6 serial line control register (lcrn), Figure 1115. serial line control register (lcrn) – Intel 386 User Manual
Page 312
11-25
ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL I/O UNIT
11.3.6 Serial Line Control Register (LCR
n)
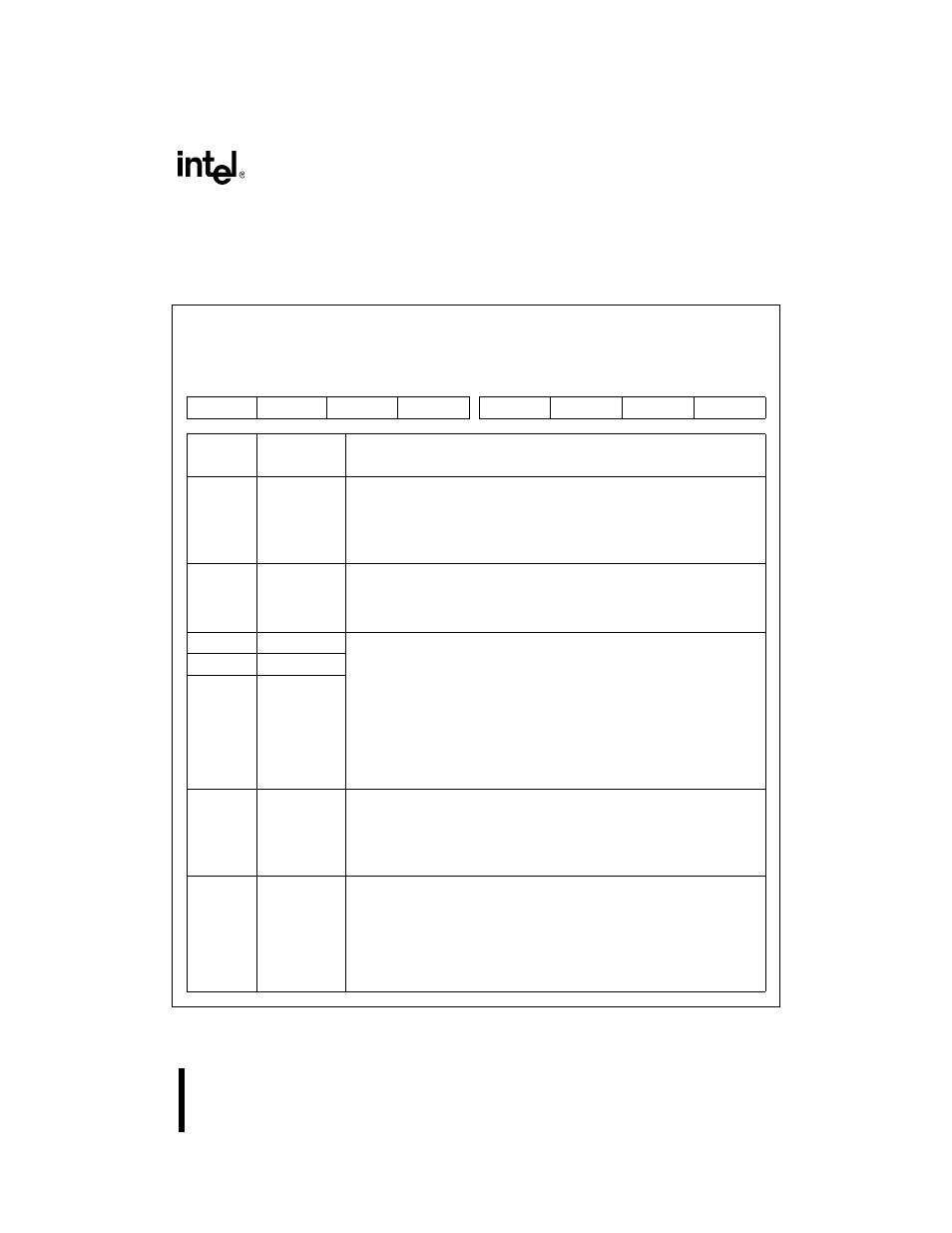
Use LCRn to provide access to the multiplexed registers, send a break condition, and determine
the data frame for receptions and transmissions.
Figure 11-15. Serial Line Control Register (LCR
n
)
Serial Line Control
LCR0, LCR1
(read/write)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
LCR0
LCR1
F4FBH
F8FBH
03FBH
02FBH
00H
00H
7
0
DLAB
SB
SP
EPS
PEN
STB
WLS1
WLS0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7
DLAB
Divisor Latch Access Bit:
This bit determines which of the multiplexed registers is accessed.
0 = Allows access to the receiver and transmit buffer registers (RBR
n and
TBR
n) and the interrupt enable register (IERn).
1 = Allows access to the divisor latch registers (DLL
n and DLHn).
6
SB
Set Break:
0 = No effect on TXD
n.
1 = Forces the TXD
n pin to the spacing (logic 0) state for as long as bit is
set.
5
SP
Sticky Parity, Even Parity Select, and Parity Enable:
These bits determine whether the control logic produces (during
transmission) or checks for (during reception) even, odd, no, or forced
parity.
SP
EPS
PEN
Function
X
X
0
parity disabled (no parity option)
0
0
1
produce or check for odd parity
0
1
1
produce or check for even parity
1
0
1
produce or check for forced parity (parity bit = 1)
1
1
1
produce or check for forced parity (parity bit = 0)
4
EPS
3
PEN
2
STB
Stop Bits:
This bit specifies the number of stop bits transmitted and received in each
serial character.
0 = 1 stop bit
1 = 2 stop bits (1.5 stop bits for 5-bit characters)
1–0
WLS1:0
Word Length Select:
These bits specify the number of data bits in each transmitted or received
serial character.
00 = 5-bit character
01 = 6-bit character
10 = 7-bit character
11 = 8-bit character
