10 pid control (pr. 88 to pr. 94 ), Age 117 – MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC FR-S520E User Manual
Page 127
117
Operation selection function parameters
2
F
UNCT
IO
NS
2.10.10 PID control (Pr. 88
to Pr. 94
)
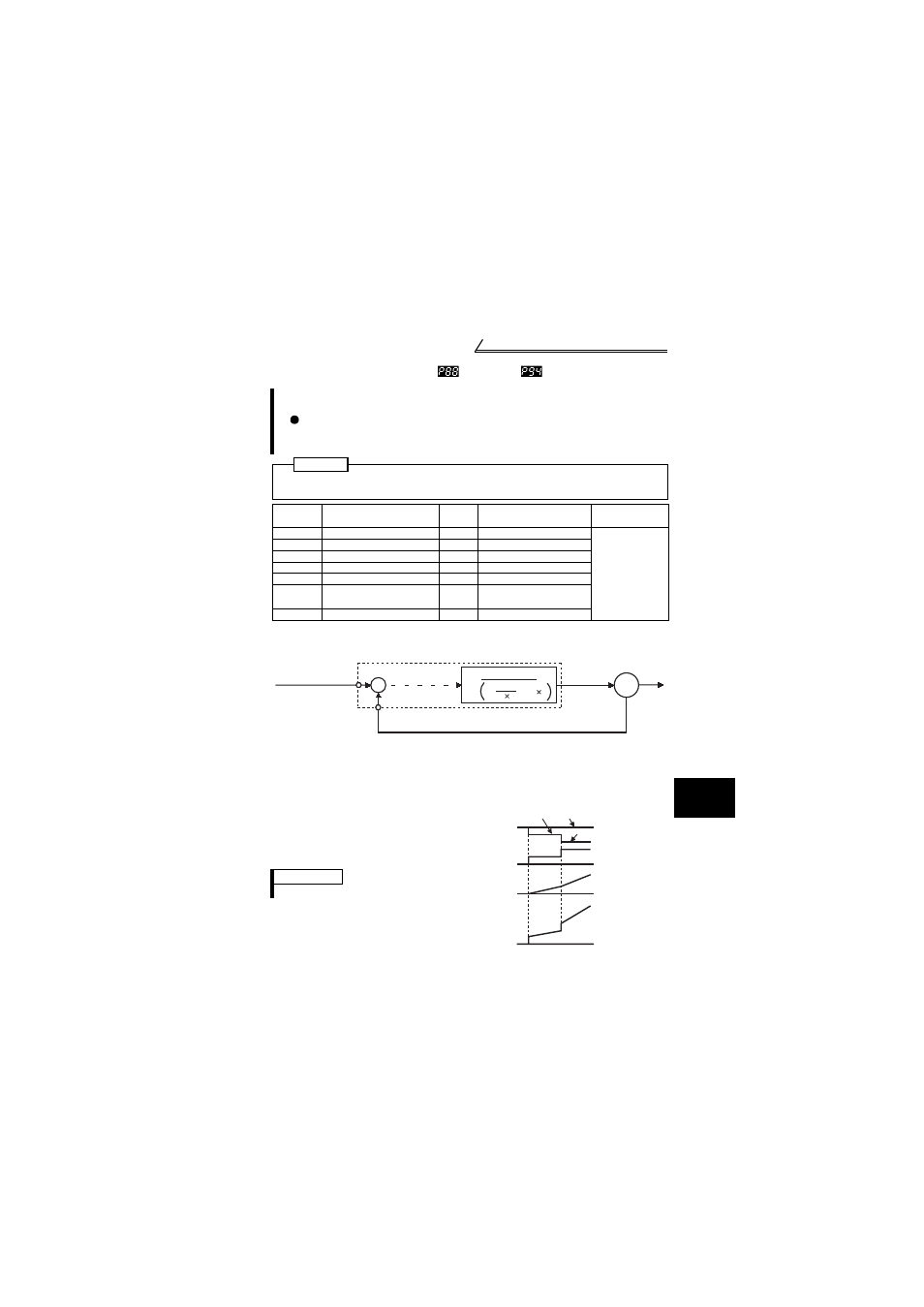
(1) Basic PID control configuration
(2) PID action overview
The inverter can be used to exercise process control, e.g. flow rate, air volume
or pressure.
The voltage input signal (0 to +5V or 0 to +10V) or Pr. 93 setting is used as a
set point and the 4 to 20mADC current input signal used as a feedback value
to constitute a feedback system for PID control.
POINT
Made valid by turning on the X14 signal. Use Pr. 60 to Pr. 63 (input terminal function
selection) to make assignment.
Parameter
Name
Factory
Setting
Setting Range
Remarks
88
PID action selection
20
20, 21
Setting is enabled
when Pr. 30 = "1"
89
PID proportional band
100%
0.1 to 999%, - - -
90
PID integral time
1s
0.1 to 999s, - - -
91
PID upper limit
- - -
0 to 100%, - - -
92
PID lower limit
- - -
0 to 100%, - - -
93
PID action set point for PU
operation
0%
0 to 100%
94
PID differential time
- - -
0.01 to 10s, - - -
1) PI action
A combination of proportional control
action (P) and integral control action (I)
for providing a manipulated variable in
response to deviation and changes
with time.
[Operation example for stepped
changes of measured value]
REMARKS
PI action is the sum of P and I actions.
+-
IM
Kp: Proportion constant Ti: Integral time S: Operator Td: Differential time
Set point
Manipulated
variable
Motor
Feedback signal (Measured value)
Inverter circuit :
Ti S
1
1+
+Td S
Kp
PID operation
Terminal 4
Pr. 93 or Treminal 2
Deviation Set point
Measured value
Time
Time
Time
PI action
I action
P action
