Nssa area, Comparsion between the areas – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 75
4-6
z
Virtual links cannot transit (totally) stub areas.
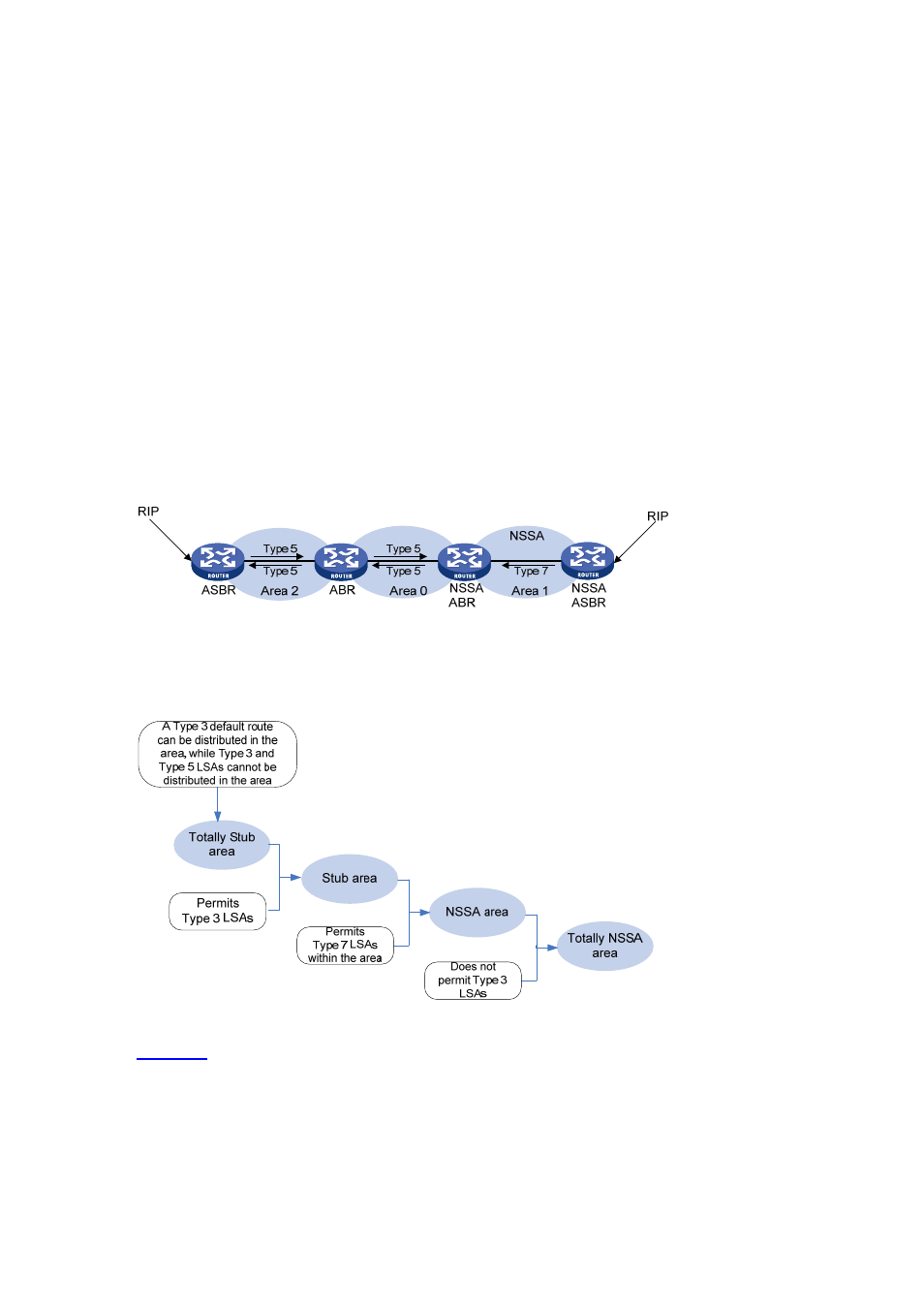
NSSA area
Similar to a stub area, an NSSA area imports no AS external LSA (Type-5 LSA) but can import Type-7
LSAs that are generated by the ASBR and distributed throughout the NSSA area. When traveling to
the NSSA ABR, Type-7 LSAs are translated into Type-5 LSAs by the ABR for advertisement to other
areas.
In the following figure, the OSPF AS contains three areas: Area 1, Area 2 and Area 0. The other two
ASs employ the RIP protocol. Area 1 is an NSSA area, and the ASBR in it translates RIP routes into
Type-7 LSAs and advertises them throughout Area 1. When these LSAs travel to the NSSA ABR, the
ABR translates Type-7 LSAs to Type-5 LSAs for advertisement to Area 0 and Area 2.
On the left of the figure, RIP routes are translated into Type-5 LSAs by the ASBR of Area 2 and
distributed into the OSPF AS. However, Area 1 is an NSSA area, so these Type-5 LSAs cannot travel
to Area 1.
Like stub areas, virtual links cannot transit NSSA areas.
Figure 4-4 NSSA area
Comparsion between the areas
Figure 4-5 Comparison between the areas
shows the comparison of the areas:
z
In a totally stub area, the ABR can distribute a Type 3 default route, while it does not distribute
external routes and inter-area routes.
z
Compared with a totally stub area, a stub area can import inter-area routes.
z
Compared with a stub area, an NSSA area can import external routes through Type 7 LSAs
advertised by the ASBR.
