2 determining priority, Figure 92. methods for changing the default inter – Intel 386 User Manual
Page 206
9-7
INTERRUPT CONTROL UNIT
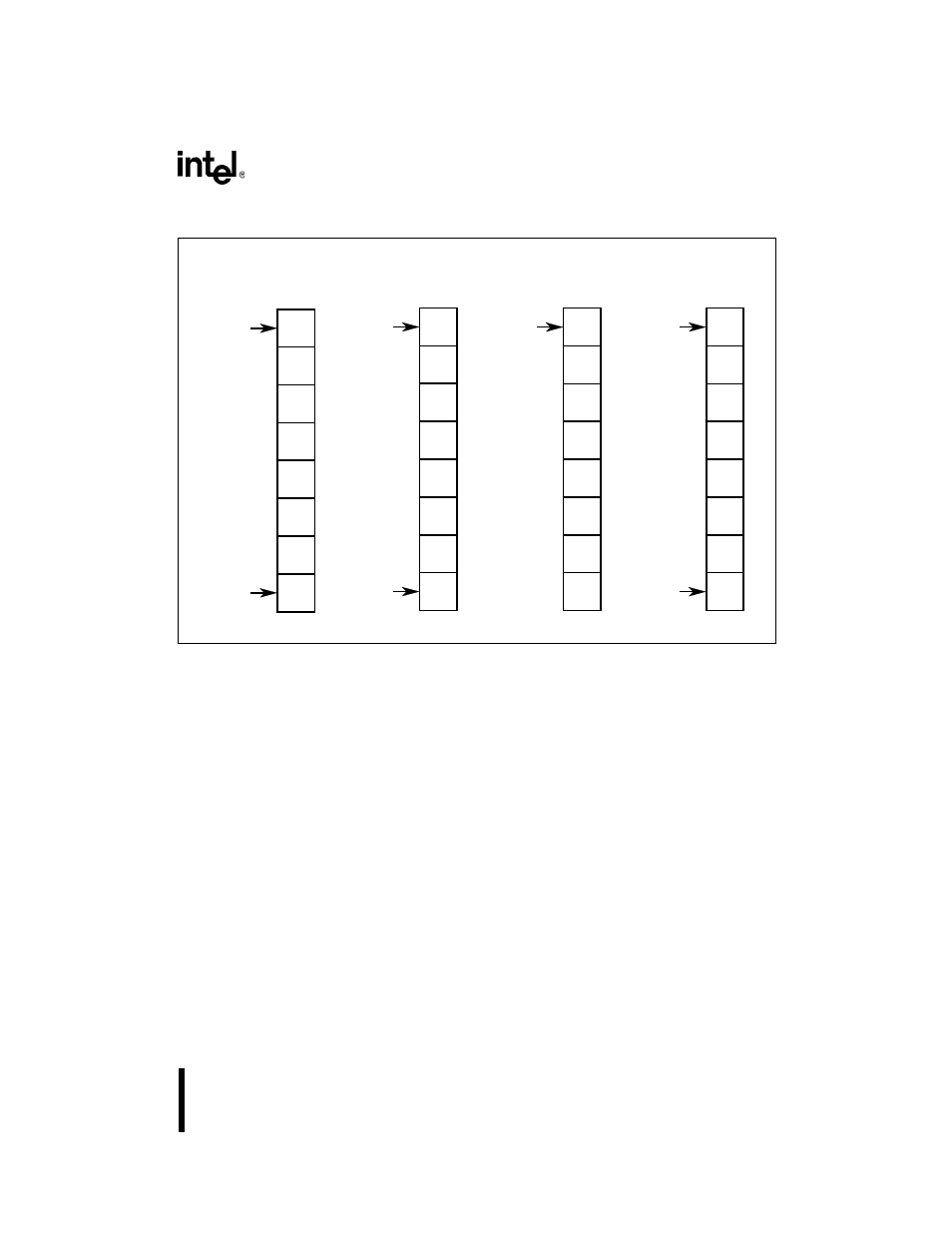
Figure 9-2. Methods for Changing the Default Interrupt Structure
9.2.2.2
Determining Priority
There are three modes that determine relative priorities, i.e., whether a level higher, lower, or
equal to another level has higher or lower interrupt priority.
Fully nested
In the fully nested mode, higher level IR signals have higher interrupt
priority. In this mode, when an 82C59A receives multiple interrupt
requests, it passes the highest level request to the core (or to the
master if the 82C59A is a slave). The core stops processing the lower
level request, processes the higher level request, then returns to finish
the lower level request.
Special fully nested
The special fully nested mode allows higher or equal level IR signals
to have higher interrupt priority. In this mode, if the core is
processing an interrupt, a higher or equal level interrupt request is
passed through to the core. Also, since all interrupts from the slave
are directed into a single IR line (IR2) on the master (the master does
not know the priorities of the slave interrupts it receives), this mode
enables a higher-level interrupt on the slave to interrupt the
IR0
Highest
Level
Lowest
Level
IR1
IR2
IR3
IR4
IR5
IR6
IR7
Specific
Rotation
IR6
Becomes
Highest
Level
Specified
Lowest
Level
IR7
IR0
IR1
IR2
IR3
IR4
IR5
Default
Automatic
Rotation
(After)
IR5
Becomes
Highest
Level
IR6
IR7
IR0
IR1
IR2
IR3
IR4
Assigned
Lowest
Level
After Being
Serviced
A2303-02
Automatic
Rotation
(Before)
IR4
Highest
Level
Before
Being
Serviced
IR5
IR6
IR7
IR0
IR1
IR2
IR3
