5 changing channel or reference selection, Changing channel or reference, Table 22-1 – Rainbow Electronics ATmega64M1 User Manual
Page 230
230
8209A–AVR–08/09
ATmega16M1/32M1/64M1
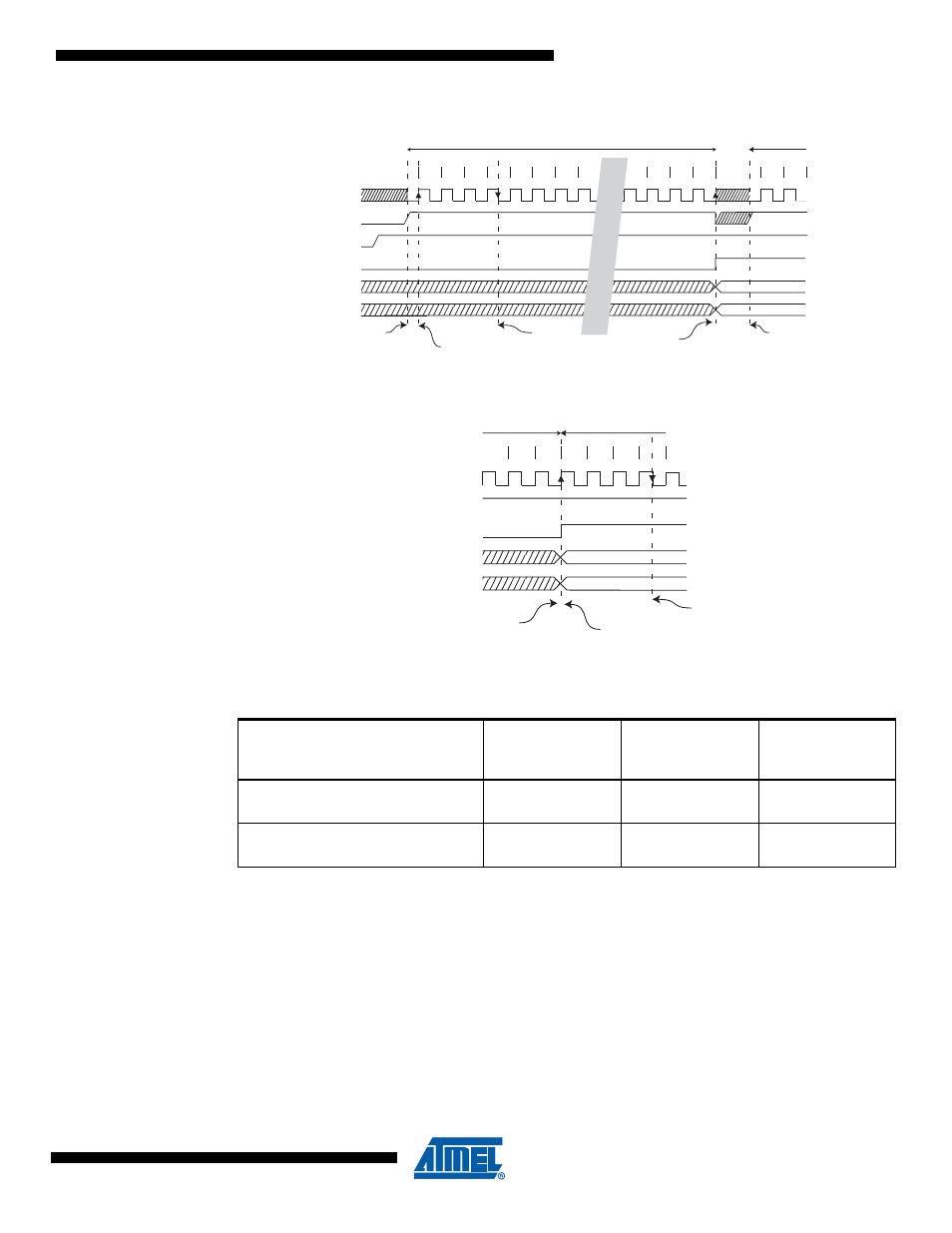
Figure 22-6. ADC Timing Diagram, Auto Triggered Conversion
Figure 22-7. ADC Timing Diagram, Free Running Conversion
22.5
Changing Channel or Reference Selection
The MUXn and REFS1:0 bits in the ADMUX Register are single buffered through a temporary
register to which the CPU has random access. This ensures that the channels and reference
selection only takes place at a safe point during the conversion. The channel and reference
selection is continuously updated until a conversion is started. Once the conversion starts, the
channel and reference selection is locked to ensure a sufficient sampling time for the ADC. Con-
tinuous updating resumes in the last eight ADC clock cycle before the conversion completes
(ADIF in ADCSRA is set). Note that the conversion starts on the second following rising CPU
clock edge after ADSC is written. The user is thus advised not to write new channel or reference
selection values to ADMUX until two ADC clock cycle after ADSC is written.
Table 22-1.
ADC Conversion Time
Condition
First Conversion
Normal
Conversion,
Single Ended
Auto Triggered
Conversion
Sample & Hold
(Cycles from Start of Conversion)
13.5
3.5
2
Conversion Time
(Cycles)
25
15.5
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
11
12
13
14
Sign and MSB of Result
LSB of Result
ADC Clock
Trigger
Source
ADIF
ADCH
ADCL
Cycle Number
1
2
One Conversion
Next Conversion
Conversion
Complete
Prescaler
Reset
ADATE
Prescaler
Reset
Sample &
Hold
MUX and REFS
Update
12
13
14
Sign and MSB of Result
LSB of Result
ADC Clock
ADSC
ADIF
ADCH
ADCL
Cycle Number
1
2
One Conversion
Next Conversion
3
4
Conversion
Complete
Sample & Hold
MUX and REFS
Update
5
