4 – dr-scan sequence, 3 – communication via tap – Maxim Integrated DS4830A Optical Microcontroller User Manual
Page 162
DS4830A User’s Guide
162
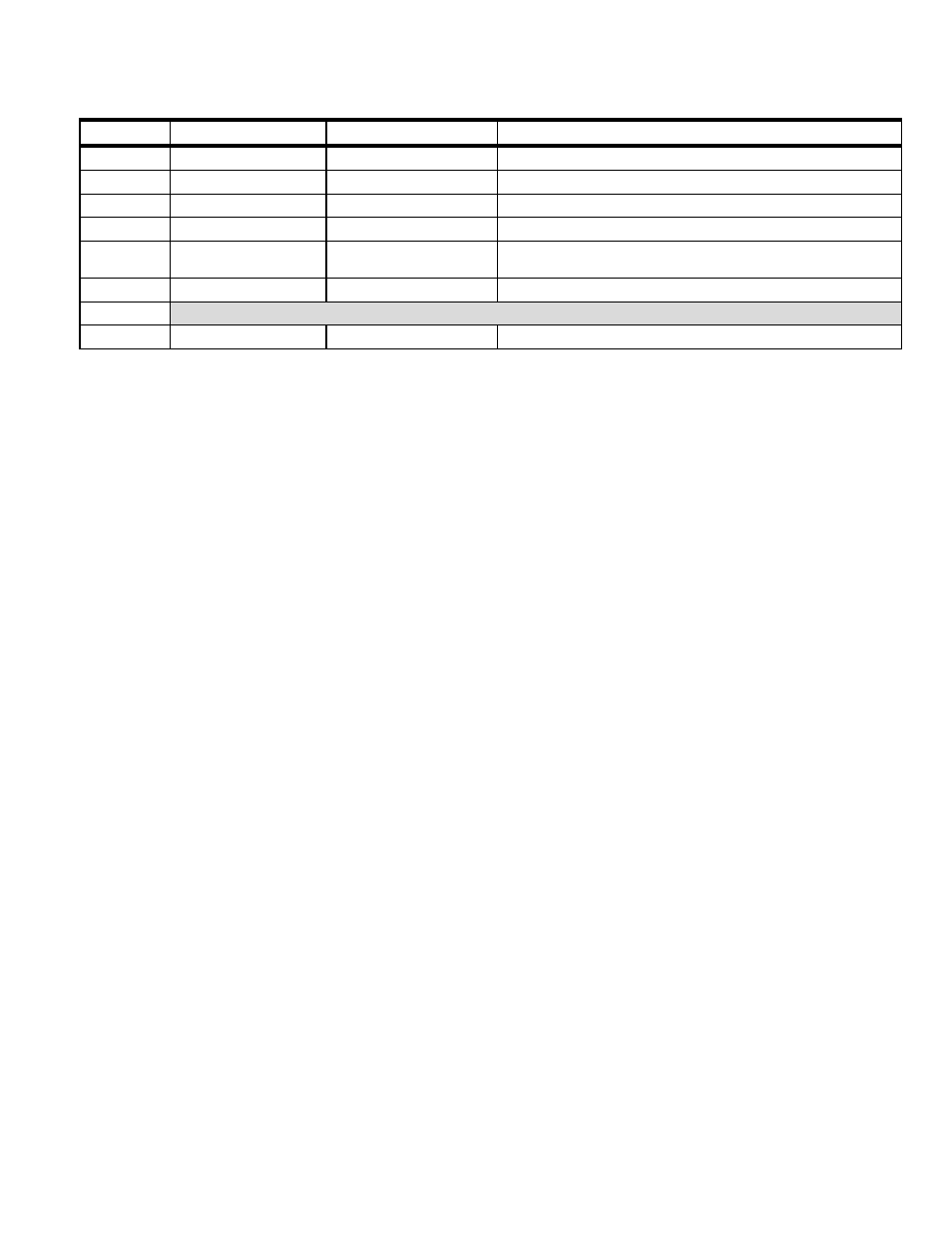
Table 20-3: Instruction Register (IR2:0) Encodings
IR2:0
INSTRUCTION
FUNCTION
SERIAL DATA SHIFT REGISTER SELECTION
000
Extest
No operation
Unchanged. Retain previous selection
001
Sample/Preload
No operation
Unchanged. Retain previous selection
010
Debug
In-circuit debug mode
10-bit shift register
011
By-pass
No operation (default)
1-bit shift register
100
System
Programming
Bootstrap function
3-bit shift register
101
By-pass
No operation (default)
1-bit shift register
110
Reserved
111
By-pass
No operation (default)
1-bit shift register
The Extest (IR2:0 = 000b) and Sample/Preload (IR2:0 = 001b) instructions are mandated by the JTAG standard,
however, the DS4830A does not intend to make practical use of these instructions. Hence, these instructions are
treated as no operations but may be entered into the instruction register without affecting the on-chip system logic or
pins and does not change the existing serial data register selection between TDI and TDO.
The By-pass (IR2:0 = 011b, 101b, or 111b) instruction is also mandated by the JTAG standard. The By-pass
instruction is fully implemented by the DS4830A to provide a minimum length serial data path between the TDI and
the TDO pins. This is accomplished by providing a single cell bypass shift register. When the instruction register is
updated with the By-pass instruction, a single bypass register bit is connected serially between TDI and TDO in the
Shift-DR state. The instruction register automatically defaults to the By-pass instruction when the TAP is in the Test-
Logic-Reset state. The By-pass instruction has no effect on the operation of the on-chip system logic.
The Debug (IR2:0 = 010b) and System Programming (IR2:0 = 100b) instructions are private instructions which are
intended solely for in-circuit debug and in-system programming operations respectively. If the instruction register is
updated with the Debug instruction, a 10-bit serial shift register is formed between the TDI and TDO pins in the Shift-
DR state. If the System Programming instruction is entered into the instruction register (IR2:0), a 3-bit serial data
shift register is formed between the TDI and TDO pins in the Shift-DR state.
Instruction register (IR2:0) settings other than those listed and described above are reserved for internal use. As can
be seen in Figure 20-2, the instruction register serves to select the length of the serial data register between TDI and
TDO during the Shift-DR state.
20.2.4 – DR-Scan Sequence
Once the instruction register has been configured to a desired state (mode), transactions are performed via a data
buffer register associated with that mode. These data transactions are executed serially in a manner analogous to
the process used to load the instruction register and are grouped in the TAP Controller state sequence starting from
the Select-DR-Scan state. In the TAP controller state sequence, the Shift-DR state allows internal data to be shifted
out through the TDO pin while the external data is shifted in simultaneously via the TDI pin. Once a complete data
pattern is shifted in, input data can be latched into the parallel buffer of the selected register on the falling edge of
TCK in the Update-DR state. On the same TCK falling edge, in the Update-DR state, the internal parallel buffer is
loaded to the data shift register for output. This Shift-DR/Update-DR process serves as the basis for passing
information between the external host and the DS4830A. These data register transactions occur in the data register
portion of the TAP controller state sequence diagram and have no effect on the instruction register.
20.3 – Communication via TAP
The TAP controller is in Test-Logic-Reset state after a power-on-reset. During this initial state, the instruction register
contains By-pass instruction and the serial path defined between the TDI and TDO pins for the Shift-DR state is the
1-bit bypass register. All TAP signals (TCK, TMS, TDI, and TDO) default to being weakly pulled high internally on
any reset. The TAP controller will remain in the Test-Logic-Reset state as long as TMS is held high. The TCK and
TMS signals may be manipulated by the host to transition to other TAP states. The TAP controller will remain in a
given state whenever TCK is held low.
For the host to establish a specific data communication link, a private instruction must be loaded into the IR2:0
register. Once the instruction is latched in the instruction parallel buffer at the Update-IR state, it is recognized by the
TAP controller and the communication channel is established. In-Circuit Debug or In-System Programming
