Ospf packet formats, Ospf packet header – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 79
4-10
Note that:
z
The DR election is available on broadcast, NBMA interfaces rather than P2P, or P2MP interfaces.
z
A DR is an interface of a router and belongs to a single network segment. The router’s other
interfaces may be a BDR or DRother.
z
After DR/BDR election and then a new router joins, it cannot become the DR immediately even if it
has the highest priority on the network.
z
The DR may not be the router with the highest priority in a network, and the BDR may not be the
router with the second highest priority.
OSPF Packet Formats
OSPF packets are directly encapsulated into IP packets. OSPF has the IP protocol number 89. The
OSPF packet format is shown below (taking a LSU packet as an example).
Figure 4-8 OSPF packet format
OSPF packet header
OSPF packets are classified into five types that have the same packet header, as shown below.
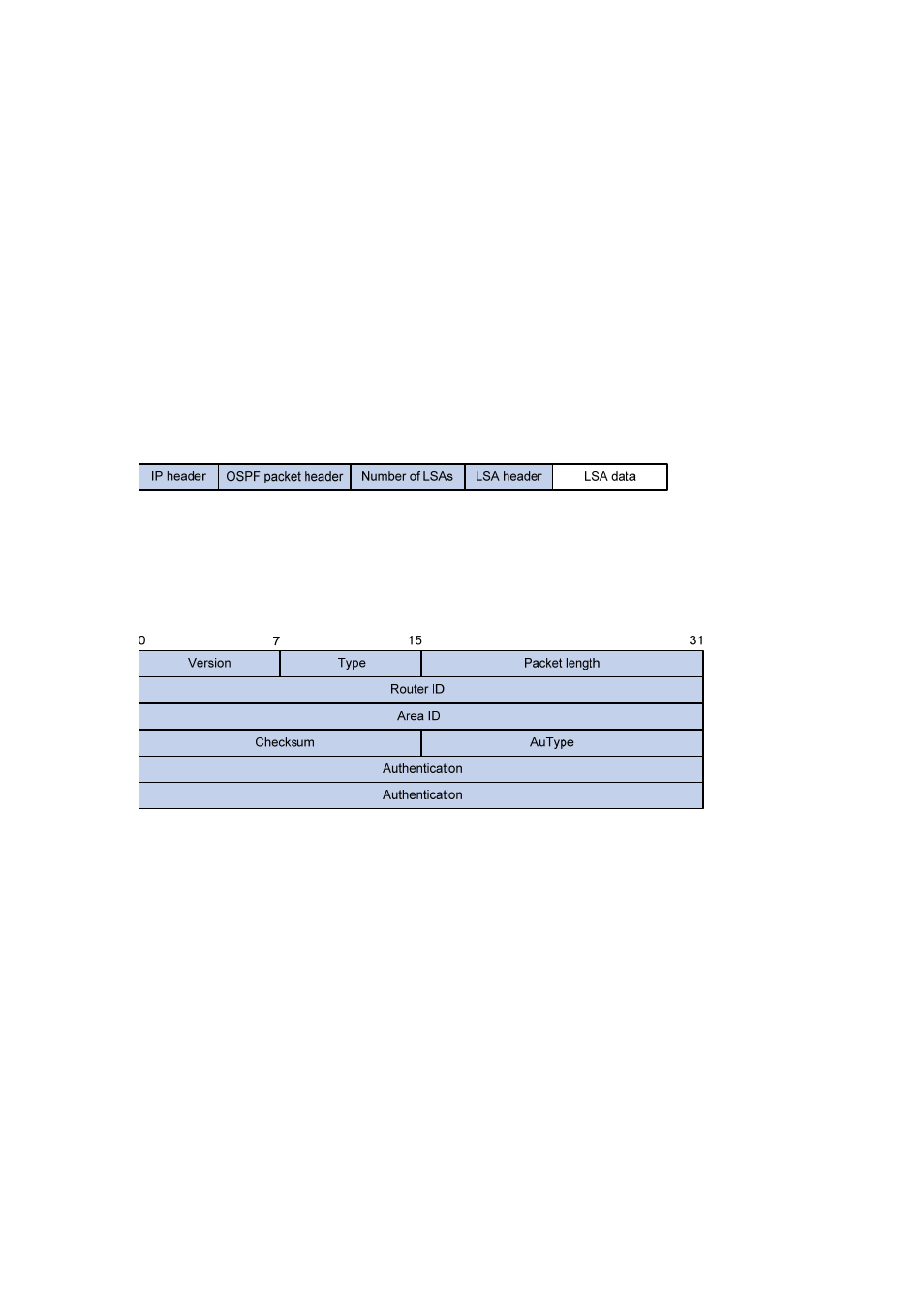
Figure 4-9 OSPF packet header
z
Version: OSPF version number, which is 2 for OSPFv2.
z
Type: OSPF packet type from 1 to 5, corresponding with hello, DD, LSR, LSU and LSAck
respectively.
z
Packet length: Total length of the OSPF packet in bytes, including the header.
z
Router ID: ID of the advertising router.
z
Area ID: ID of the area where the advertising router resides.
z
Checksum: Checksum of the message.
z
Autype: Authentication type from 0 to 2, corresponding with non-authentication, simple (plaintext)
authentication and MD5 authentication respectively.
z
Authentication: Information determined by authentication type. It is not defined for authentication
type 0. It is defined as password information for authentication type 1, and defined as Key ID, MD5
authentication data length and sequence number for authentication type 2.
