Bgp route advertisement rules – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 213
6-10
z
BGP has no route computation algorithm, so it cannot implement load balancing according to
metrics of routes. However, BGP has abundant route selection rules, through which, it selects
available routes for load balancing and adds load balancing to route selection rules.
z
BGP implements load balancing only on routes that have the same AS_PATH, ORIGIN,
LOCAL_PREF and MED.
z
BGP load balancing is applicable between eBGP peers, between iBGP peers and between
confederations.
z
If multiple routes to the same destination are available, BGP selects a configurable number of
routes for load balancing.
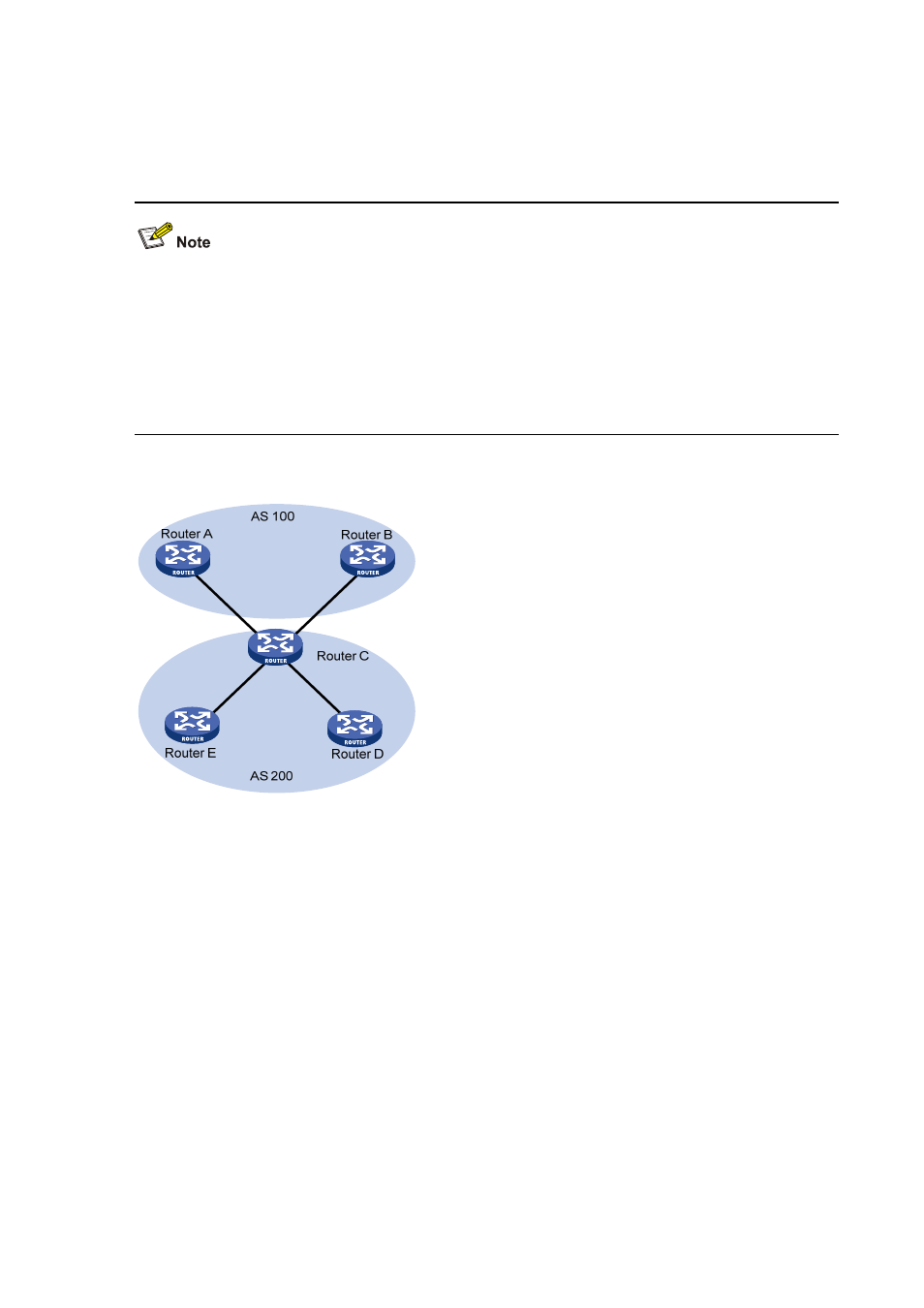
Figure 6-10 Network diagram for BGP load balancing
In the above figure, Router D and Router E are iBGP peers of Router C. Router A and Router B both
advertise a route destined for the same destination to Router C. If load balancing is configured and the
two routes have the same AS_PATH attribute, ORIGIN attribute, LOCAL_PREF and MED, Router C
installs both the two routes to its route table for load balancing. After that, Router C forwards to Router
D and Router E the route that has AS_PATH unchanged but has NEXT_HOP changed to Router C;
other BGP transitive attributes are those of the best route.
BGP route advertisement rules
The current BGP implementation supports the following route advertisement rules:
z
When multiple feasible routes to a destination exist, the BGP speaker advertises only the best
route to its peers.
z
A BGP speaker advertises only routes used by itself.
z
A BGP speaker advertises routes learned through eBGP to all BGP peers, including both eBGP
and iBGP peers.
z
A BGP speaker does not advertise routes from an iBGP peer to other iBGP peers.
