Setting up ratio control, Setting up ratio control 73, Variable in cascade example 73 – Watlow CPC400 User Manual
Page 87
CPC400 Series User’s Guide
Chapter 3: Operation and Setup
Doc. 0600-2900-2000
Watlow Anafaze
73
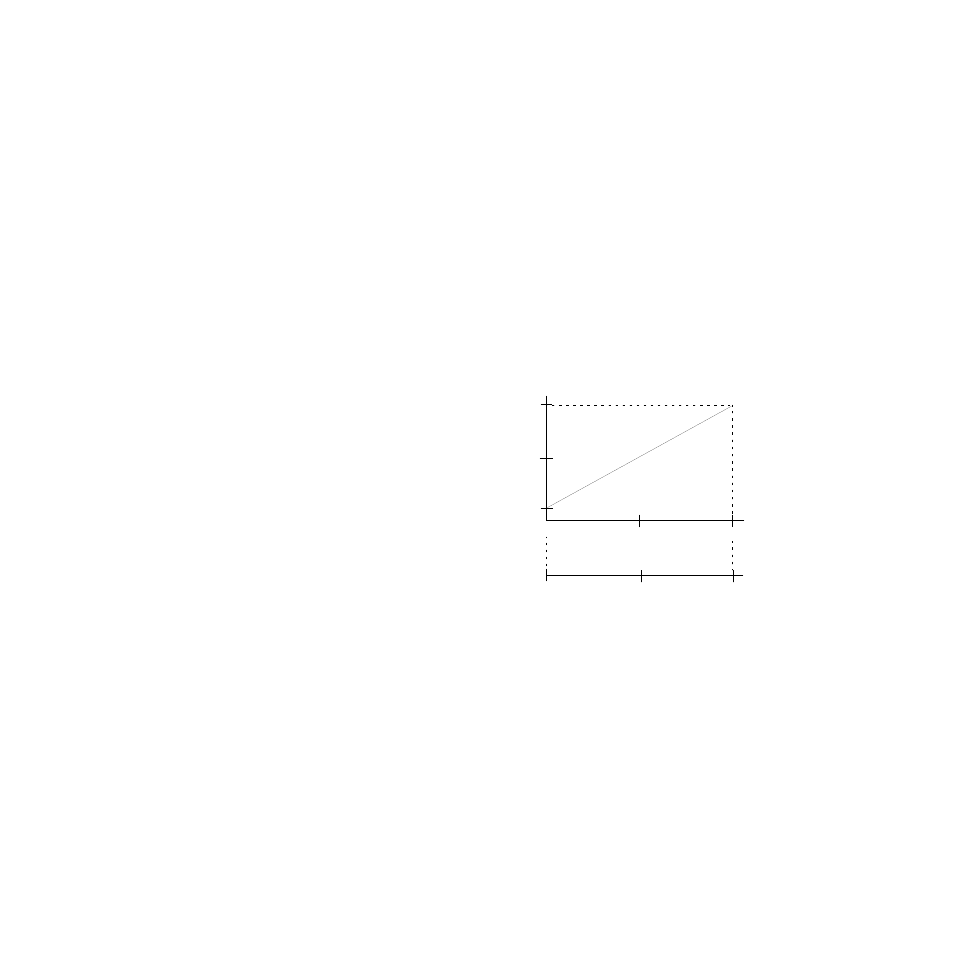
As the temperature in the middle of the tank (loop 1) drops,
the output goes up proportionally and the set point of loop
2 goes up proportionally. Thus heat is added to the system
at the element even though the temperature near the ele-
ment may have been at the desired temperature.
With proportional control, when loop 1 is at set point, its
output is 0 percent, and the set point of loop 2 is equal to
the desired temperature 150°F. If the temperature of the
loop 1 drops below 149°F, the deviation results in a propor-
tional output of 10 percent. This results in an increase to
the set point for loop 2 equal to 10 percent of the set point
range. In this case the range is 40°F (190 - 150°F = 40°F),
and 10 percent of 40°F is 4°F.
So when the temperature at loop 1 drops 1°F, the set point
of loop 2 increases by 4°F until the output of loop 1 is 100
percent and the set point of loop 2 is 190°F. At this point,
further decreases of the loop 1 process variable have no ad-
ditional affect on loop 2. Figure 3.12 illustrates this rela-
tionship.
Figure 3.12 Relationship of Secondary Loop
Set Point to Primary Loop Process
Variable in Cascade Example
Setting Up Ratio Control
Ratio control allows the process variable of one loop (mas-
ter loop), multiplied by a ratio, to be the set point of another
loop (ratio loop). You can assign any process variable to de-
termine the set point of a ratio loop.
By adjusting the ratio control parameters, you can adjust
the influence that the master loop process variable has on
the set point of the ratio loop
Set P
oint of the Secondar
y Loop
(Engineer
ing Units)
Process Variable of Primary Loop (ºF)
Heat Output of Primary Loop
(Percent of Full Scale)
0%
50%
100%
150ºF
145ºF
140ºF
190ºF
170ºF
150ºF
