Figure 19 effect of the default cqos coefficient – Nortel Networks NN43001-314 User Manual
Page 75
Adaptive Network Bandwidth Management
75
Multiple Appearance Directory Numbers (MADN) can exist on different
zones. Calls to an MADN are handled the same as other IP Phone calls,
and are subject to the same bandwidth limitations.
New SNMP alarms are provided to monitor the system. When the
bandwidth limit between zones is reduced below configured levels, an alarm
is raised. A Warning alarm and an Unacceptable alarm, each corresponding
to a drop below a configured threshold, are used. When the bandwidth
returns to normal, the alarm is cleared. If the bandwidth limit reaches
zero, an additional Unacceptable alarm is raised. These alarms allow the
system administrator to monitor the system and take corrective action
when required.
Adaptive Network Bandwidth Management configuration
parameters
Packet Loss (pl), Jitter (j) and Delay (d) measurements, along with the R
factor (r) in IP Phone 200x Phase II telephones, are used to calculate the
QoS level for the zones. The coefficients for these QoS measurements
packet loss (Cpl), jitter (Cj), delay (Cd), and the R factor (Cr) can be
configured and are used to calculate the rate of bandwidth change.
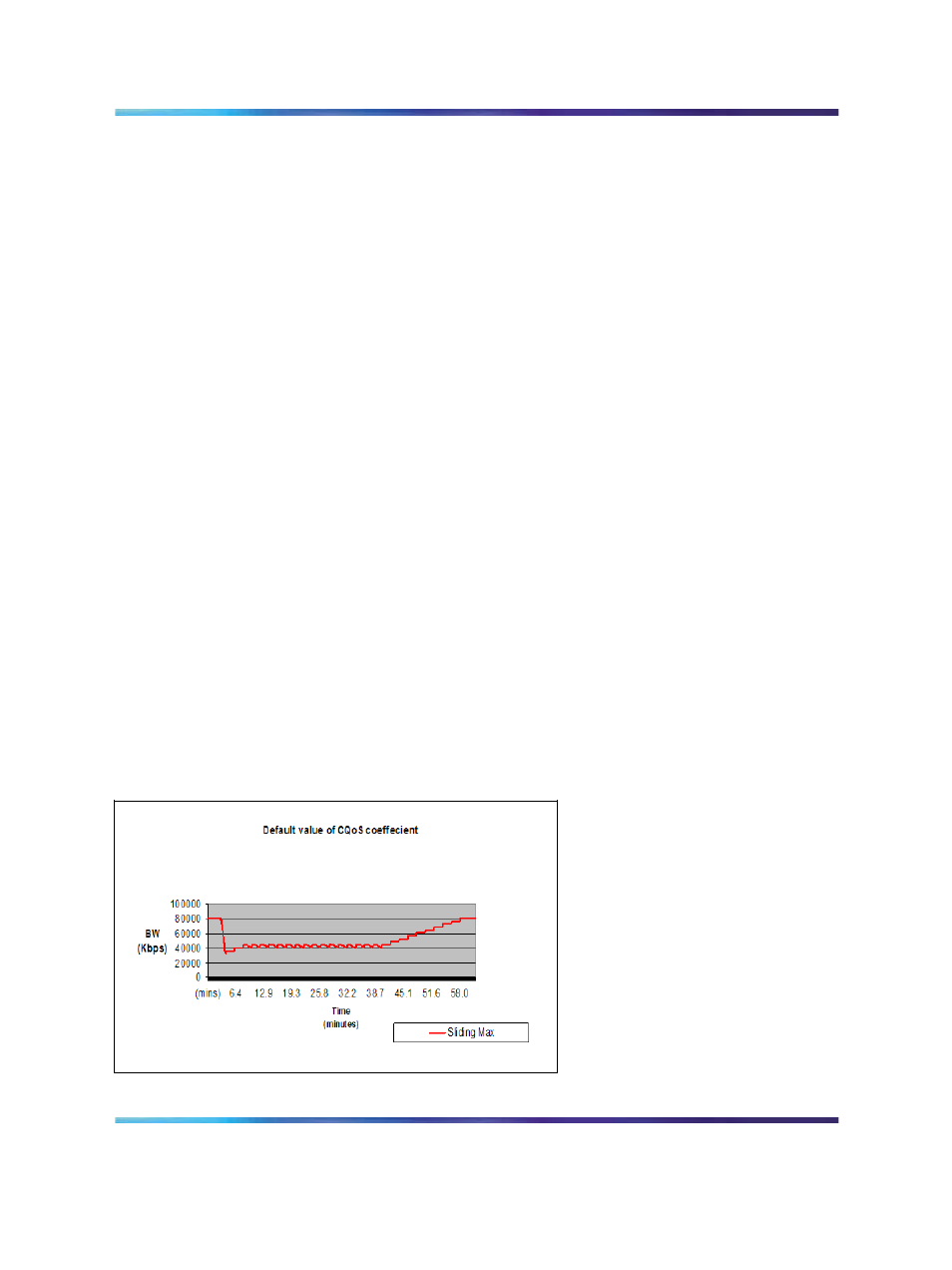
Increasing them from their default values causes the Sliding Maximum to
decrease faster in response to the specific QoS alarm.
The QoS Coefficient (CQoS) can be varied from its default value. Increasing
this value causes the Sliding Maximum to change more rapidly in response
to QoS alarms. However, making this value too large will result in loss
of overall bandwidth, as shown in
Figure 19 "Effect of the default CQos
below and
Figure 20 "Effect of a higher CQoS
Figure 19
Effect of the default CQos Coefficient
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Branch Office Installation and Commissioning
NN43001-314
01.02
Standard
Release 5.0
20 June 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
.
