H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 234
6-31
1.1.1.1/24, you need to configure Router B to set itself as the next hop (3.1.1.1/24) for the route to be
sent to Router C.
Figure 6-17 Next hop attribute configuration
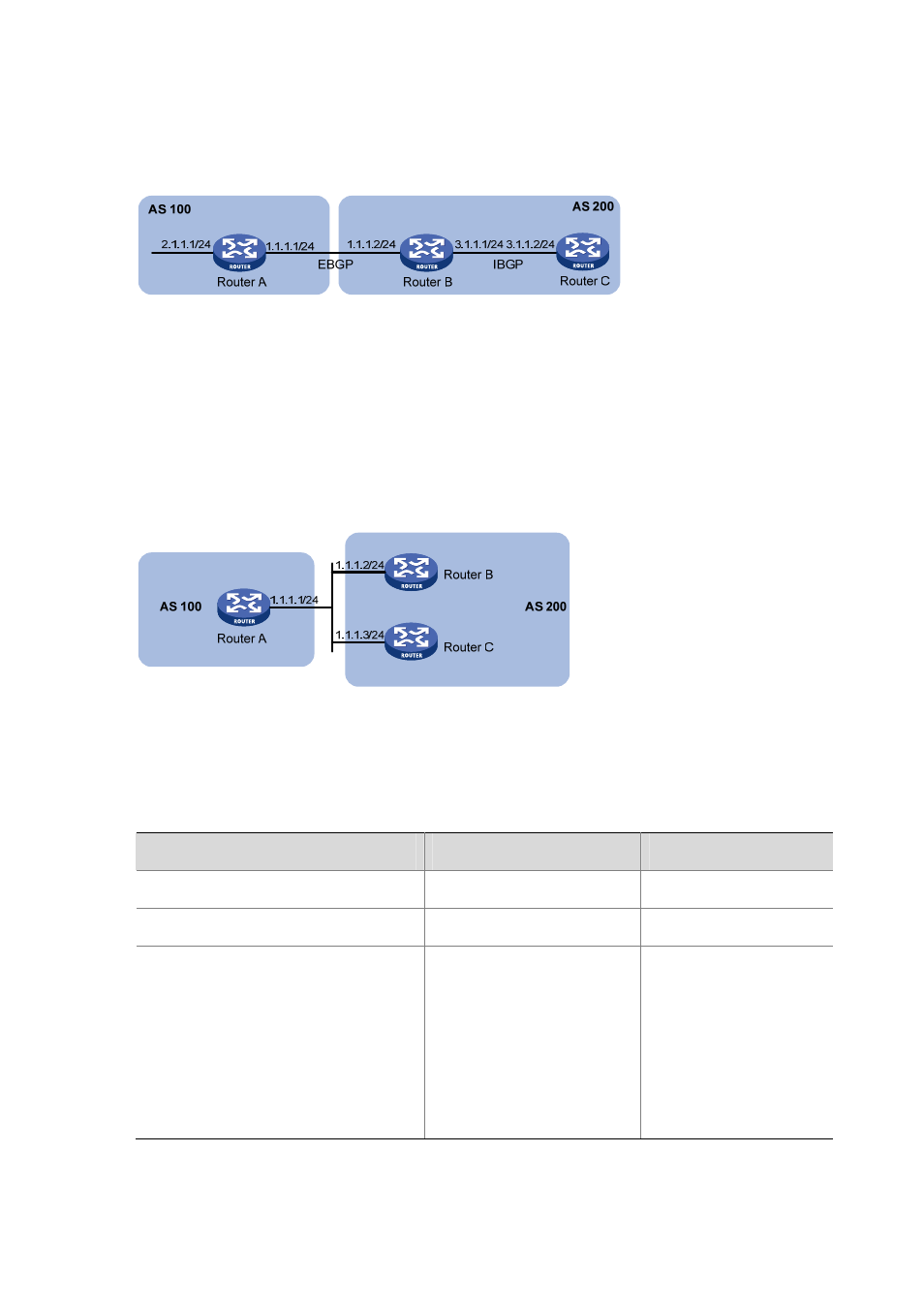
If a BGP router has two peers on a common broadcast network, it does not set itself as the next hop for
routes sent to an eBGP peer by default. As shown below, Router A and Router B establish an eBGP
neighbor relationship, and Router B and Router C establish an iBGP neighbor relationship. They are
on the same broadcast network 1.1.1.0/24. When Router B sends eBGP routes to Router A, it does not
set itself as the next hop by default. However, you can configure Router B to set it as the nexthop
(1.1.1.2/24) for routes sent to Router A by using the peer next-hop-local command as needed.
Figure 6-18 Next hop attribute configuration
Note that: if you have configured BGP load balancing on a BGP router, the router will set it as the next
hop for routes sent to an iBGP peer/peer group regardless of whether the peer next-hop-local
command is configured.
Follow these steps to configure the next hop attribute:
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
Enter system view
system-view
—
Enter BGP view
bgp as-number
—
Specify the router as the next hop of routes
sent to a peer/peer group
peer { group-name |
ip-address } next-hop-local
Optional
By default, the router sets it
as the next hop for routes
sent to an eBGP peer/peer
group, but does not set it as
the next hop for routes sent
to an iBGP peer/peer group.
