Intel 253666-024US User Manual
Page 337
Vol. 2A 3-291
INSTRUCTION SET REFERENCE, A-M
FADD/FADDP/FIADD—Add
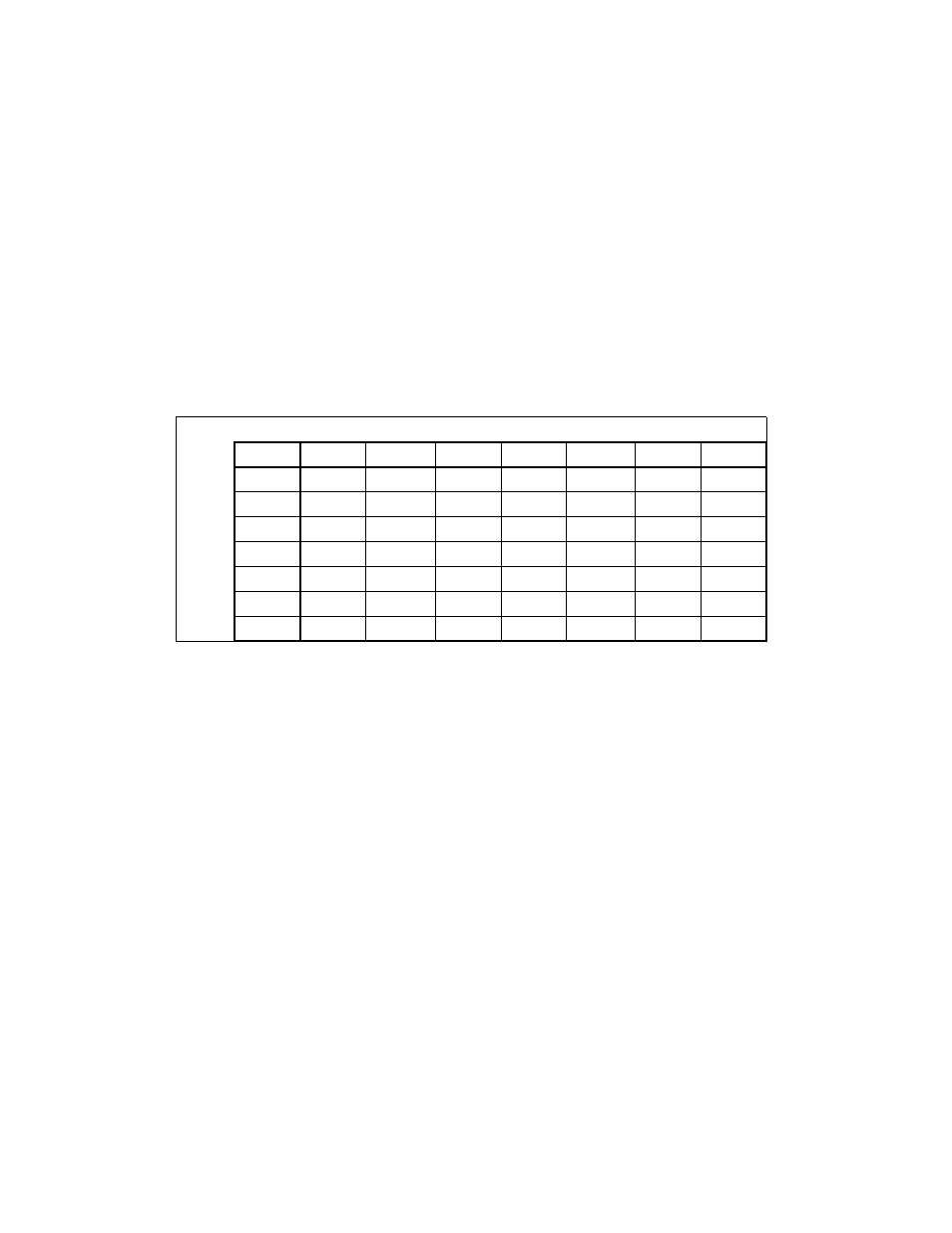
The table on the following page shows the results obtained when adding various
classes of numbers, assuming that neither overflow nor underflow occurs.
When the sum of two operands with opposite signs is 0, the result is +0, except for the
round toward −∞ mode, in which case the result is −0. When the source operand is an
integer 0, it is treated as a +0.
When both operand are infinities of the same sign, the result is ∞ of the expected
sign. If both operands are infinities of opposite signs, an invalid-operation exception
is generated. See Table 3-23.
This instruction’s operation is the same in non-64-bit modes and 64-bit mode.
Operation
IF Instruction
=
FIADD
THEN
DEST ← DEST + ConvertToDoubleExtendedPrecisionFP(SRC);
ELSE (* Source operand is floating-point value *)
DEST ← DEST + SRC;
FI;
IF Instruction
=
FADDP
THEN
PopRegisterStack;
FI;
Table 3-23. FADD/FADDP/FIADD Results
DEST
-∞
−F
−0
+0
+F
+∞
NaN
-∞
-∞
-∞
-∞
-∞
-∞
*
NaN
−F or −I
-∞
−F
SRC
SRC
±F or ±0
+∞
NaN
SRC
−0
-∞
DEST
−0
±0
DEST
+∞
NaN
+0
-∞
DEST
±0
+0
DEST
+∞
NaN
+F or +I
-∞
±F or ±0
SRC
SRC
+F
+∞
NaN
+∞
*
+∞
+∞
+∞
+∞
+∞
NaN
NaN
NaN
NaN
NaN
NaN
NaN
NaN
NaN
NOTES:
F Means finite floating-point value.
I Means integer.
* Indicates floating-point invalid-arithmetic-operand (#IA) exception.
