Adjustment rules for pid controllers, Adjustment.rules.for.pid.controllers – Burkert Type 8793 User Manual
Page 245
245
Additional technical information
41.
ADJUSTMENT RULES FOR PID CONTROLLERS
The control system Type 8793 features a self-optimization function for the structure and parameters of the integrated
process controller. The determined PID parameters can be seen via the operating menu and re-optimized at will for
an empirical path.
The regulatory literature includes a series of adjustment rules which can be used in experimental ways to determine
a favorable setting for the controller parameters. To avoid incorrect settings, always observe the conditions under
which the particular adjustment rules have been drawn up. Apart from the properties of the control process and the
controller itself, the aspect whether a change in the disturbance variable or command variable is to be corrected
plays a role.
41.1. Adjustment rules according to Ziegler and Nichols
(oscillation method)
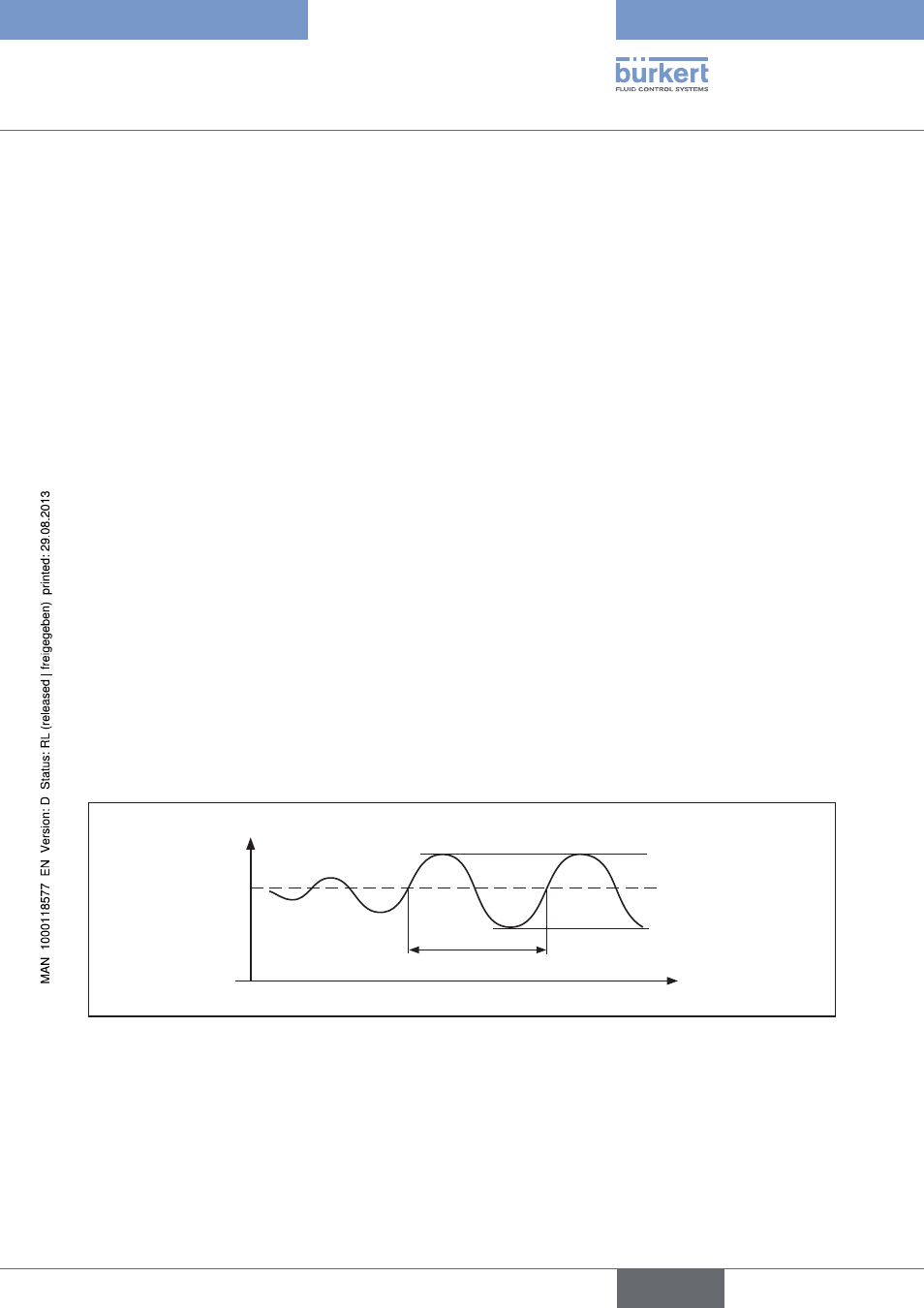
With this method the controller parameters are adjusted on the basis of the behavior of the control circuit at the
stability limit. The controller parameters are first adjusted so that the control circuit starts to oscillate. The occurring
critical characteristic values suggest a favorable adjustment of the controller parameters. A prerequisite for the
application of this method of course is that the control circuit is oscillated.
Procedure
→
Set controller as P-controller (i.e. Tn = 999, Tv = 0), first select a low value for Kp
→
Set required set-point value
→
Increase Kp until the control variable initiates an undamped continuous oscillation.
The proportionality coefficient (proportional gain) set at the stability limit is designated as K
krit
. The resulting oscil-
lation duration is designated as T
krit
.
Progress.of.the.control.variable.at.the.stability.limit
X
Time
Tkrit t
Actual value
Figure 140: Progress of the control variable PID
english
Type 8792, 8793
