Verilink Access Manager 2000 (896-502037-001) Product Manual User Manual
Page 161
Configuring nodes
Access Manager 2000 User Manual
5
-37
An ounce of prevention . . .
When you configure a node, you’re actually creating access to a location
in the database where an informational “picture” of the node is stored and
can be modified. A
Node ID
provides a means of access to the database
and a reference to the location within the database.
Every network manager which communicates with a given node must use
the same
Node ID
for that node and have the same “picture” or
representation of that node.
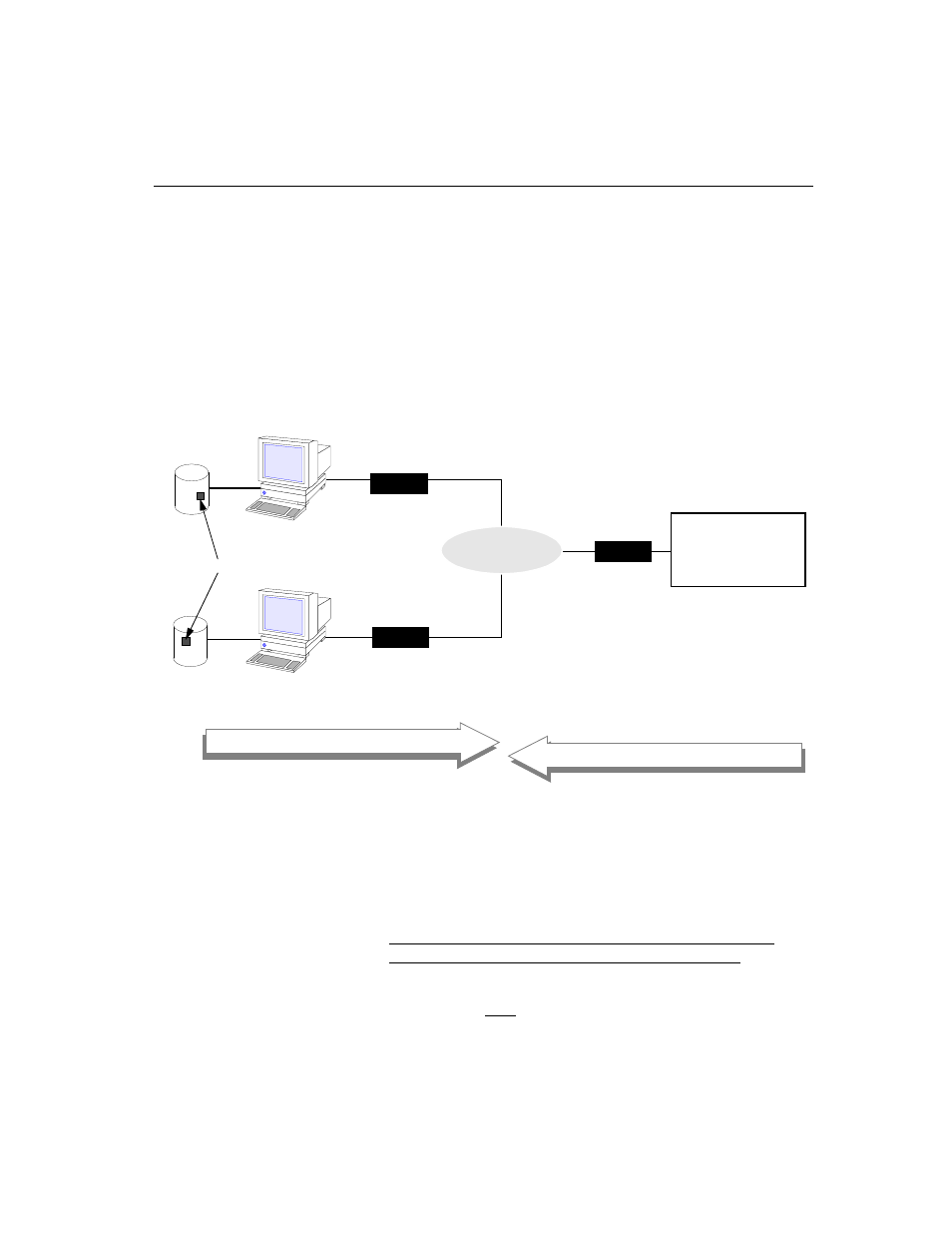
Figure 5-6
Access Manager’s view of the node
As a consequence, review these pointers to avoid errors:
1. When using two Access Managers to manage the same node, enter
the same node configuration data in the Node Definition screen at
both Access Managers. Yes, this creates a redundant information
base.
The only deviation from this rule occurs when using modems
operating at different baud rates. This is explained in #3.
2. When setting up alternate alarm paths to two different Access
Managers, you must make the same entries for Alarm Path
Access Manager #1
Access Manager #2
Telephone
Network
Modem A
Modem B
Modem C
941-1131
653-1111
2400 baud
1200 baud
Node ID: 12
Node Name: SMITH
Location: FRESNO
Node ID: 12
AS2000 System Node
Query Path
Alarm Path
945-2211
2400 baud
Primary
Secondary
