Ripng packet format, Basic format, Rte format – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 282
8-2
RIPng supports split horizon and poison reverse to prevent routing loops and route redistribution.
Each RIPng router maintains a routing database, including route entries of all reachable destinations.
A route entry contains the following information:
z
Destination address: IPv6 address of a host or a network.
z
Next hop address: IPv6 address of a neighbor along the path to the destination.
z
Egress interface: Outbound interface that forwards IPv6 packets.
z
Metric: Cost from the local router to the destination.
z
Route time: Time that elapsed since a route entry is last changed. Each time a route entry is
modified, the routing time is set to 0.
z
Route tag: Identifies the route, used in a routing policy to control routing information. For
information about routing policy, see Routing Policy Configuration in the Layer 3 - IP Routing
Configuration Guide.
RIPng Packet Format
Basic format
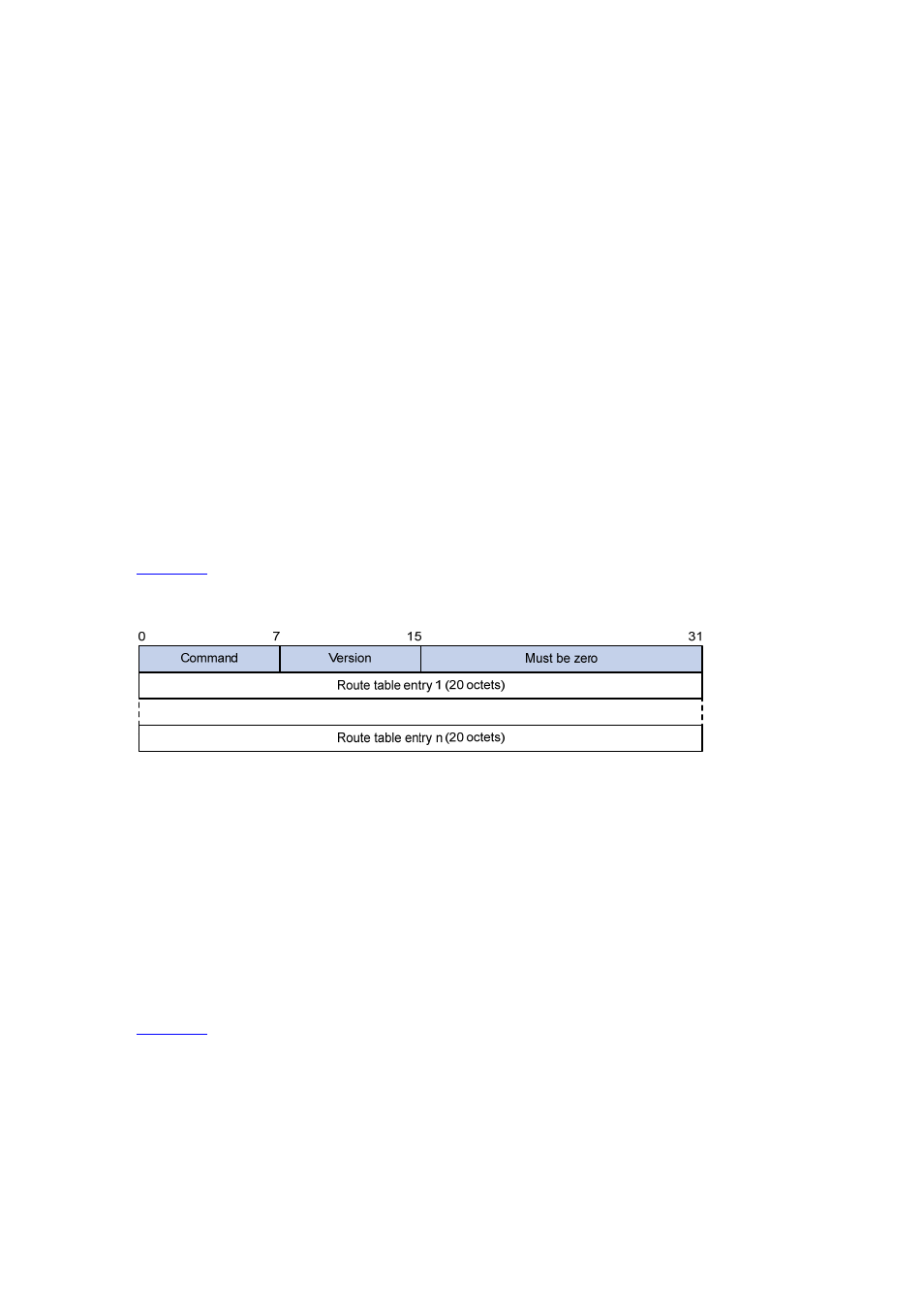
A RIPng packet consists of a header and multiple route table entries (RTEs). The maximum number of
RTEs in a packet depends on the IPv6 MTU of the sending interface.
shows the packet format of RIPng.
Figure 8-1 RIPng basic packet format
…
z
Command: Type of message. 0x01 indicates Request, 0x02 indicates Response.
z
Version: Version of RIPng. It can only be 0x01 currently.
z
RTE: Route table entry, 20 bytes for each entry.
RTE format
There are two types of RTEs in RIPng.
z
Next hop RTE: Defines the IPv6 address of a next hop
z
IPv6 prefix RTE: Describes the destination IPv6 address, route tag, prefix length and metric in the
RIPng routing table.
shows the format of the next hop RTE:
