9 interrupt id register (iirn), Figure 1118. interrupt id register (iirn) – Intel 386 User Manual
Page 315
Intel386™ EX EMBEDDED MICROPROCESSOR USER’S MANUAL
11-28
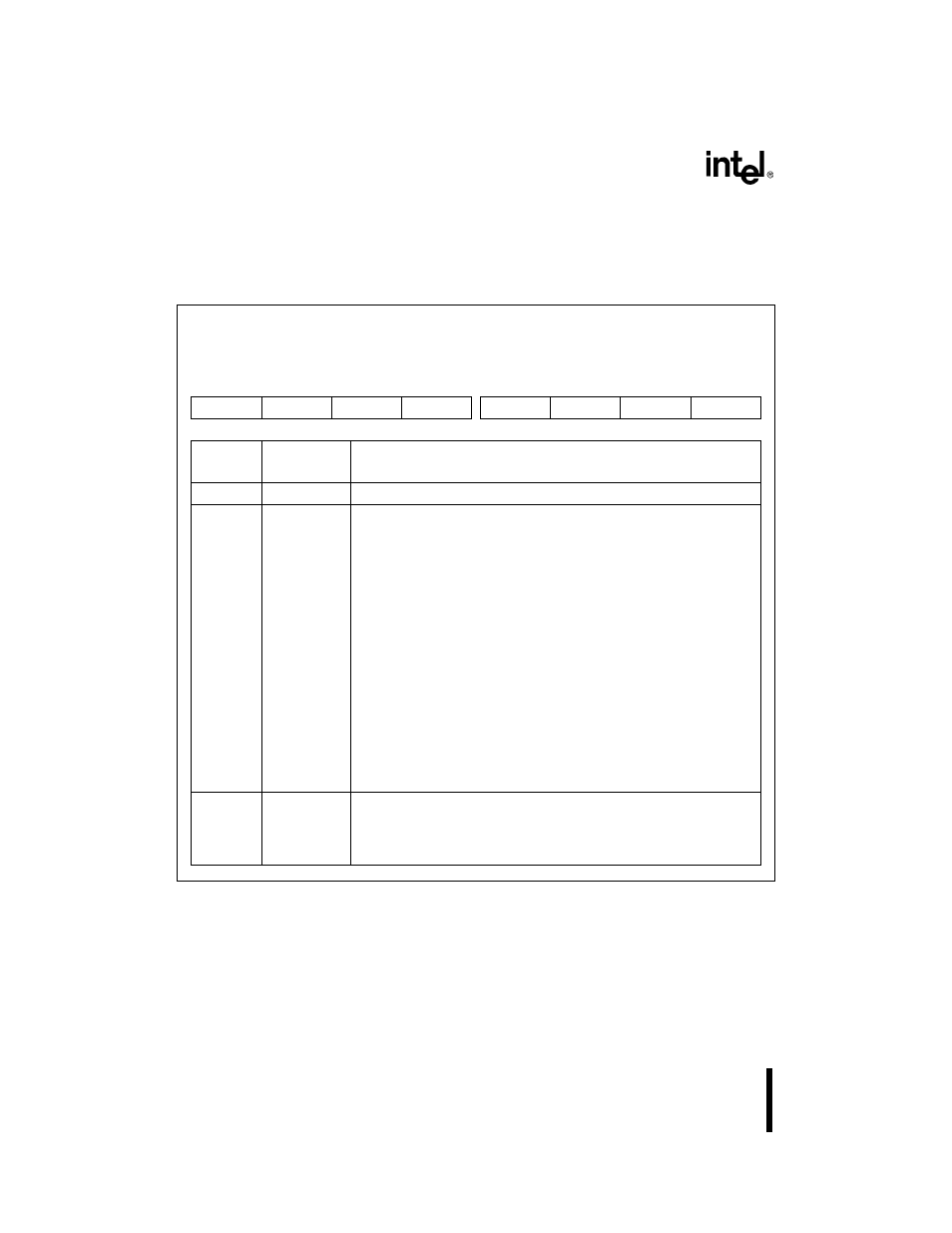
11.3.9 Interrupt ID Register (IIR
n)
Use the IIRn to determine whether an interrupt is pending and, if so, which status signal generated
the interrupt request.
Figure 11-18. Interrupt ID Register (IIR
n
)
Interrupt ID
IIR0, IIR1
(read only)
Expanded Addr:
ISA Addr:
Reset State:
IIR0
IIR1
F4FAH
F8FAH
03FAH
02FAH
01H
01H
7
0
—
—
—
—
—
IS2
IS1
IP#
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7–3
—
Reserved. These bits are undefined.
2
IS2:1
Interrupt Source:
If an interrupt is pending (bit 0 = 0), these bits specify which status signal
caused the pending interrupt.
IS2
IS1
Interrupt Source
0
0
modem status signal*
0
1
transmitter buffer empty signal
1
0
receive buffer full signal
1
1
receiver line status signal**
* When one of the modem input signals (CTS
n#, DSRn#, RIn#, and
DCD
n#) changes state, the modem status signal is activated.
** A framing error, overrun error, parity error, or break interrupt activates
the receiver line status signal.
Reading the modem status register clears the modem status signal.
Reading the IIR
n register or writing to the transmit buffer register clears
the transmit buffer empty signal. Reading the receive buffer register
clears the receive buffer full signal. Reading the receive buffer register or
the serial line status register clears the LSR
n error bits, which clears the
receiver line status signal.
0
IP#
Interrupt Pending:
This bit indicates whether an interrupt is pending.
0 = Interrupt is pending
1 = No interrupt is pending
