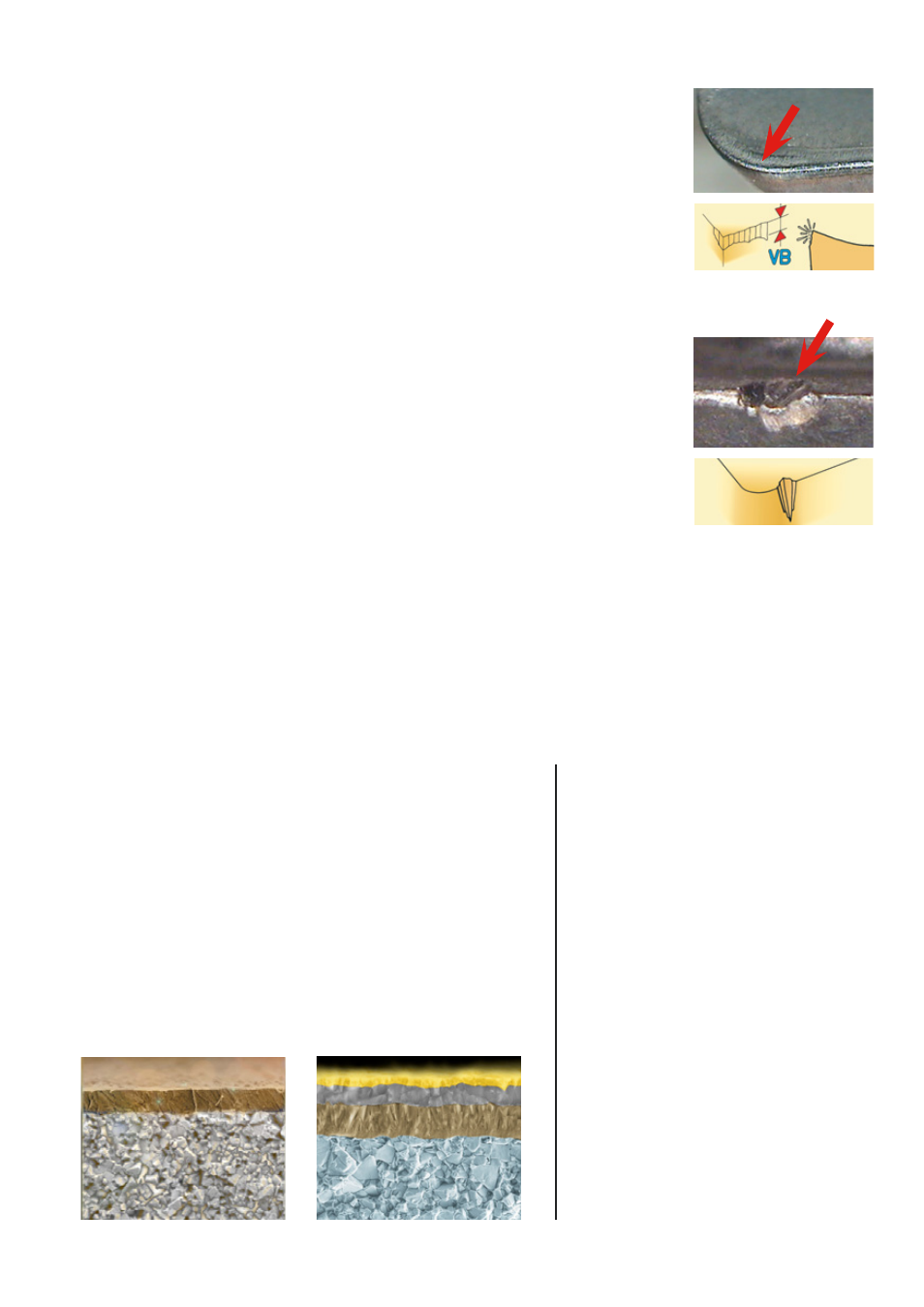
Flank wear
Rapid flank wear causing poor surface finish or out of tolerance.
Cause: Cutting speed too high or insufficient wear resistance.
Remedy: Reduce cutting speed.
Select a more wear resistant grade.
Cause: Chip thickness too low.
Remedy: Increase feed.
Notch wear
Notch wear causing poor surface finish and risk of insert breakage.
Cause: Work hardening materials.
Remedy: Select round insert/reduce a
p
.
The common causes of tool failure are excessive flank wear, notch-
ing at the cutting edge, and the inability to reach surface finish and
accuracy requirements. Other contributing factors include excessive
crater depth and destruction of the cutting edge by fracture. HRSA
also tend to work-harden making subsequent passes more prone
to notch wear.
Typical wear patterns in HRSA milling
PVD-TiAlN-coated carbide
grade for milling of heat
resistant super alloys at
medium speeds. Good
resistance to built-up
edge and plastic deforma-
tion.
Tough MT-CVD coated carbide for
milling of cast heat resistant alloys.
Good resistance to high tempera-
tures.
Complementary
First choice
Combination of micro-grain carbide
and a wear resistant PVD coating
enables very sharp cutting edges
that resist fatigue and micro-chip-
ping. Enables higher cutting speeds
and longer tool life.
Combination of high
toughness cemented car-
bide with a thin CVD coat-
ing resulting in a grade
that withstands vibration
and other difficult cutting
conditions. Enables longer
tool life and high security.
