Figure 9-7. receive done-queue descriptor, Figure 9-6. receive free-queue structure – Rainbow Electronics DS3131 User Manual
Page 84
DS3131
84 of 174
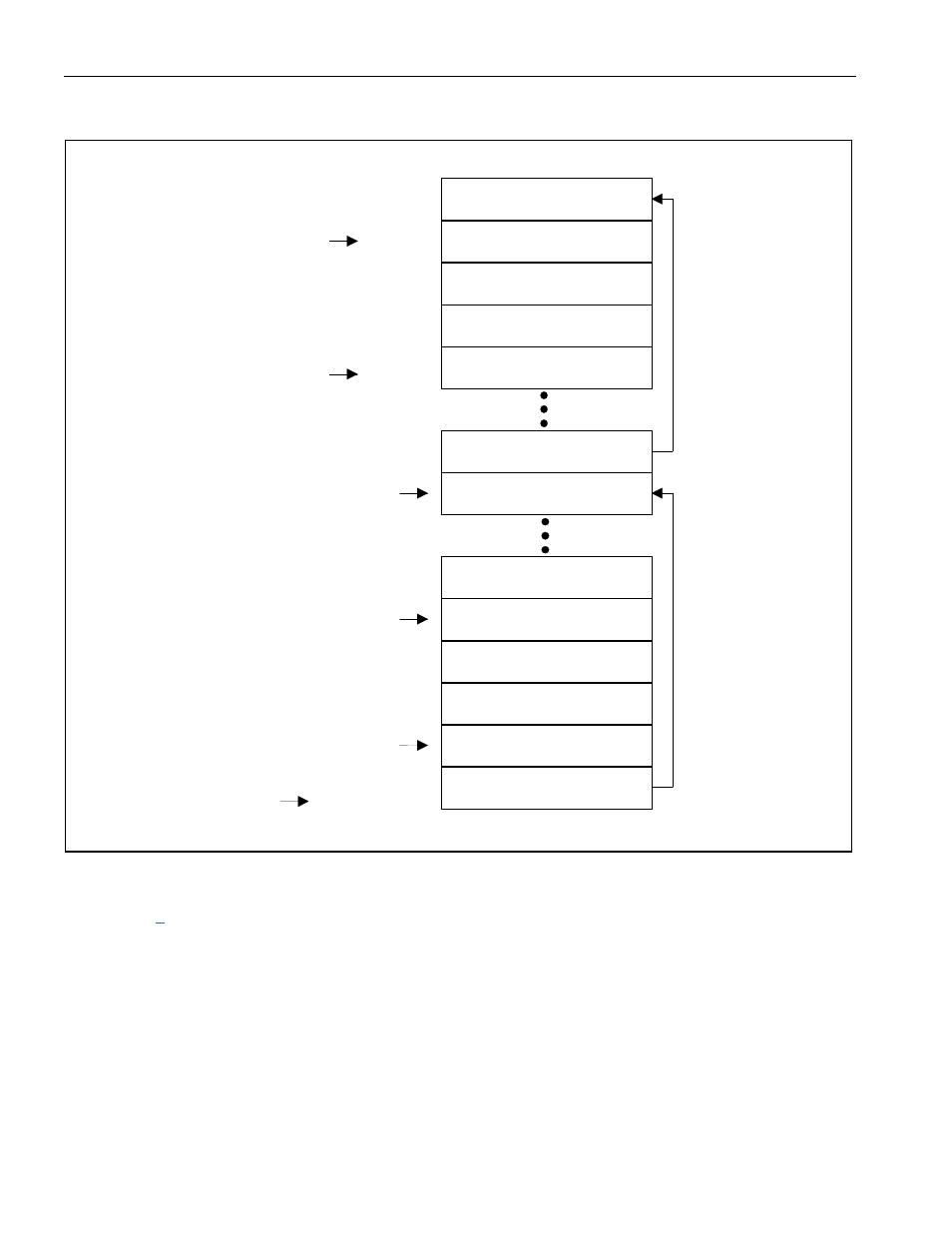
Figure 9-6. Receive Free-Queue Structure
Once the receive DMA is activated (by setting the RDE control bit in the master configuration register,
see Section
5
), it can begin reading data out of the free queue. It knows where to read data out of the free
queue by reading the read pointer and adding it to the base address to obtain the actual 32-bit address.
Once the DMA has read the free queue, it increments the read pointer by two dwords. A check must be
made to ensure the incremented address does not equal or exceed either the receive free-queue small-
buffer start address (in the case of the large buffer circular queue) or the receive free-queue end address
(in the case of the small buffer circular queue). If the incremented address does equal or exceed either of
these addresses, the incremented read pointer is set equal to 0000h.
Base + 00h
Base + 08h
Base + 10h
Base + 18h
Base + 20h
Base + End Address
Free-Queue Large Buffer
Host Write Pointer
Free-Queue Large Buffer
DMA Read Pointer
Maximum of 65,536
Free-Queue Descriptors
DMA Acquired
Free-Queue Descriptor
Free-Queue Small Buffer
DMA Read Pointer
Free-Queue Small Buffer
Host Write Pointer
Free-Queue Small Buffer
Start Address
Large
Buffer
Circular
Queue
Small
Buffer
Circular
Queue
Host Readied
Free-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Free-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Free-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Free-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Free-Queue Descriptor
DMA Acquired
Free-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Free-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Free-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Free-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Free Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Free-Queue Descriptor
Host Readied
Free-Queue Descriptor
