Address resolution, Neighbor unreachability detection, Duplicate address detection – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 909
1-6
z
H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches do not support RS, RA, or Redirect message.
z
Of the above mentioned IPv6 NDP functions, H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches support the
following three functions: address resolution, neighbor unreachability detection, and duplicate
address detection. The subsequent sections present a detailed description of these three functions
and relevant configuration.
The NDP mainly provides the following functions:
Address resolution
Similar to the ARP function in IPv4, a node acquires the link-layer address of neighbor nodes on the
same link through NS and NA messages.
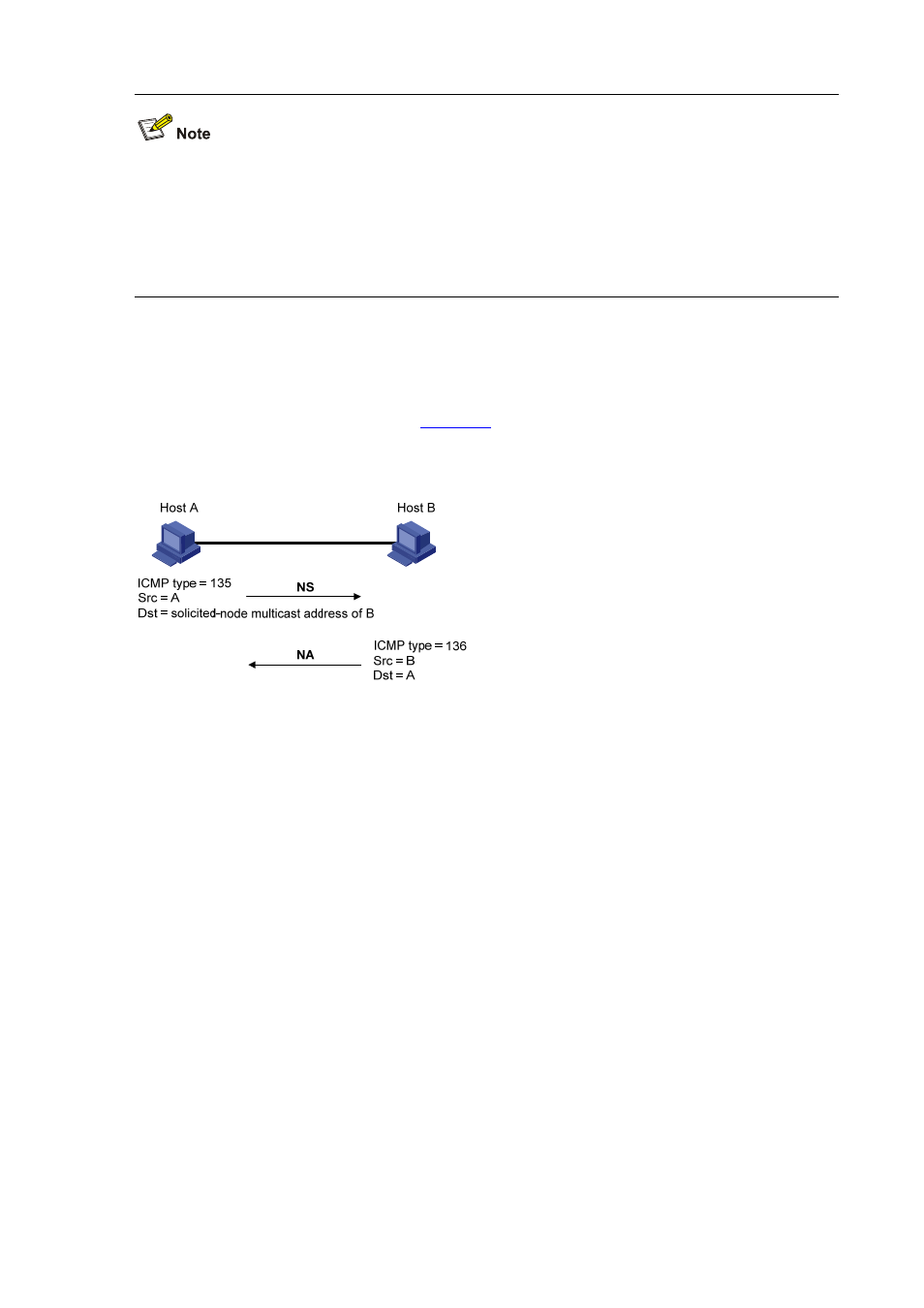
Figure 1-3
shows how node A acquires the link-layer address
of node B.
Figure 1-3 Address resolution
The address resolution procedure is as follows:
1) Node A multicasts an NS message. The source address of the NS message is the IPv6 address of
the interface of node A and the destination address is the solicited-node multicast address of node
B. The NS message contains the link-layer address of node A.
2) After receiving the NS message, node B judges whether the destination address of the packet is
the corresponding solicited-node multicast address of its own IPv6 address. If yes, node B learns
the link-layer address of node A and returns an NA message containing the link-layer address of
node B in the unicast mode.
3) Node A acquires the link-layer address of node B from the NA message. After that, node A and
node B can communicate with each other.
Neighbor unreachability detection
After node A acquires the link-layer address of its neighbor node B, node A can verify whether node B is
reachable according to NS and NA messages.
1) Node A sends an NS message whose destination address is the IPv6 address of node B.
2) If node A receives an NA message from node B, node A considers that node B is reachable.
Otherwise, node B is unreachable.
Duplicate address detection
After a node acquires an IPv6 address, it should perform the duplicate address detection to determine
whether the address is being used by other nodes (similar to the gratuitous ARP function). The
