1 mirroring configuration, Mirroring overview, Local port mirroring – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 618: Remote port mirroring, Mirroring configuration
1-1
1
Mirroring Configuration
Mirroring Overview
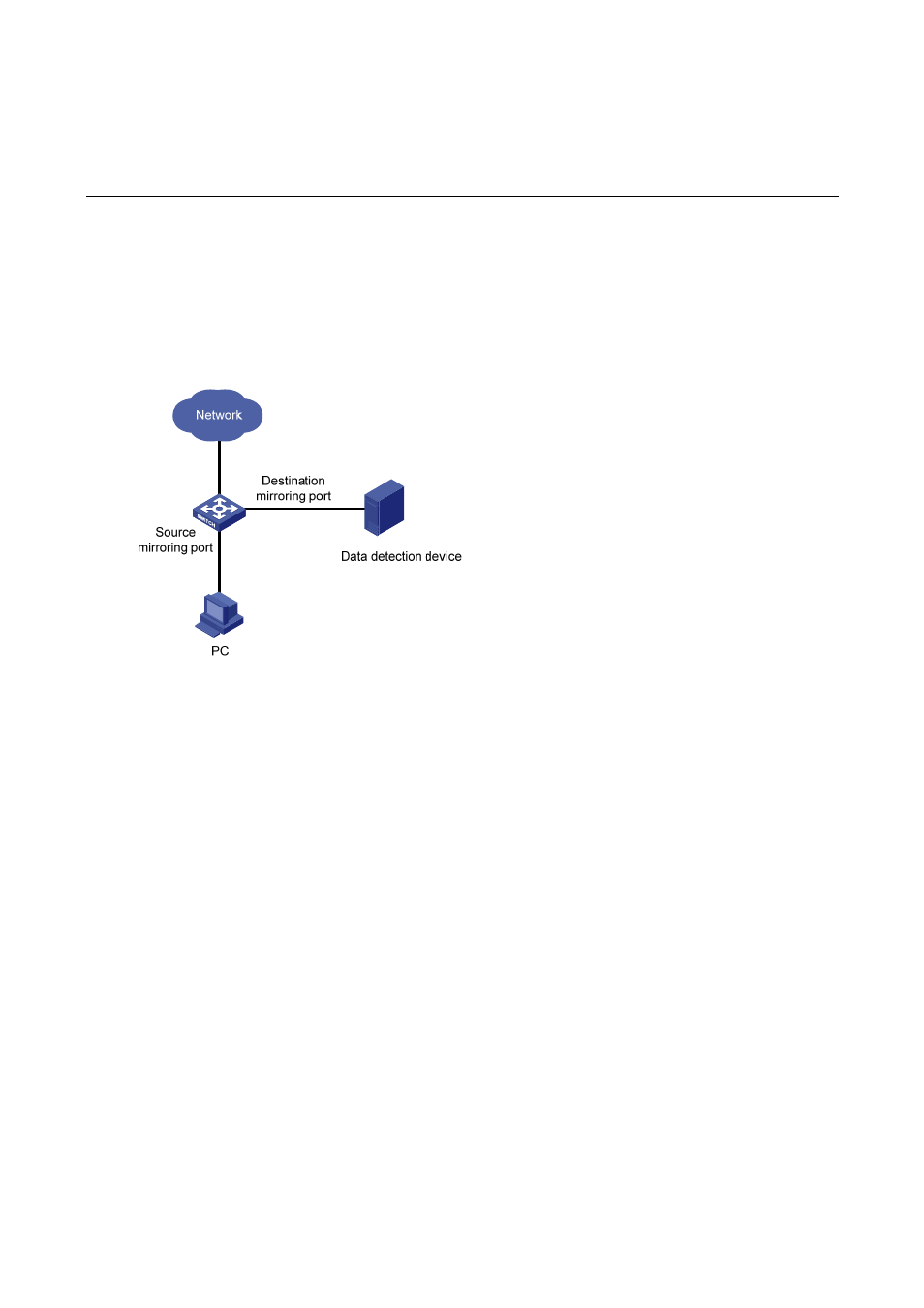
Mirroring refers to the process of copying packets of one or more ports (source ports) to a destination
port which is connected to a data detection device. Users can then use the data detection device to
analyze the mirrored packets on the destination port for monitoring and troubleshooting the network.
Figure 1-1 A port mirroring implementation
H3C S3100 series Ethernet switches support two kinds of port mirroring: local port mirroring and remote
port mirroring.
z
Local port mirroring: a device copies packets passing through one or more source ports of the
device to the destination port.
z
Remote port mirroring implements port mirroring through the remote source mirroring group and
remote destination mirroring group. The device copies the packets of the source port to the
reflector port, which then broadcasts the packets in the remote-probe VLAN. After the remote
device receives the packets, it compares the VLAN ID of the packets with that of the remote-probe
VLAN on the remote device. If the VLAN IDs are identical, the remote device forwards the packets
to the destination port of the remote destination mirroring group.
Local Port Mirroring
In local port mirroring, packets passing through one or more source ports of a device are copied to the
destination port on the same device for packet analysis and monitoring. In this case, the source ports
and the destination port must be located on the same device.
Remote Port Mirroring
Remote port mirroring does not require the source and destination ports to be on the same device. The
source and destination ports can be located on multiple devices across the network. Therefore,
administrators can monitor the traffic on remote devices conveniently.
