7 dimm sparing mode memory configuration, 8 single branch mode sparing, 9 dual branch mode sparing – Kontron TIGH2U Carrier Grade Server User Manual
Page 43: Dimm sparing mode memory configuration, Single branch mode sparing, Dual branch mode sparing
Kontron Carrier Grade Server TIGH2U
December 2009
Product Guide, rev.1.2
43
Server Component Installations and Upgrades—TIGH2U Server
3.4.2.7
DIMM Sparing Mode Memory Configuration
The MCH provides DIMM sparing capabilities. Sparing is a RAS feature that involves configuring a
DIMM to be placed in reserve so it can be use to replace a DIMM that fails. DIMM sparing occurs
within a given bank of memory and is not supported across branches.
There are two supported memory sparing configurations:
•
•
3.4.2.8
Single Branch Mode Sparing
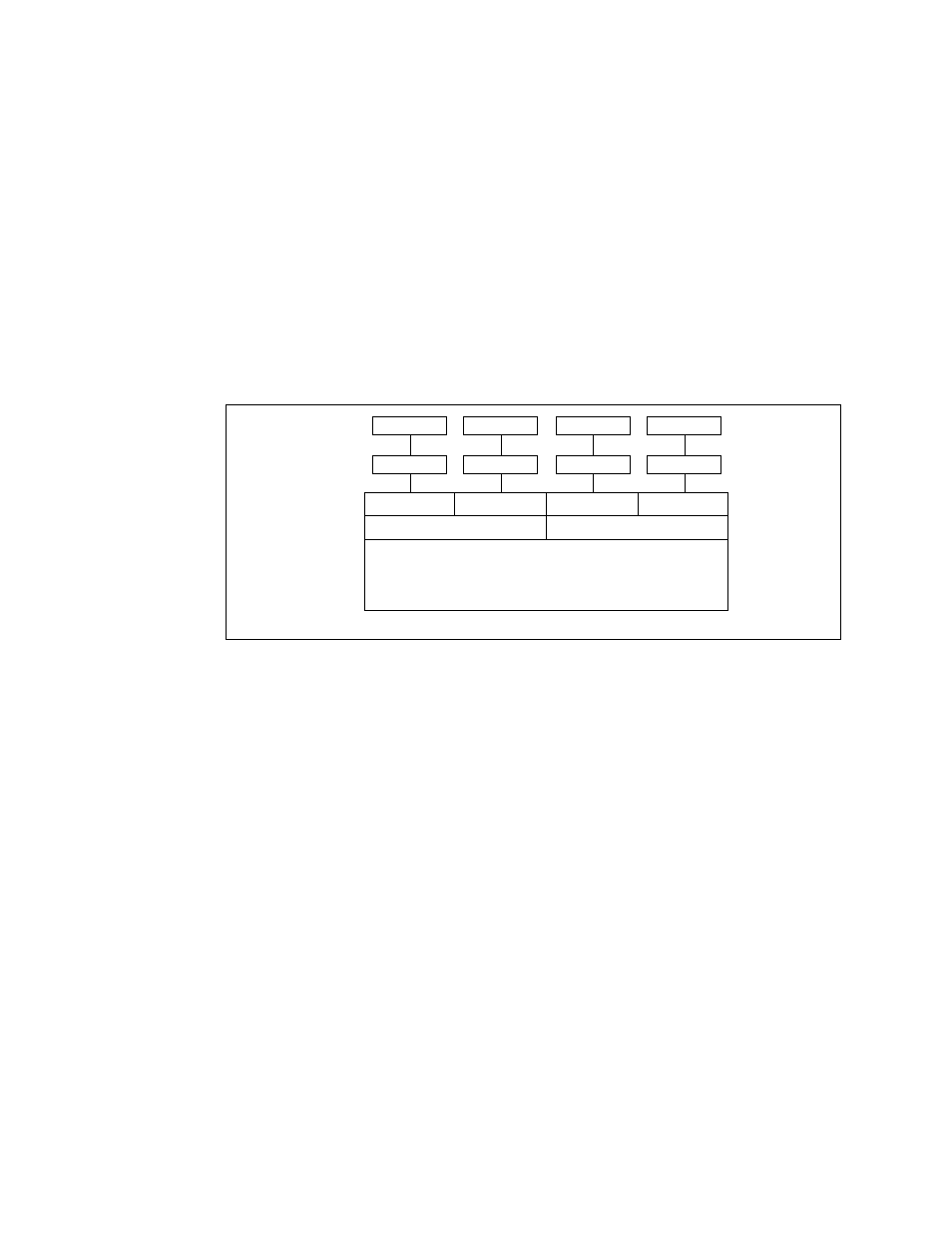
shows the single branch memory sparing configuration.
Figure 25.
Single Branch Mode Sparing DIMM Configuration
TS000300
Channel A
Branch 0
Intel
®
5000P Memory Controller Hub
Channel B
DIMM A2
DIMM A1
DIMM B2
DIMM B1
Channel C
Branch 1
Channel D
DIMM C2
DIMM C1
Slot 2
Slot 1
DIMM D2
DIMM D1
The following rules apply:
• DIMM A1 and DIMM B1 must be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM A2 and DIMM B2 must be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM A1 and DIMM A2 need not be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM B1 and DIMM B2 need not be identical in organization, size and speed.
• Sparing should be enabled in BIOS setup. The BIOS configures Rank Sparing Mode.
• The larger of the pairs {DIMM A1, DIMM B1} and {DIMM A2, DIMM B2} will be selected as the
spare pair unit.
3.4.2.9
Dual Branch Mode Sparing
Dual branch mode sparing requires that all eight DIMM sockets be populated and must comply with
the following population rules:
• DIMM A1 and DIMM B1 must be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM A2 and DIMM B2 must be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM C1 and DIMM D1 must be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM C2 and DIMM D2 must be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM A1 and DIMM A2 need not be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM B1 and DIMM B2 need not be identical in organization, size and speed.
• DIMM C1 and DIMM C2 need not be identical in organization, size and speed.
