Figure 55. interrupt configuration register (intc, On.) figure 5-5 des – Intel 386 User Manual
Page 83
Intel386™ EX EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSOR USER’S MANUAL
5-10
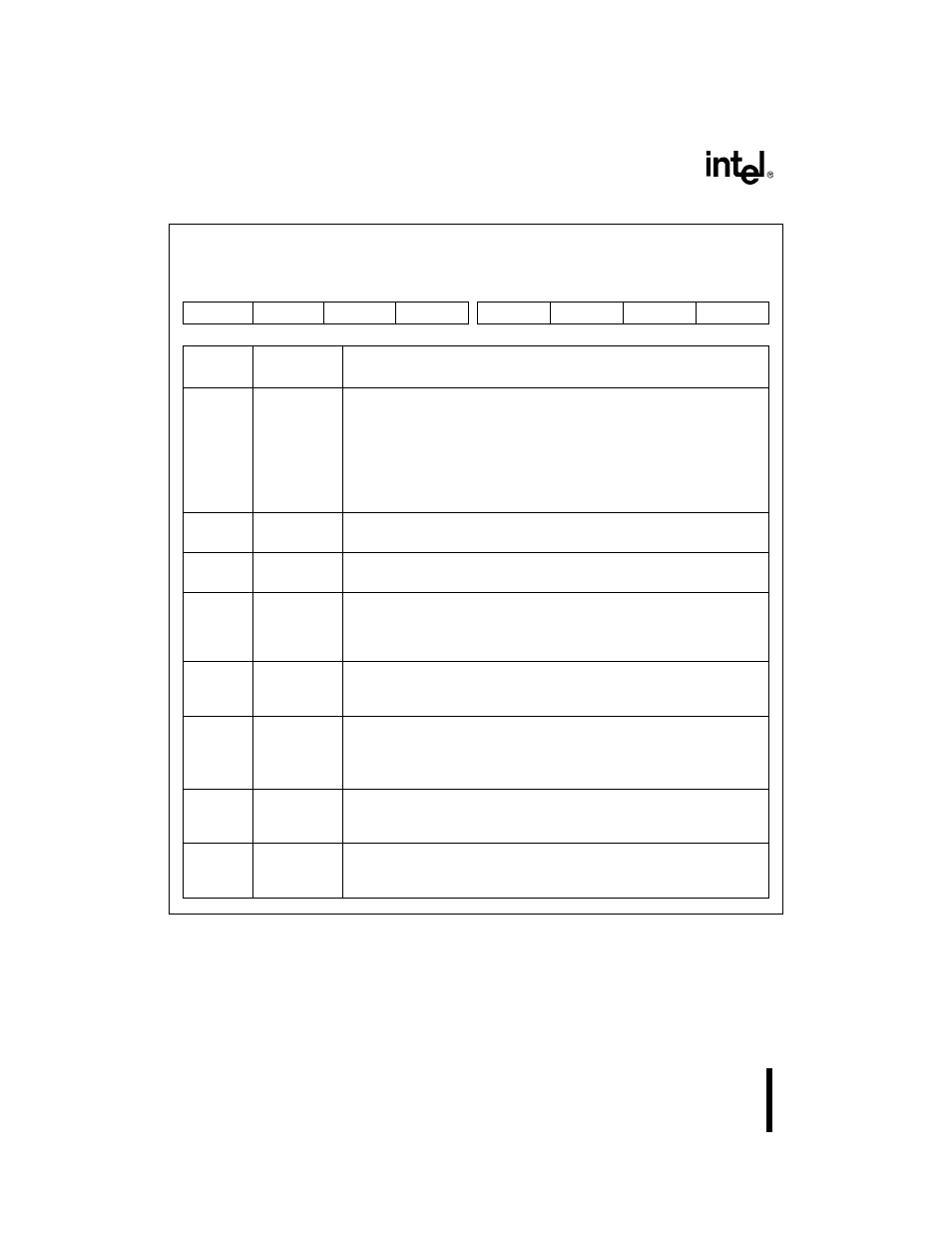
Figure 5-5. Interrupt Configuration Register (INTCFG)
Interrupt Configuration
INTCFG
(read/write)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
F832H
—
00H
7
0
CE
IR3
IR4
SWAP
IR6
IR5/IR4
IR1
IR0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7
CE
Cascade Enable:
0 = Disables the cascade signals CAS2:0 from appearing on the A18:16
address lines during interrupt acknowledge cycles.
1 = Enables the cascade signals CAS2:0, providing access to external
slave 82C59A devices. The cascade signals are used to address
specific slaves. If enabled, slave IDs appear on the A18:16 address
lines during interrupt acknowledge cycles, but are high during idle
cycles.
6
IR3
Internal Master IR3 Connection:
See Table 5-1 on page 5-8 for all the IR3 configuration options.
5
IR4
Internal Master IR4 Connection:
See Table 5-2 on page 5-8 for all the IR4 configuration options.
4
SWAP
INT6/DMAINT Connection:
0 = Connects DMAINT to the slave IR4. Connects INT6 to the slave IR5.
1 = Connects the INT6 pin to the slave IR4. Connects DMAINT to the slave
IR5.
3
IR6
Internal Slave IR6 Connection:
0 = Connects V
SS
to the slave IR6 signal.
1 = Connects the INT7 pin to the slave IR6 signal.
2
IR5/IR4
Internal Slave IR4 or IR5 Connection:
These depend on whether INTCFG.4 is set or clear.
0 = Connects V
SS
to the slave IR5 signal.
1 = Connects either the INT6 pin or DMAINT to the slave IR5 signal.
1
IR1
Internal Slave IR1 Connection:
0 = Connects the SSIO interrupt signal (SSIOINT) to the slave IR1 signal.
1 = Connects the INT5 pin to the slave IR1 signal.
0
IR0
Internal Slave IR0 Connection:
0 = Connects V
SS
to the slave IR0 signal.
1 = Connects the INT4 pin to the slave IR0 signal.
