Introduction to ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 908
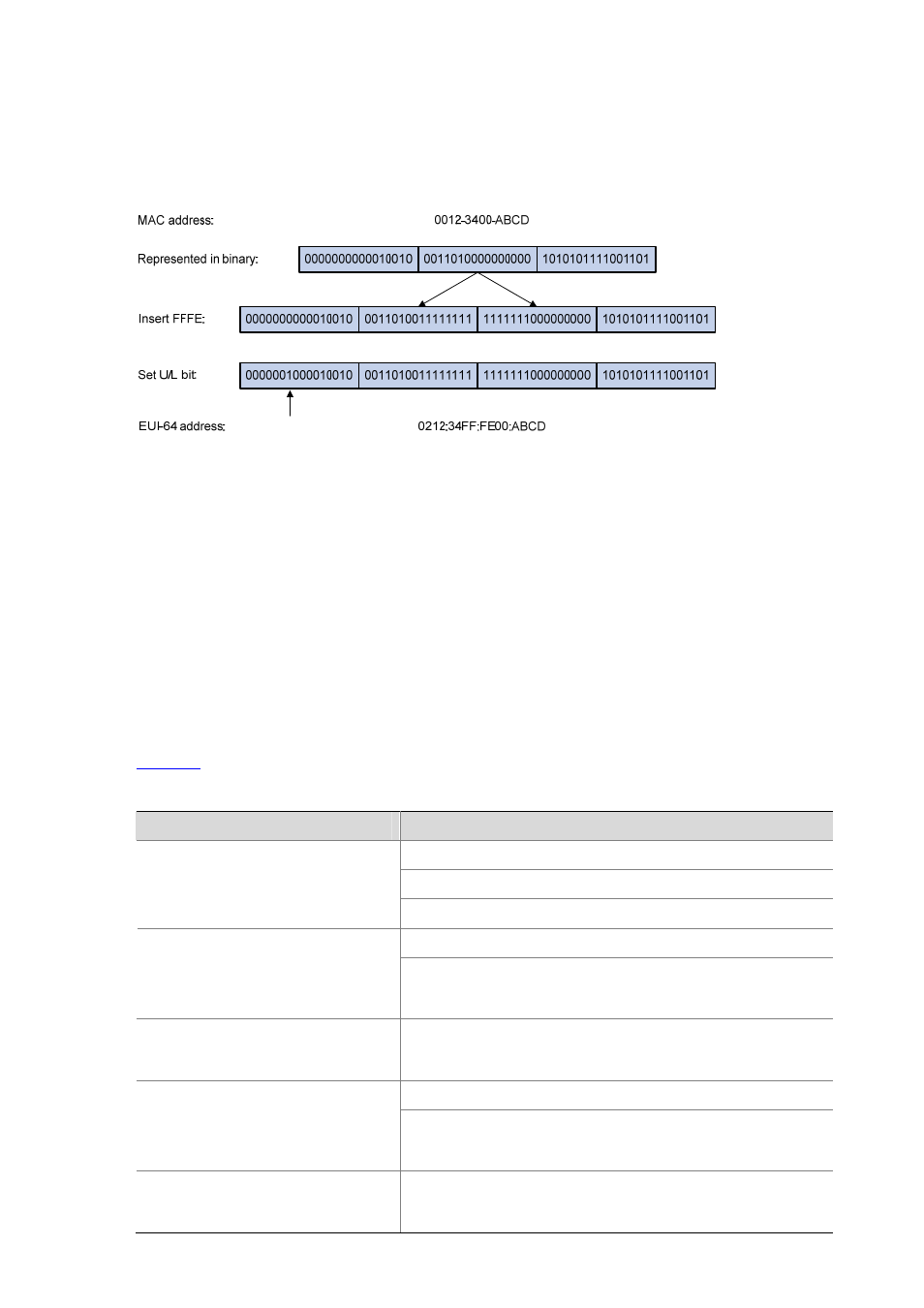
1-5
hexadecimal number FFFE needs to be inserted in the middle of MAC addresses (behind the 24
high-order bits).To ensure the interface identifier obtained from a MAC address is unique, it is
necessary to set the universal/local (U/L) bit (the seventh high-order bit) to “1”. Thus, an interface
identifier in EUI-64 format is obtained.
Figure 1-2 Convert a MAC address into an EUI-64 address
Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol
The IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol (NDP) uses five types of ICMPv6 messages to implement the
following functions:
z
Address resolution
z
Neighbor unreachability detection
z
Duplicate address detection
z
Router/prefix discovery
z
Address autoconfiguration
z
Redirection
Table 1-3
lists the types and functions of ICMPv6 messages used by the NDP.
Table 1-3 Types and functions of ICMPv6 messages
ICMPv6 message
Function
Used to acquire the link-layer address of a neighbor
Used to verify whether the neighbor is reachable
Neighbor solicitation (NS) message
Used to perform a duplicate address detection
Used to respond to a neighbor solicitation message
Neighbor advertisement (NA) message
When the link layer address changes, the local node initiates a
neighbor advertisement message to notify neighbor nodes of the
change.
Router solicitation (RS) message
After started, a host sends a router solicitation message to request
the router for an address prefix and other configuration information
for the purpose of autoconfiguration.
Used to respond to a router solicitation message
Router advertisement (RA) message
With the RA message suppression disabled, the router regularly
sends a router advertisement message containing information such
as address prefix and flag bits.
Redirect message
When a certain condition is satisfied, the default gateway sends a
redirect message to the source host so that the host can reselect a
correct next hop router to forward packets.
