Master configuration register description, Tatus and, Nterrupt – Rainbow Electronics DS3131 User Manual
Page 37: 2 master configuration register description
DS3131
37 of 174
5.2 Master Configuration Register Description
The master configuration (MC) register is used by the host to enable the receive and transmit DMAs as
well as to control their PCI bus bursting attributes and select which port the BERT is dedicated to.
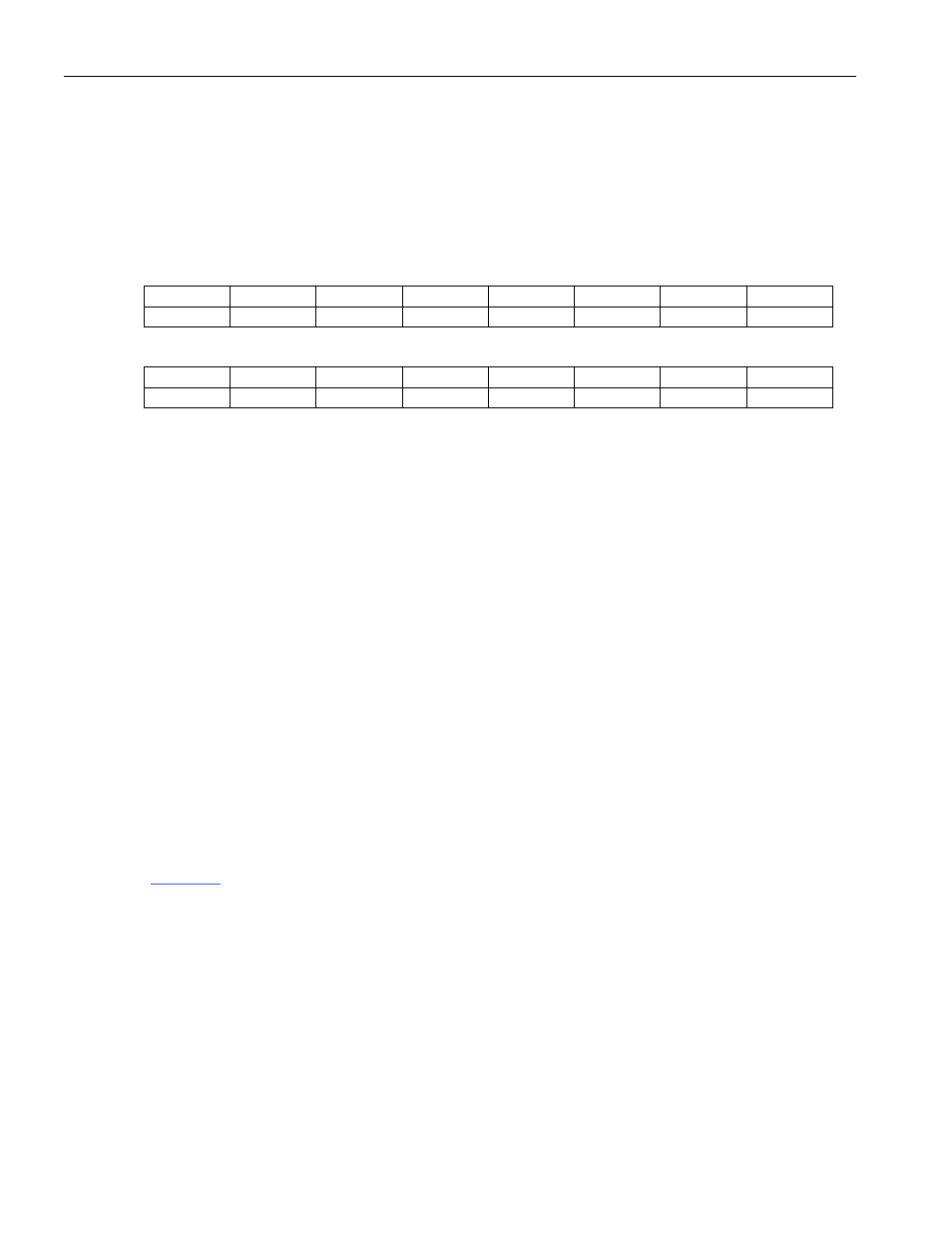
Register Name:
MC
Register Description:
Master Configuration Register
Register Address:
0010h
Bit
# 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
BPS0 PBO RFPC1
RFPC0 TDE DT1 DT0 RDE
Default
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit
# 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Name TFPC1
TFPC0
reserved
BPS5 BPS4 BPS3 BPS2 BPS1
Default
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Note:
Bits that are underlined are read-only; all other bits are read-write.
Bit 0/Receive DMA Enable (RDE). This bit is used to enable the receive DMA. When it is set to 0, the receive
DMA does not pass any data from the receive FIFO to the PCI bus, even if one or more HDLC channels is
enabled. On device initialization, the host should fully configure the receive DMA before enabling it through this
bit.
0 = receive DMA is disabled
1 = receive DMA is enabled
Bit 1/DMA Throttle Select Bit 0 (DT0); Bit 2/DMA Throttle Select Bit 1 (DT1). These two bits select the
maximum burst length that the receive and transmit DMA is allowed on the PCI bus. The DMA can be restricted
to a maximum burst length of just 32 dwords (128 Bytes) or it can be incrementally adjusted up to 256 dwords
(1024 Bytes). The host selects the optimal length based on a number of factors, including the system environment
for the PCI bus, the number of HDLC channels being used, and the trade-off between channel latency and bus
efficiency.
00 = burst length maximum is 32 dwords
01 = burst length maximum is 64 dwords
10 = burst length maximum is 128 dwords
11 = burst length maximum is 256 dwords
Bit 3/Transmit DMA Enable (TDE). This bit is used to enable the transmit DMA. When it is set to 0, the
transmit DMA does not pass any data from the PCI bus to the transmit FIFO, even if one or more HDLC channels
is enabled. On device initialization, the host should fully configure the transmit DMA before enabling it through
this bit. See
Table 8-A
.
0 = transmit DMA is disabled
1 = transmit DMA is enabled
Bit 4/Receive FIFO Priority Control Bit 0 (RFPC0); Bit 5/Receive FIFO Priority Control Bit 1 (RFPC1).
These two bits select the algorithm the FIFO uses to determine which HDLC channel gets the highest priority to
the DMA to transfer data from the FIFO to the PCI bus. In the priority-decoded scheme, the lower the HDLC
channels number, the higher the priority.
00 = all HDLC channels are serviced round robin
01 = HDLC channels 1 and 2 are priority decoded; other HDLC channels are round robin
10 = HDLC channels 1 to 4 are priority decoded; other HDLC channels are round robin
11 = HDLC channels 1 to 16 are priority decoded; other HDLC channels are round robin
