Rip version, Rip message format, Ripv1 message format – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 38
3-3
4) RIP ages out routes by adopting an aging mechanism to keep only valid routes.
RIP Version
RIP has two versions, RIPv1 and RIPv2.
RIPv1, a classful routing protocol, supports message advertisement via broadcast only. RIPv1 protocol
messages do not carry mask information, which means it can only recognize routing information of
natural networks such as Class A, B, C. That is why RIPv1 does not support discontiguous subnets.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol. Compared with RIPv1, RIPv2 has the following advantages.
z
Supporting route tags. Route tags are used in routing policies to flexibly control routes.
z
Supporting masks, route summarization and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR).
z
Supporting designated next hops to select the best next hops on broadcast networks.
z
Supporting multicast routing update to reduce resource consumption. Only RIPv2 routers can
receive such update messages.
z
Supporting plain text authentication and MD5 authentication to enhance security.
RIPv2 has two types of message transmission: broadcast and multicast. Multicast is the default type
using 224.0.0.9 as the multicast address. The interface working in the RIPv2 broadcast mode can also
receive RIPv1 messages.
RIP Message Format
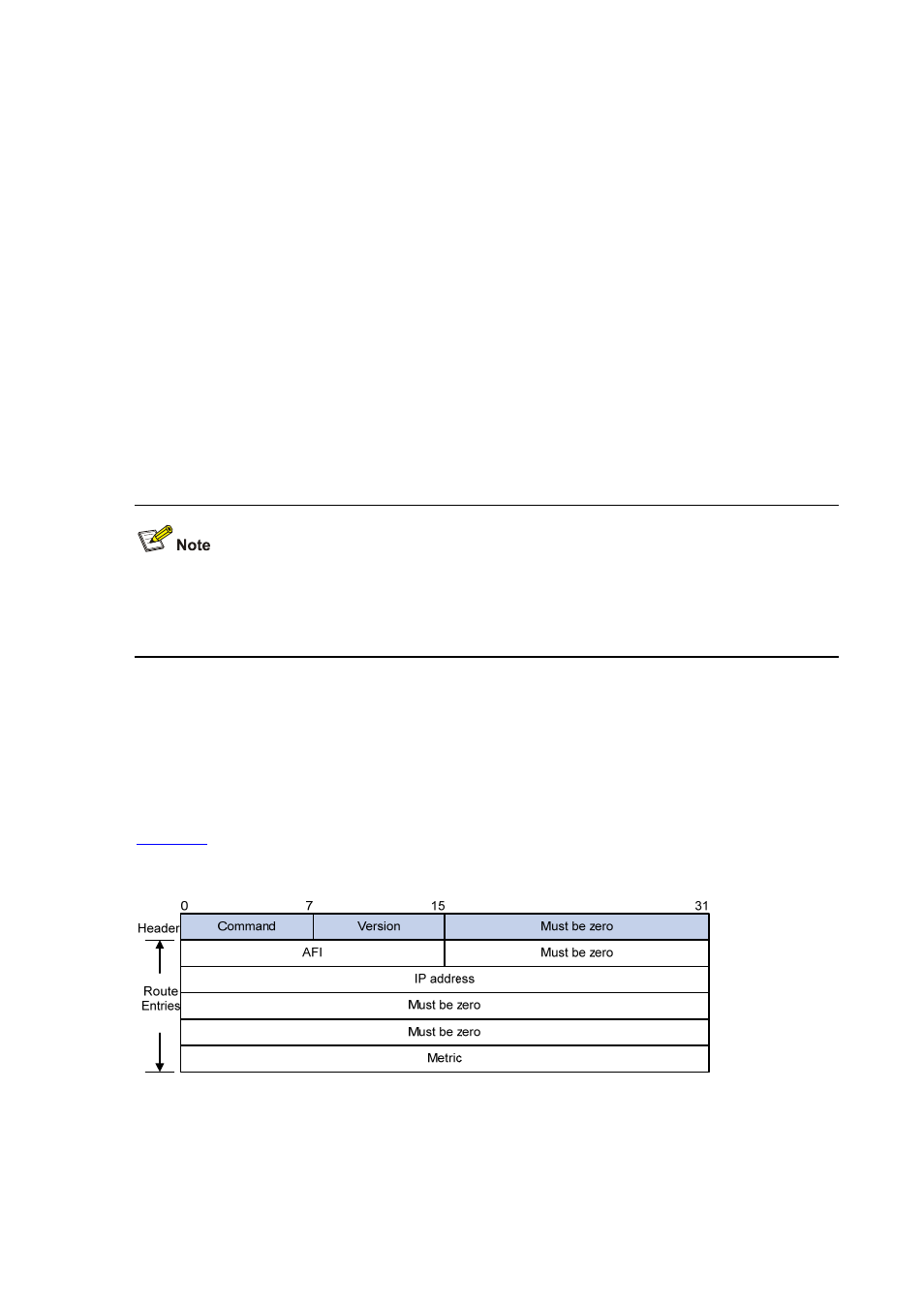
A RIP message consists of a header and up to 25 route entries. (A RIPv2 authentication message uses
the first route entry as the authentication entry, so it has up to 24 route entries.)
RIPv1 message format
shows the format of RIPv1 message.
Figure 3-1 RIPv1 Message Format
z
Command: Type of message. 1 indicates request, which is used to request all or part of the
routing information from the neighbor, and 2 indicates response, which contains all or part of the
routing information. A response message consists of up to 25 route entries.
