Intel 253666-024US User Manual
Page 188
3-142 Vol. 2A
CMPSD—Compare Scalar Double-Precision Floating-Point Values
INSTRUCTION SET REFERENCE, A-M
CMPSD—Compare Scalar Double-Precision Floating-Point Values
Description
Compares the low double-precision floating-point values in the source operand
(second operand) and the destination operand (first operand) and returns the results
of the comparison to the destination operand. The comparison predicate operand
(third operand) specifies the type of comparison performed. The comparison result is
a quadword mask of all 1s (comparison true) or all 0s (comparison false).
The source operand can be an XMM register or a 64-bit memory location. The desti-
nation operand is an XMM register. The result is stored in the low quadword of the
destination operand; the high quadword remains unchanged. The comparison predi-
cate operand is an 8-bit immediate, the first 3 bits of which define the type of
comparison to be made (see Table 3-7). Bits 4 through 7 of the immediate are
reserved.
The unordered relationship is true when at least one of the two source operands
being compared is a NaN; the ordered relationship is true when neither source
operand is a NaN.
A subsequent computational instruction that uses the mask result in the destination
operand as an input operand will not generate a fault, because a mask of all 0s corre-
sponds to a floating-point value of +0.0 and a mask of all 1s corresponds to a QNaN.
Some of the comparisons listed in Table 3-7 can be achieved only through software
emulation. For these comparisons the program must swap the operands (copying
registers when necessary to protect the data that will now be in the destination
operand), and then perform the compare using a different predicate. The predicate
to be used for these emulations is listed in Table 3-7 under the heading Emulation.
Compilers and assemblers may implement the following two-operand pseudo-ops in
addition to the three-operand CMPSD instruction. See Table 3-10.
Opcode
Instruction
64-Bit
Mode
Compat/
Leg Mode
Description
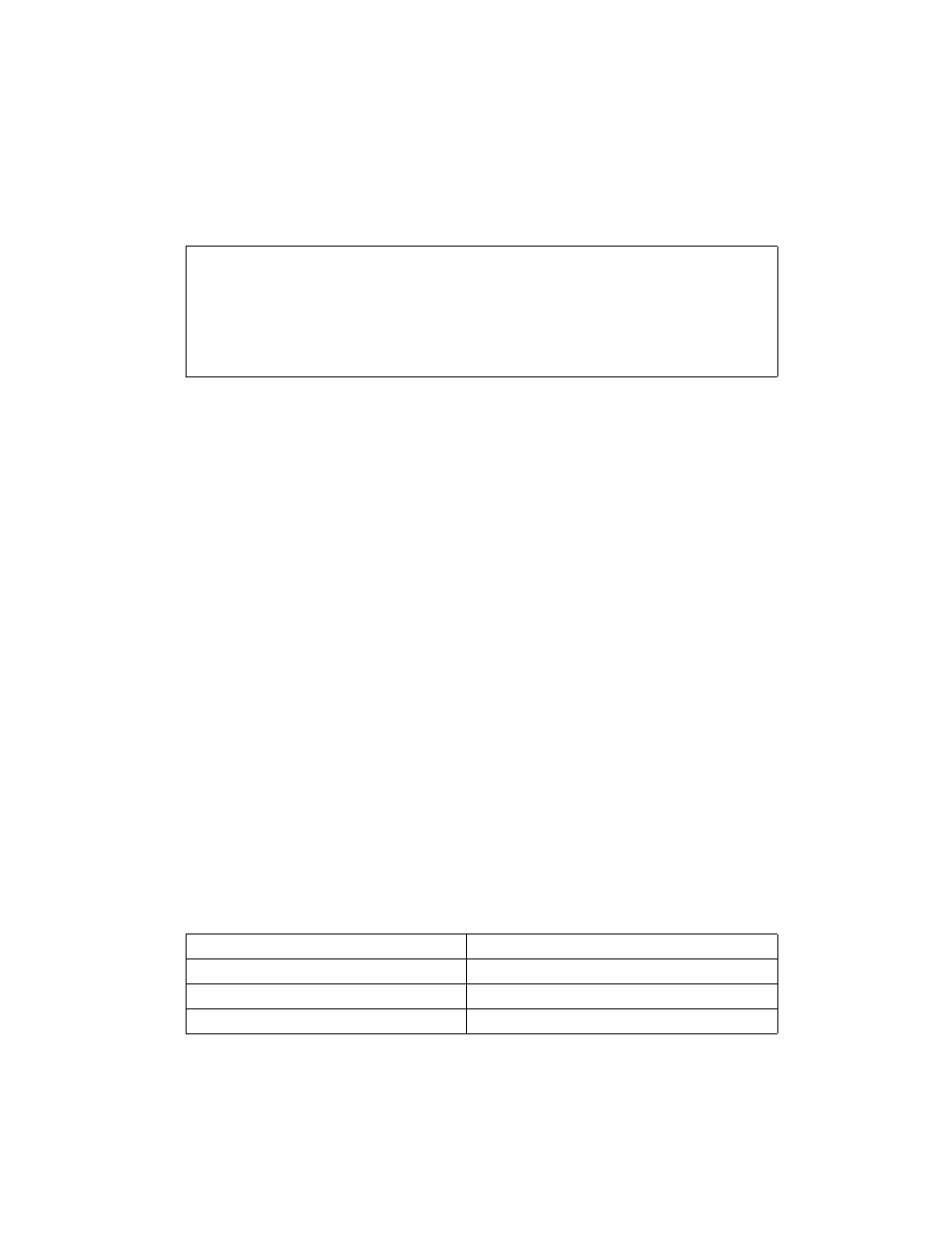
F2 0F C2 /r ib
CMPSD xmm1,
xmm2/m64, imm8
Valid
Valid
Compare low double-
precision floating-point
value in xmm2/m64 and
xmm1 using imm8 as
comparison predicate.
Table 3-10. Pseudo-Ops and CMPSD
Pseudo-Op
Implementation
CMPEQSD xmm1, xmm2
CMPSD xmm1,xmm2, 0
CMPLTSD xmm1, xmm2
CMPSD xmm1,xmm2, 1
CMPLESD xmm1, xmm2
CMPSD xmm1,xmm2, 2
