MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC FR-S520E User Manual
Page 128
118
Operation selection function parameters
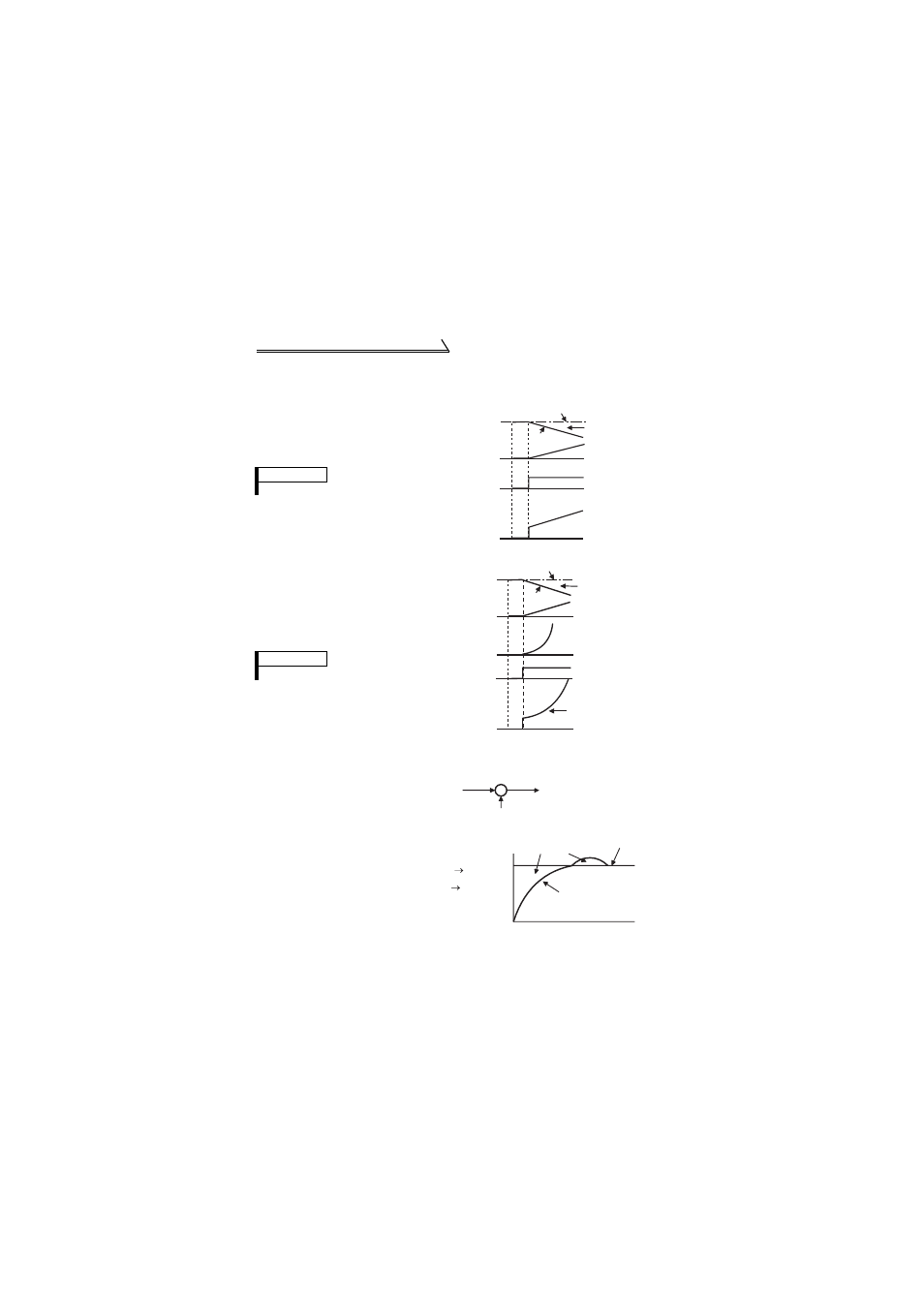
2) PD action
A combination of proportional control
action (P) and differential control action
(D) for providing a manipulated
variable in response to deviation speed
to improve the transient characteristic.
[Operation example for proportional
changes of measured value]
REMARKS
PD action is the sum of P and D actions.
3) PID action
The PI action and PD action are
combined to utilize the advantages of
both actions for control.
REMARKS
The PID action is the sum of P, I and D actions.
4) Reverse action
Increases the manipulated
variable (output frequency) if
deviation X = (set point -
measured value) is positive, and
decreases the manipulated
variable if deviation is negative.
Deviation
Set point
Time
Time
Time
PD action
D action
P action
Measured
value
Time
Time
Time
Deviation
P action
D action
PID action
Set point
Measured
value
Time
I action
y=at +bt+c
2
Set point
Feedback signal
(Measured value)
+
-
[Heating]
Deviation
Set point
X>0
X<0
Cold up
Hot down
Measured value
